👉 Click the link below and request access—I’ll approve it for you shortly!
https://www.notion.so/MSKMRI-KNEE-b6cbb1e1bc4741b681ecf6a40159a531?pvs=4
==============================================
✨ Join the channel to enjoy the benefits! 🚀
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4bw7o0l2rhxn1GJZGDmT9w/join
==============================================
👉 "Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚"
[Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery]
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS
==============================================
MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee
📚 Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery Now! 🌟 Available on Amazon, eBay, and Rain Collectibles! 💻 Ebook coming soon – stay tuned! ⏳ 🔗 https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS 🔗 https://www.ebay.com/itm/3875004193
www.youtube.com
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
www.amazon.com
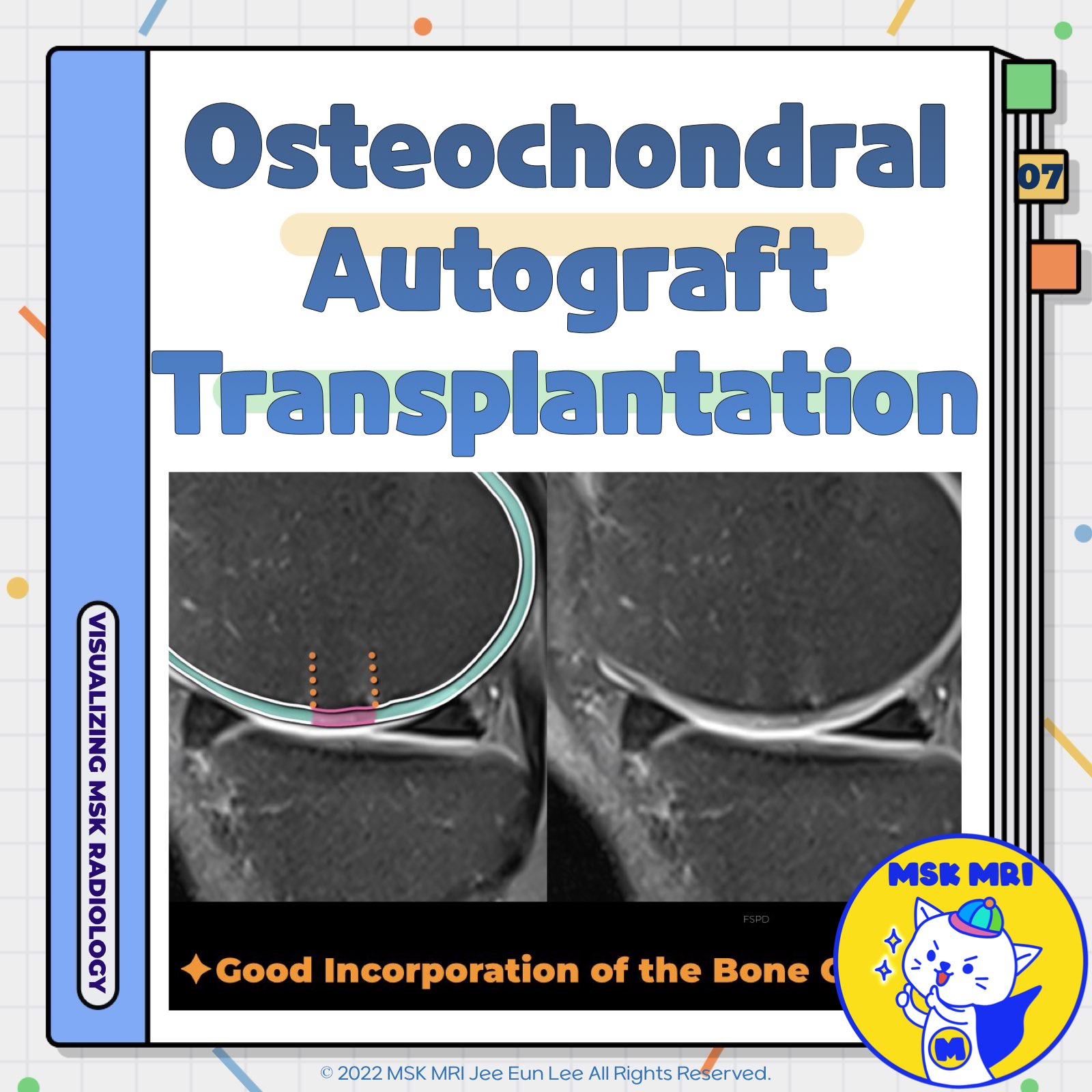
📌 Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS)
- Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS), or Mosaicplasty, is a surgical technique used to treat focal cartilage lesions in the knee by transplanting osteochondral cylinders from non-weight-bearing areas to damaged cartilage areas.
✅ Indications and Limitations
- Large Cartilage Defects: Challenging for lesions larger than 4 cm² due to donor site morbidity.
- Patient Criteria: Suitable for lesions up to 2.5 cm², typically in patients under 50 years old, but can address larger lesions.
✅ Procedure Overview
- Durability: The harvested graft with hyaline cartilage is more durable than fibrocartilage from microfracture procedures.
- Defect Types: Effective for larger, deeper, uncontained, and multiple cartilage defects.
- Graft Harvesting: Osteochondral cylinders are harvested from specific non-weight-bearing areas of the knee.
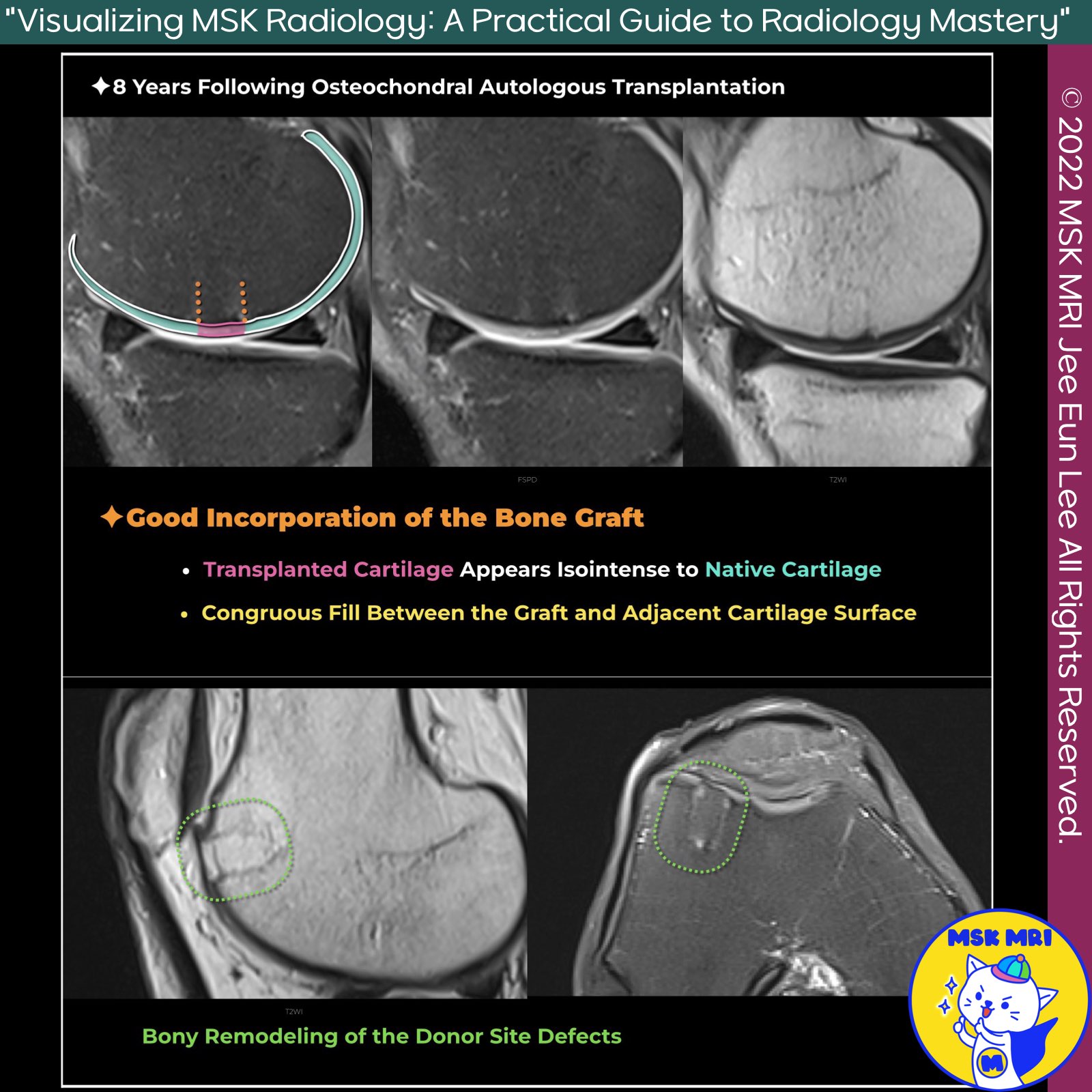
✅ Postoperative Imaging and Outcomes
- Assessment: Evaluate morphology of native and donor cartilage, fill defects, peripheral integration, and joint surface restoration.
- Early Healing: Transplanted tissue should fill the defect uniformly without gaps.
- Cartilage Thickness: Ideal match to surrounding cartilage, though patellar defects may present challenges.
✅ Healing and Complications
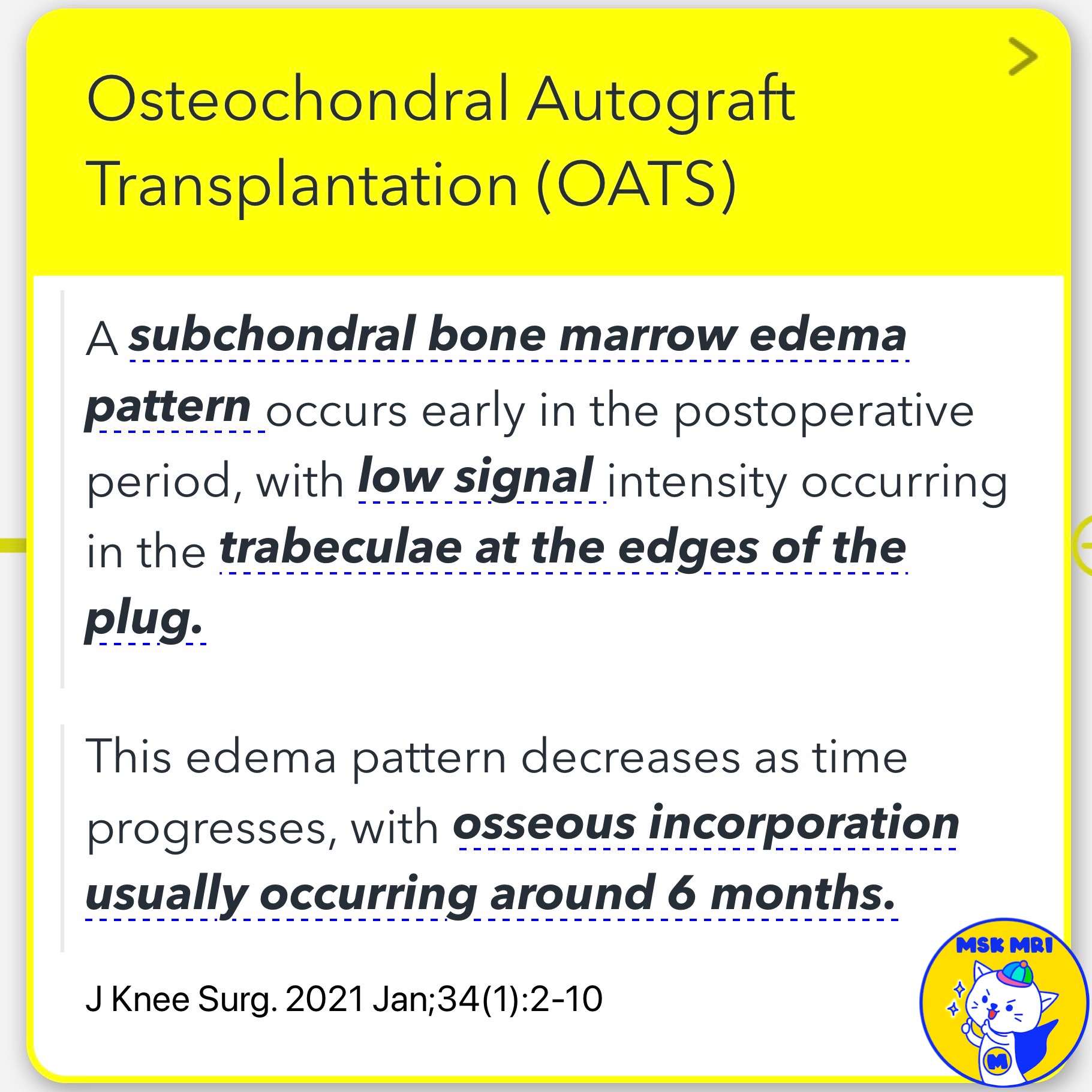
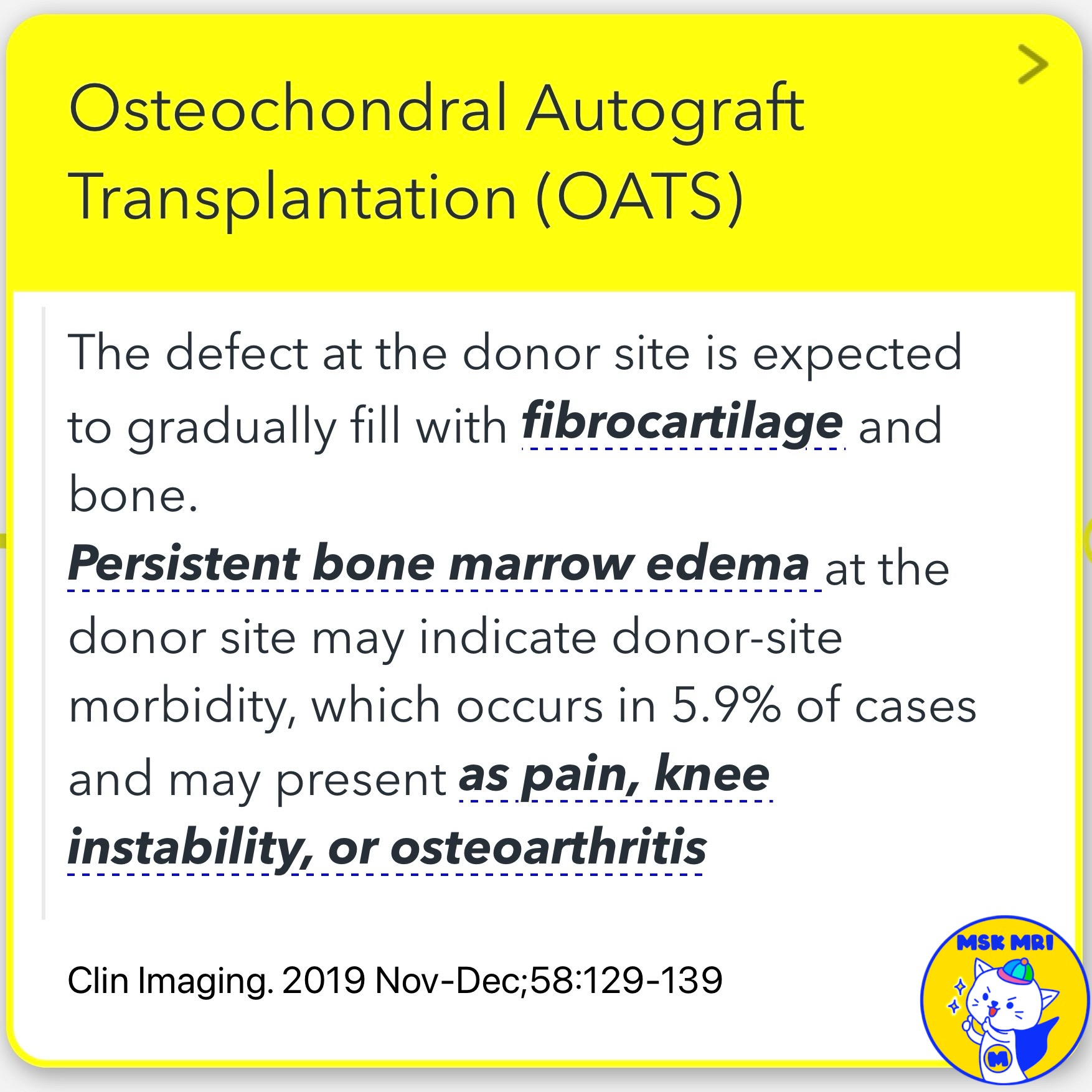
- Bone Marrow Edema: Common early postoperatively, typically resolves by 6 months.
- Donor Site Healing: Fills with fibrocartilage in 6-9 months; persistent edema may indicate morbidity.
- Edema Regression: Similar regression rates in donor and repair sites.
References
- Clin Imaging. 2019 Nov-Dec;58:129-139
- Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2022 Jun;26(3):216-229
- J Knee Surg. 2021 Jan;34(1):2-10
- J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021 Sep 25;22:101610
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#OATS #Mosaicplasty #CartilageRepair #KneeSurgery #Orthopedics #SportsMedicine #CartilageLesions #JointHealth #MedicalImaging #SurgicalTechniques
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5CD. Cartilage Repair and TKA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-C.09) MRI Findings of Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (0) | 2024.07.17 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-C.08) Poor Outcome in Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| (Fig 5-C.06) Failure of Microfracture Treatment (1) | 2024.07.17 |
| (Fig 5-C.05) MRI Findings of Microfracture Repair (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| (Fig 5-C.04) Delamination and Graft Failure of hUCB-MSCs Implantation (0) | 2024.07.17 |