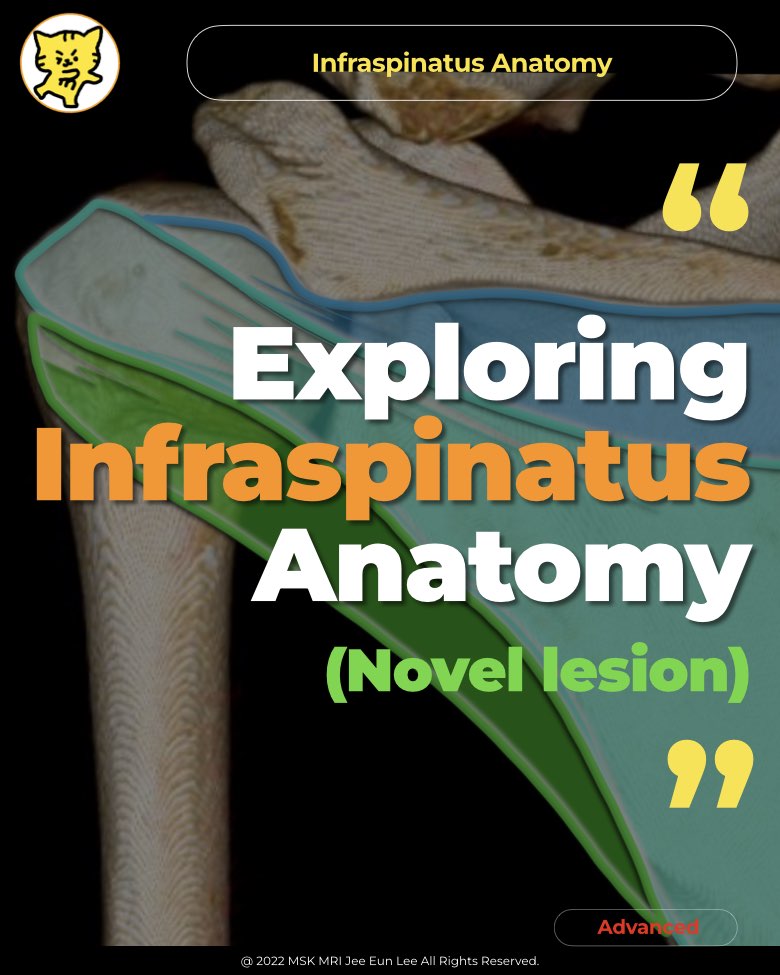
https://youtu.be/WQUtqkgICN0✨ Join the channel to enjoy the benefits! 🚀 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4bw7o0l2rhxn1GJZGDmT9w/joinhttps://youtube.com/shorts/SZjL8v-ZIL0?si=u5fqV9DEKzEqUVE3 https://heliotrope-apartment-6ac.notion.site/Shoulder-Pain-in-Young-Athletes-Is-It-Just-Normal-Growth-Acromial-Apophysiolysis-1aaa74523757802e9531ccfbb7fffbc2?pvs=4 Shoulder Pain in Young Athletes: Is It J..