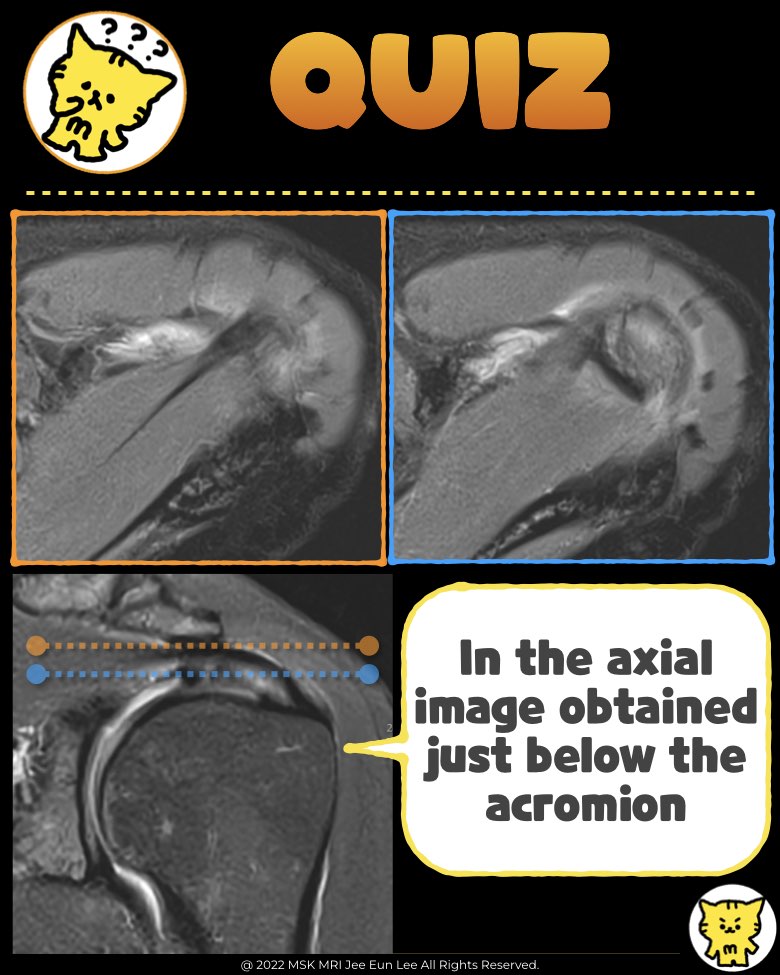
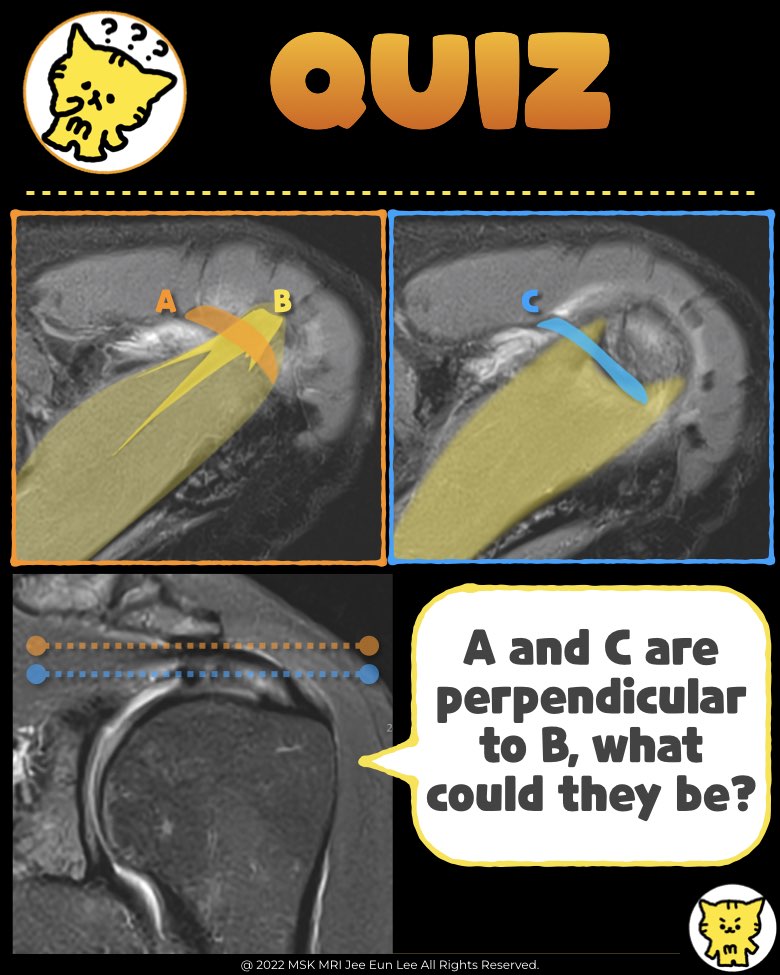
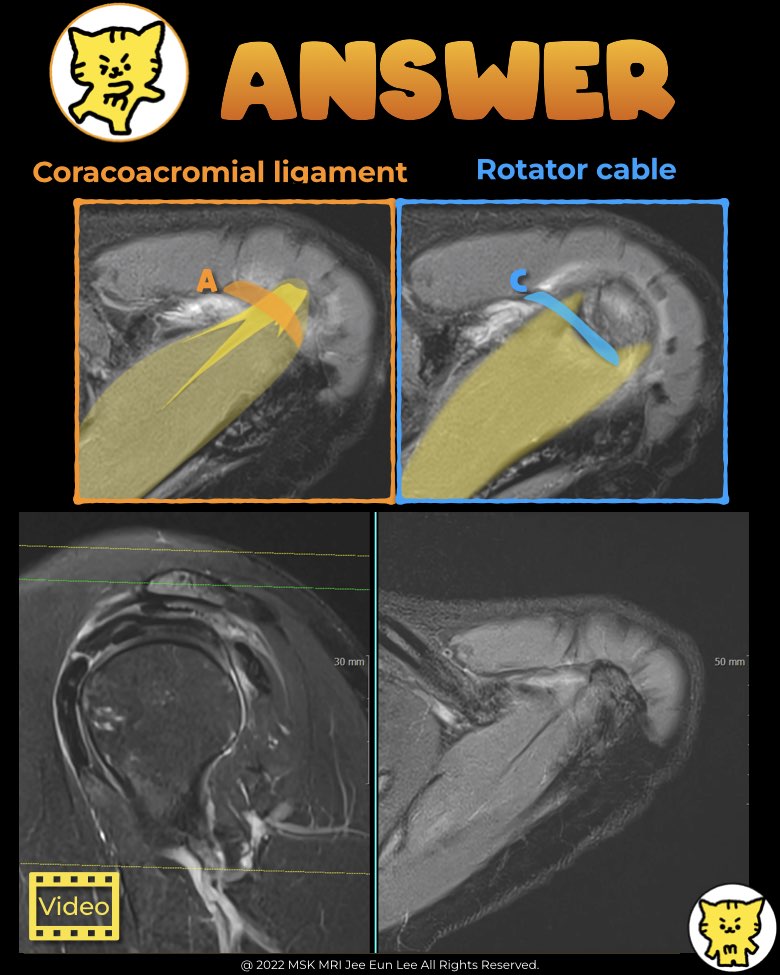
📌 Rotator Cable Overview
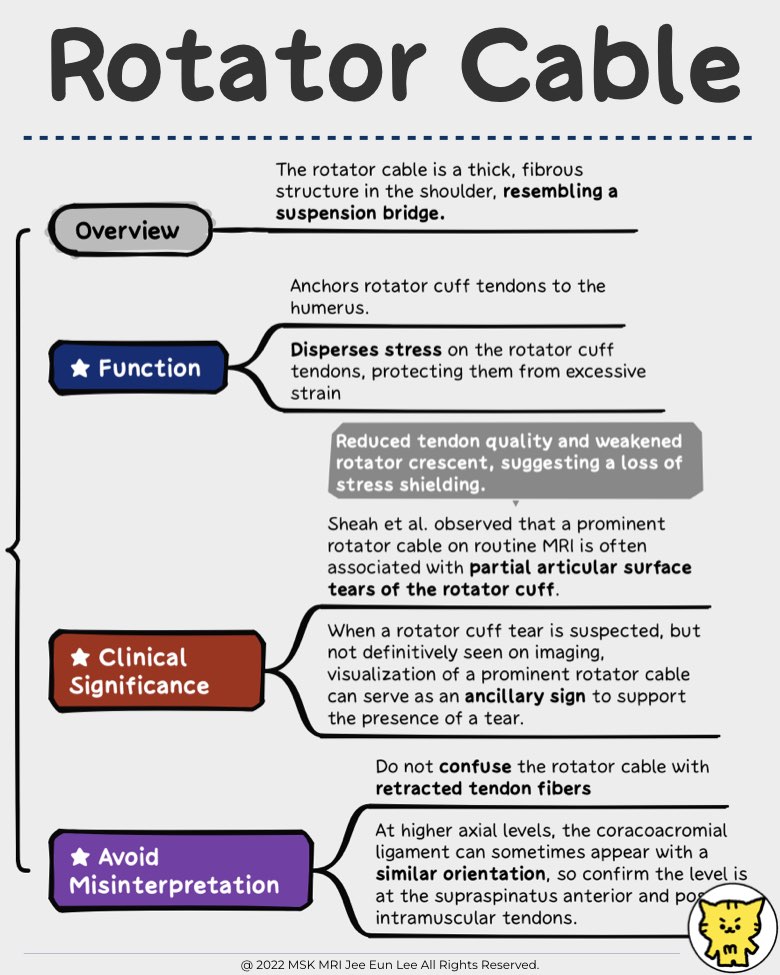
The rotator cable is a thick, fibrous structure in the shoulder, resembling a suspension bridge.
It transfers forces across the rotator cuff and helps anchor the tendons to the tubercles of the humerus.
✅ Function of the Rotator Cable
- Anchors rotator cuff tendons to the humerus.
- Assists in stabilizing the glenohumeral joint.
- Disperses stress on the rotator cuff tendons, protecting them from excessive strain.
✅ Clinical Significance on MRI
Sheah et al. observed that a prominent rotator cable on routine MRI is often associated with partial articular surface tears of the rotator cuff.
A visible rotator cable may indicate:
- Tendon retraction.
- Undersurface tendon delamination.
- Reduced tendon quality and weakened rotator crescent, suggesting a loss of stress shielding.
When a rotator cuff tear is suspected, but not definitively seen on imaging, visualization of a prominent rotator cable can serve as an ancillary sign to support the presence of a tear.
References
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013 May;200(5):1101-5.
EFORT Open Rev. 2019 Feb 20;4(2):56-62.
Sheah et al., AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009 Sep;193(3):679-86.
MRI Web Clinic — February 2013, Rotator Cuff Pitfalls, Mark H. Awh, M.D. (https://radsource.us/rotator-cuff-pitfalls/)
#RotatorCable, #ShoulderMRI, #RotatorCuffTear, #OrthopaedicImaging, #RadiologyEducation, #MRIInterpretation, #GlenohumeralJoint, #RotatorCuff, #ShoulderAnatomy, #RadiologyInsights
📌 Coracoacromial Ligament (CAL)
The coracoacromial ligament is a key component of the coracoacromial arch.
It is a triangular band composed of two fascicles.
The coracohumeral ligament is a thick bundle of fibers running perpendicular to the supraspinatus tendon fibers.
- Origin: Lateral aspect of the coracoid process.
- Insertion: Anterior, lateral, and inferior surfaces of the acromion.
- Function:
- Connects the acromion and coracoid process of the scapula.
- Strengthens the superior portion of the shoulder joint capsule.
Clinical Significance
- Coracoacromial Ligament Ossification or Thickening:
References
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013 May;200(5):1101-5.
EFORT Open Rev. 2019 Feb 20;4(2):56-62.
Sheah et al., AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009 Sep;193(3):679-86.
MRI Web Clinic — February 2013, Rotator Cuff Pitfalls, Mark H. Awh, M.D. (https://radsource.us/rotator-cuff-pitfalls/)
📌 Key Points to Avoid Misinterpretation
- Do not confuse the rotator cable with retracted tendon fibers:
A true rotator cable extends from the anterior attachment at the greater tuberosity to the posterior oblique facet insertion on axial images.
- Carefully assess the level of the image:
At higher axial levels, the coracoacromial ligament can sometimes appear with a similar orientation, so confirm the level is at the supraspinatus anterior and posterior intramuscular tendons.
#CoracoacromialLigament, #ShoulderAnatomy, #RotatorCuffTear, #SubacromialImpingement, #ShoulderMRI, #OrthopaedicImaging, #CoracohumeralLigament, #RadiologyEducation, #ShoulderStabilization, #RadiologyInsights
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"