👉 Click the link below and request access—I’ll approve it for you shortly!
https://www.notion.so/MSKMRI-KNEE-b6cbb1e1bc4741b681ecf6a40159a531?pvs=4
==============================================
✨ Join the channel to enjoy the benefits! 🚀
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4bw7o0l2rhxn1GJZGDmT9w/join
==============================================
👉 "Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚"
[Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery]
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS
==============================================

Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
www.amazon.com
MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee
📚 Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery Now! 🌟 Available on Amazon, eBay, and Rain Collectibles! 💻 Ebook coming soon – stay tuned! ⏳ 🔗 https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS 🔗 https://www.ebay.com/itm/3875004193
www.youtube.com
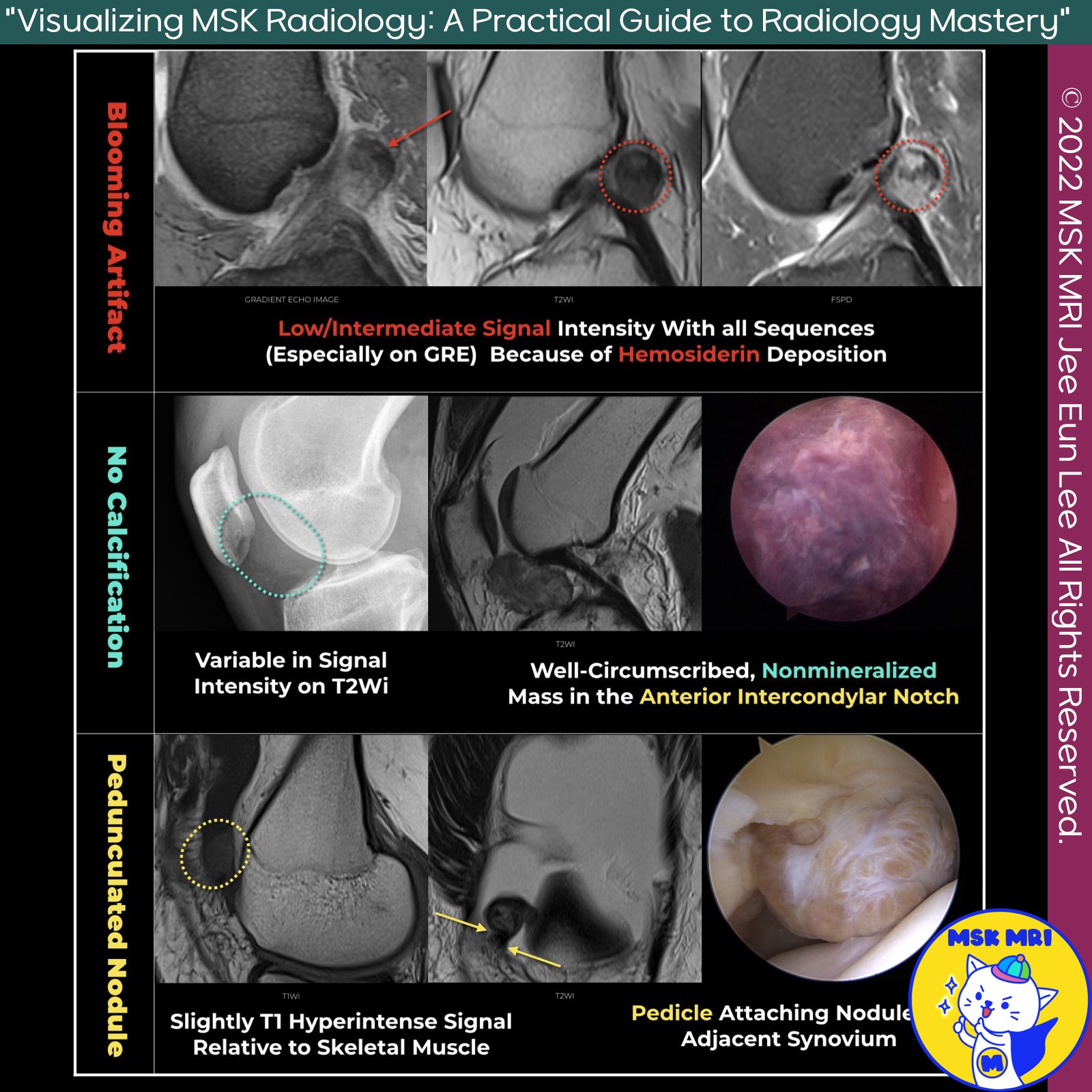
📌 Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor
- Tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is a benign synovial proliferative disorder characterized by villous and nodular projections.
- The disease may present as either localized or diffuse and is usually monoarticular, meaning it typically affects only one joint.
✅ Two types of TGCT
- Localized TGCT: Also known as focal form, formerly referred to as focal nodular synovitis.
This form is usually small, ovoid, and exhibits intermediate or low signal intensity on MRI sequences. - Diffuse TGCT: Formerly known as pigmented villonodular synovitis,
this form shows similar histological features as the localized form but involves a more extensive area of the synovium.
✅ MRI Characteristics
- Signal Intensity: TGCT is characterized by recurrent bleeding, which leads to hemosiderin deposition.
This causes a characteristic low signal intensity in all MRI sequences and magnetic susceptibility. - Localized TGCT: Most commonly appears as a small (2-3 cm) ovoid mass with intermediate or low signal intensity.
Larger polylobulated lesions are not uncommon.
In the knee, the infrapatellar fat pad is affected in two-thirds of cases, with the remainder located at the suprapatellar pouch or intercondylar notch.
References
- Radiographics. 2023 May;43(5)
. - RadioGraphics 2018; 38:2069–2101.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#TenosynovialGiantCellTumor, #TGCT, #SynovialProliferativeDisorder, #LocalizedTGCT, #DiffuseTGCT, #MRI, #MedicalImaging, #BenignTumor, #Radiology, #Synovitis




'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5E. Other' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-E.12) Lipoma Arborescens (0) | 2024.08.04 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-E.11) Synovial Low-Flow Vascular Malformation (Synovial Hemangioma) (0) | 2024.08.04 |
| (Fig 5-E.09) Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease (1) | 2024.07.23 |
| (Fig 5-E.08) Acute Gouty Arthritis vs. Septic Arthritis (0) | 2024.07.23 |
| (Fig 5-E.07) Extracapsular Locations of Tophi (0) | 2024.07.23 |