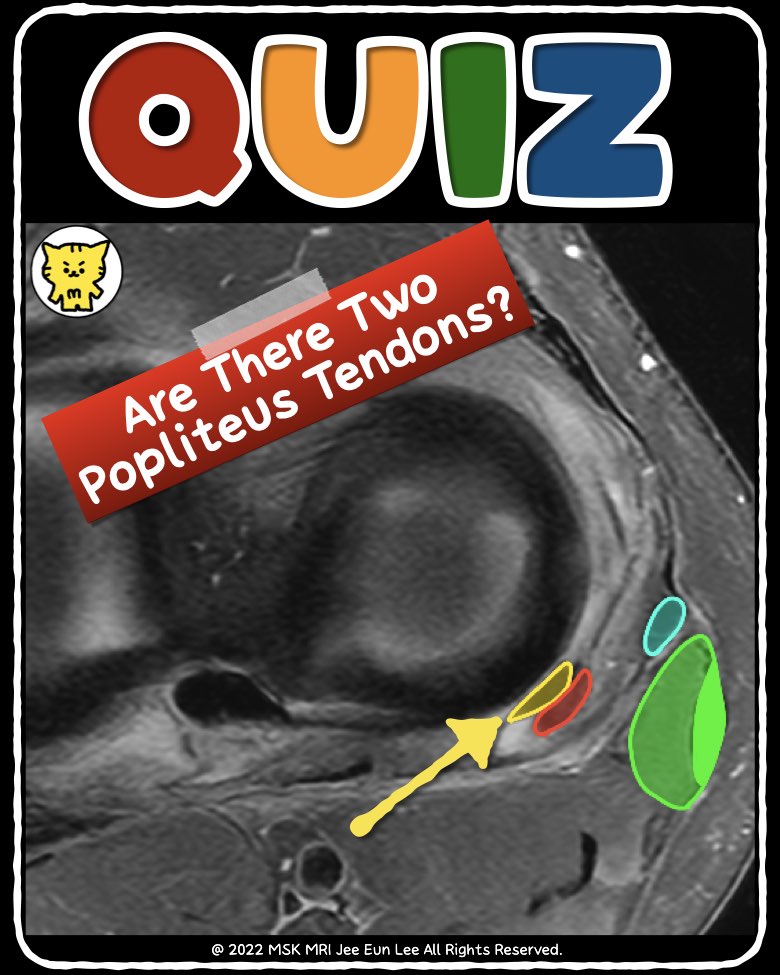
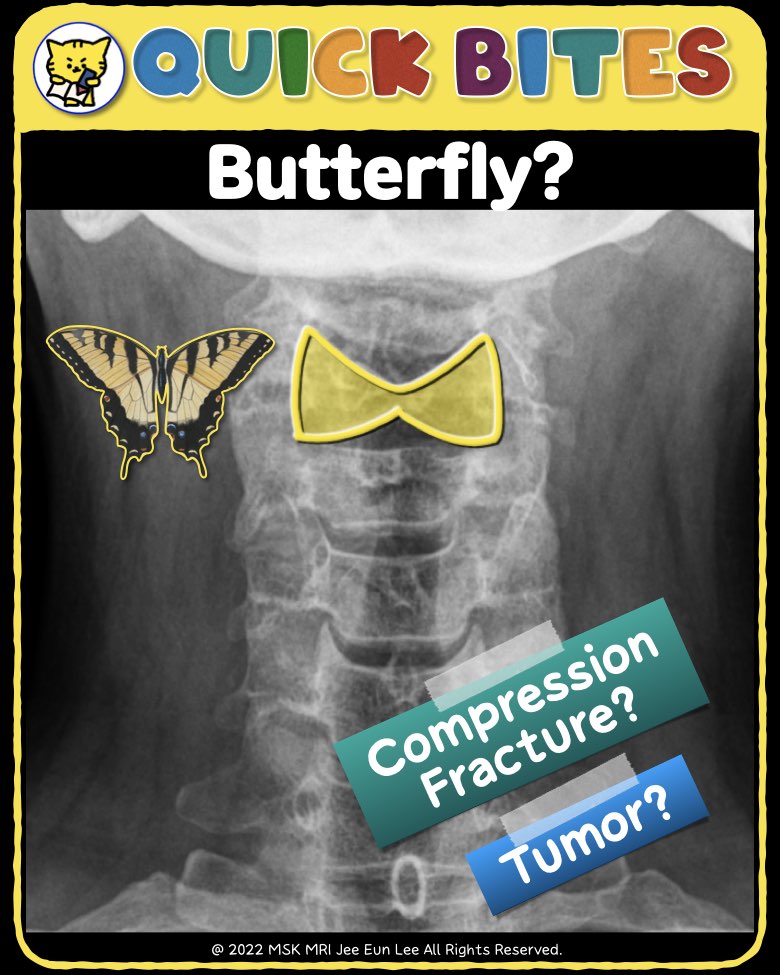
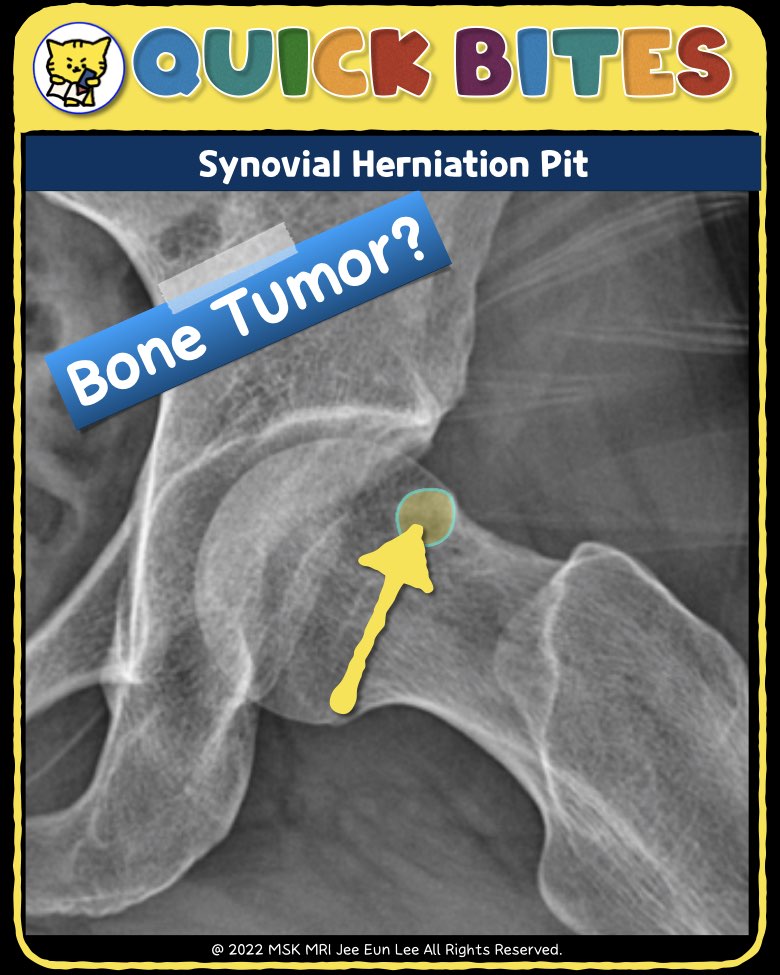
https://youtu.be/d36sXlR13ew✨ Join the channel to enjoy the benefits! 🚀https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4bw7o0l2rhxn1GJZGDmT9w/join👉 Click the link below and request access—I’ll approve it for you shortly!https://www.notion.so/MSKMRI-KNEE-b6cbb1e1bc4741b681ecf6a40159a531?pvs=4==============================================📚 Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery No..