Summary: Footprint of the Subscapularis
1. General Anatomy of the Subscapularis Footprint
- The superior footprint of the subscapularis (SSC) tendon is broad and tapered inferiorly.
- A thin muscular insertion is located below the lesser tuberosity (LT) in the surgical neck of the humerus.
- The upper two-thirds are subjected to greater tension and mechanical stress.
- The lower third is less mechanically robust.
2. Tendinous vs. Muscular Insertion
- The upper two-thirds of the insertion are tendinous, stronger, and stiffer, attaching to the lesser tuberosity, bicipital groove, and greater tuberosity.
- The lower third is a weaker, muscular insertion located at the inferior margin of the lesser tuberosity and the anterior humeral metaphysis.
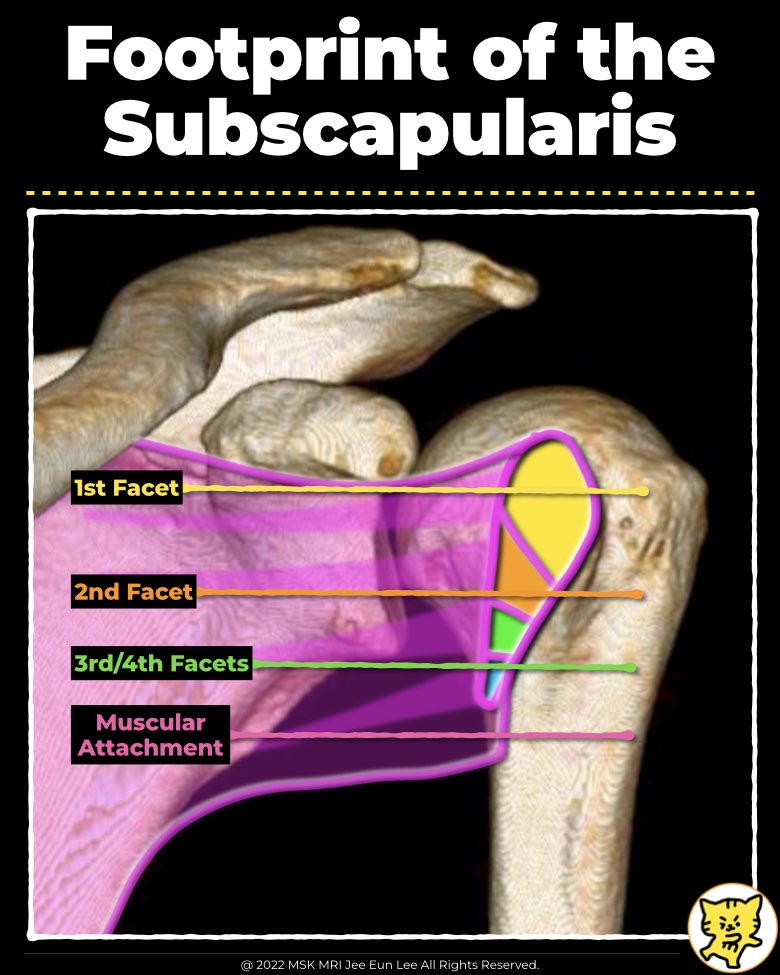
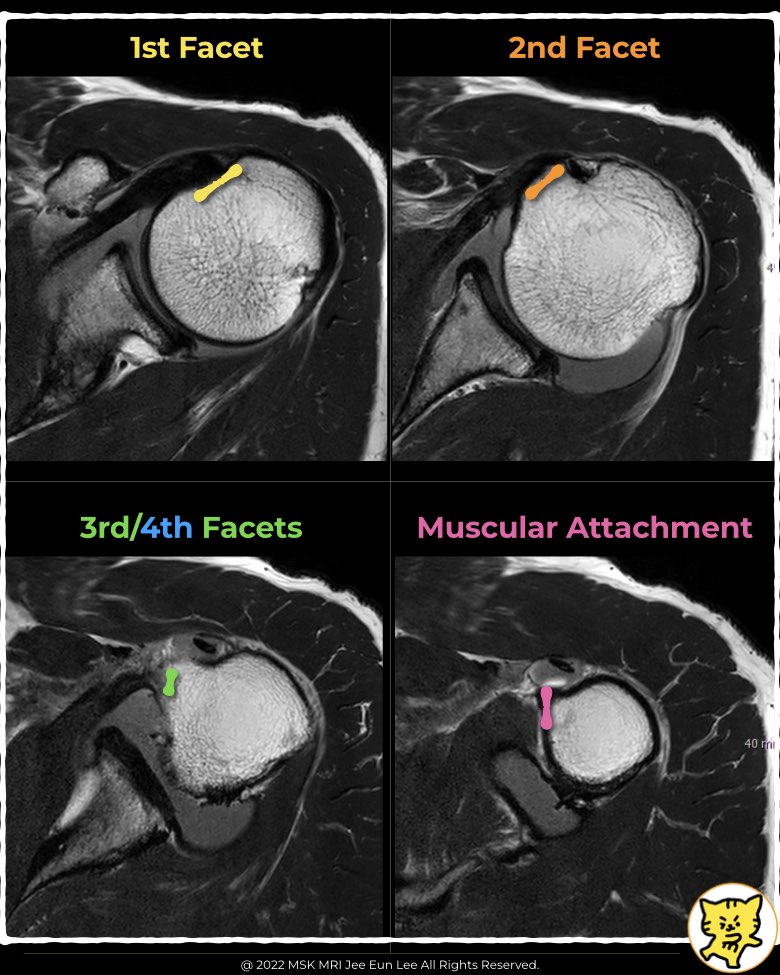
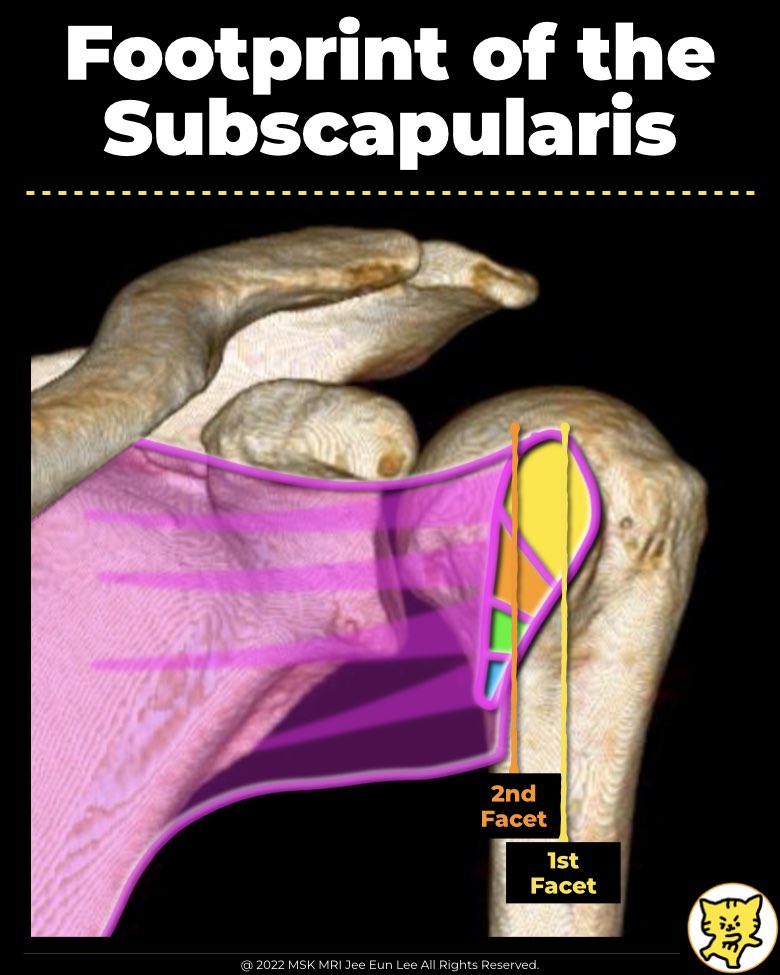
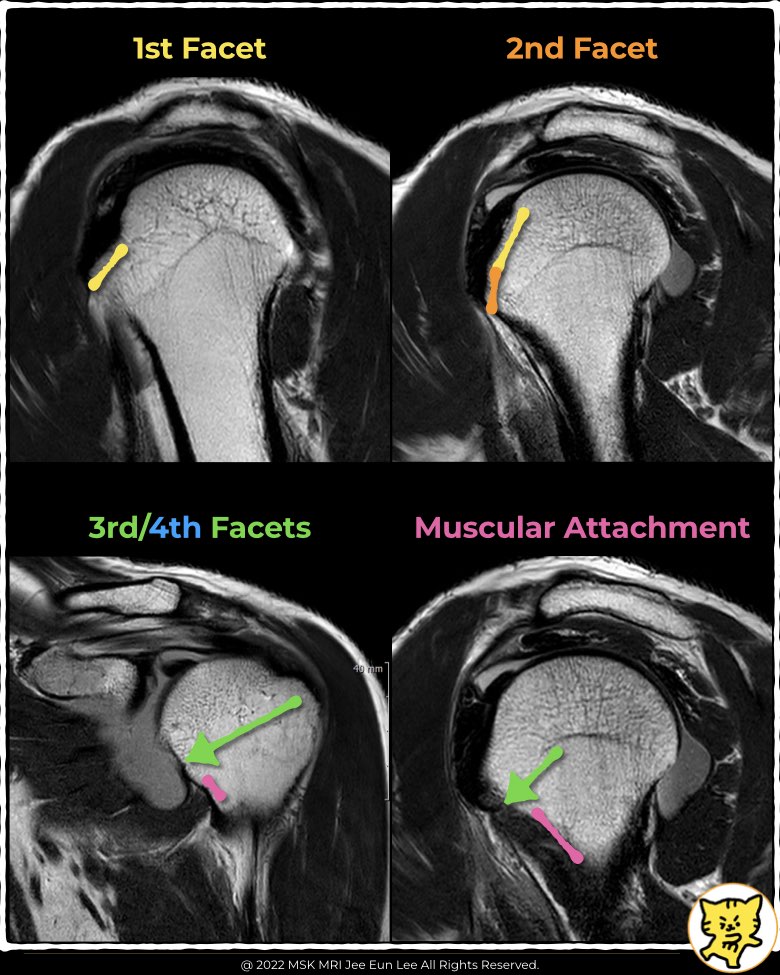
3. Facets of Subscapularis Insertion
- Yoo et al identified four facets with a total footprint size of 51.5 × 10.7 mm.
- The first facet accounts for 34% of the entire footprint and measures approximately 13.8 × 13.5 mm.
- The first facet is the largest and aligns more closely with the supraspinatus insertion angle.
- Its orientation suggests it plays a significant role in abduction (elevation) rather than rotation.
- Facets 2–4 are more parallel or beyond parallel to the humeral shaft.
References
- Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2012 May; 20(2):163-72, ix.
- Insights Imaging. 2024 Feb 27; 15(1):61.
- Arthroscopy. 2015 Jan; 31(1):19-28.
#Subscapularis, #RotatorCuff, #ShoulderAnatomy, #MuscleInsertion, #FootprintAnatomy, #TendonMechanics, #ShoulderMRI, #OrthopedicImaging, #SportsMedicine, #RadiologyInsights
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"