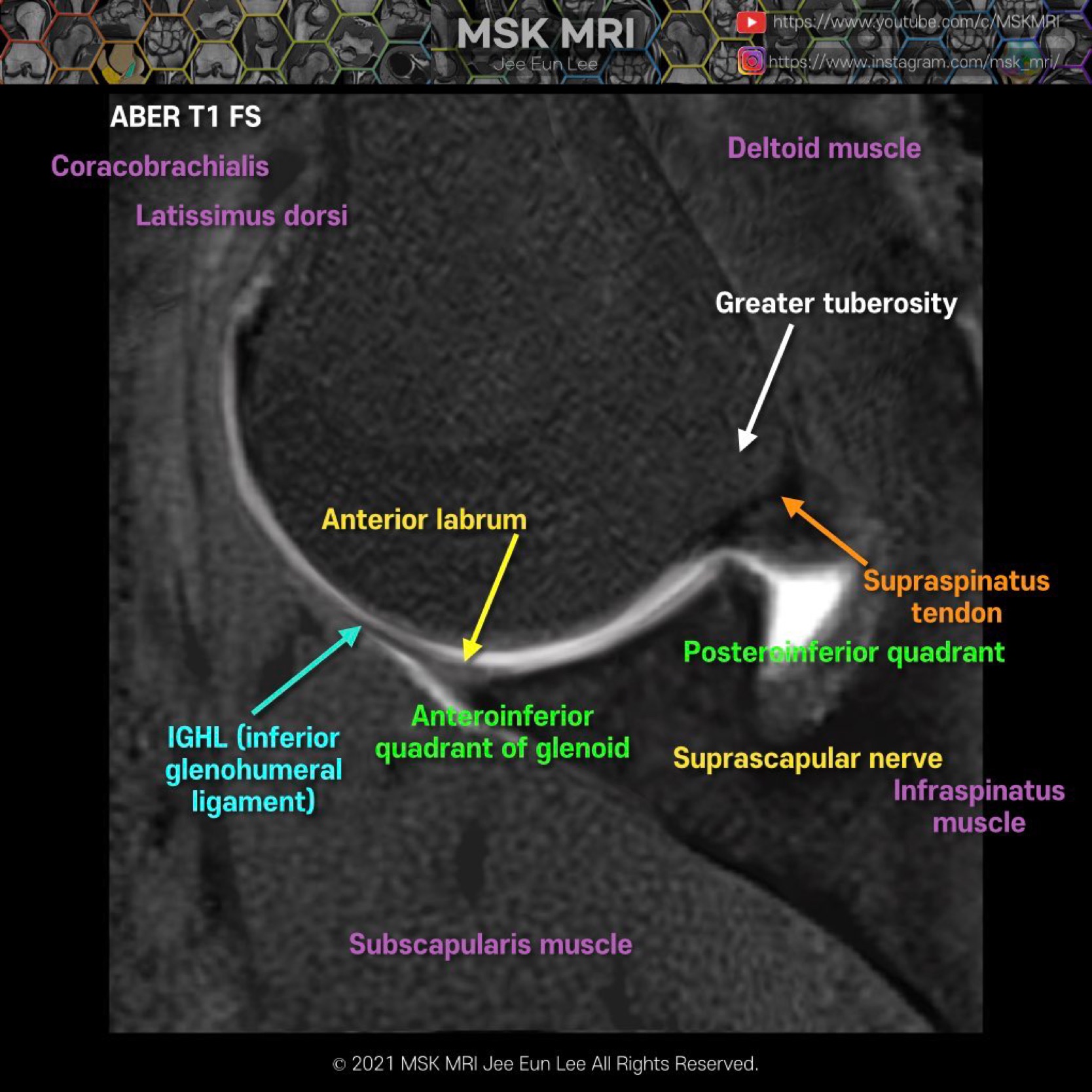
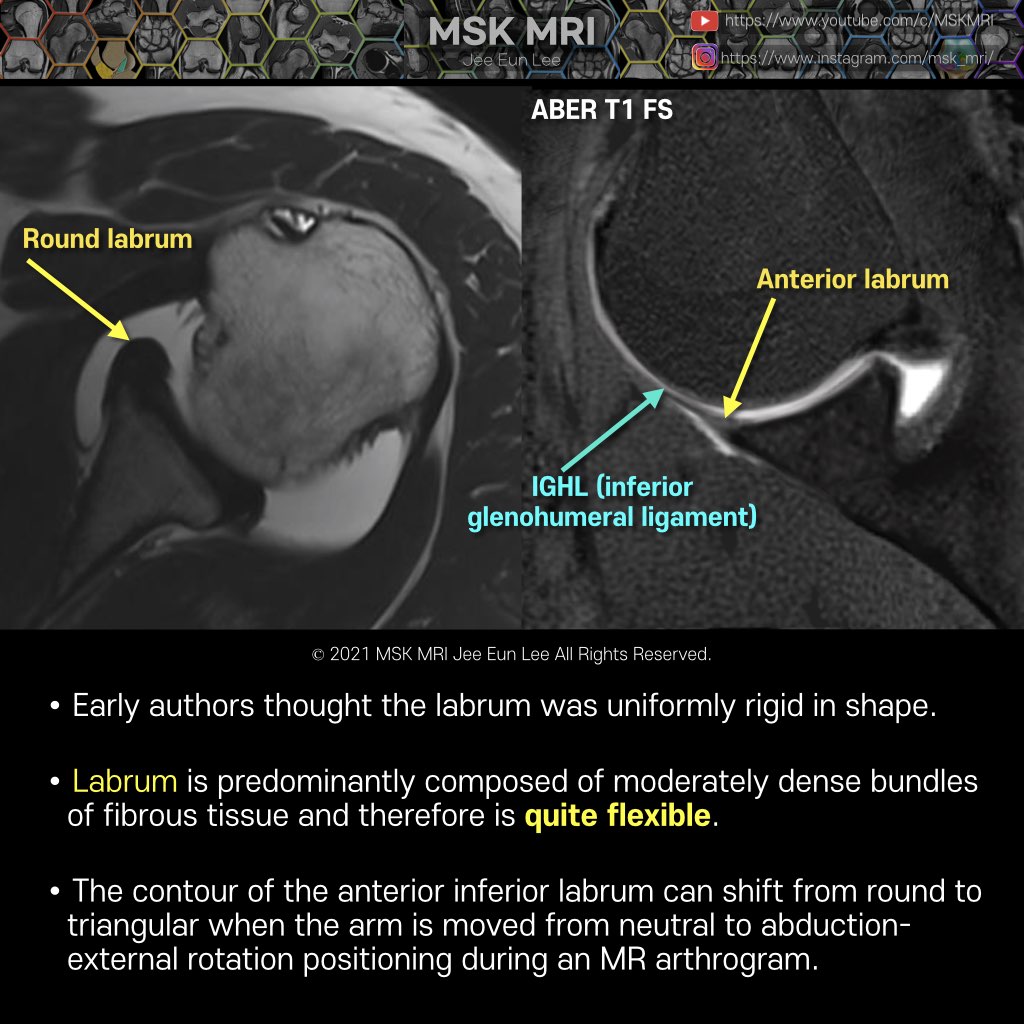
In regard to shape, the morphology of the normal labrum demonstrates considerable variability on standard MR images. The cross-sectional shape of the labrum is triangular in most cases (anterior, 64%; posterior, 47%), followed by rounded (anterior, 17%; posterior, 33%). However, in a minority of cases the normal labral shape can be blunted, cleaved, notched, or even flat. The anterior and inferi..