👉 Click the link below and request access—I’ll approve it for you shortly!
https://www.notion.so/MSKMRI-KNEE-b6cbb1e1bc4741b681ecf6a40159a531?pvs=4
==============================================
✨ Join the channel to enjoy the benefits! 🚀
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4bw7o0l2rhxn1GJZGDmT9w/join
==============================================
👉 "Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚"
[Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery]
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS
==============================================
MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee
📚 Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery Now! 🌟 Available on Amazon, eBay, and Rain Collectibles! 💻 Ebook coming soon – stay tuned! ⏳ 🔗 https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS 🔗 https://www.ebay.com/itm/3875004193
www.youtube.com
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
www.amazon.com
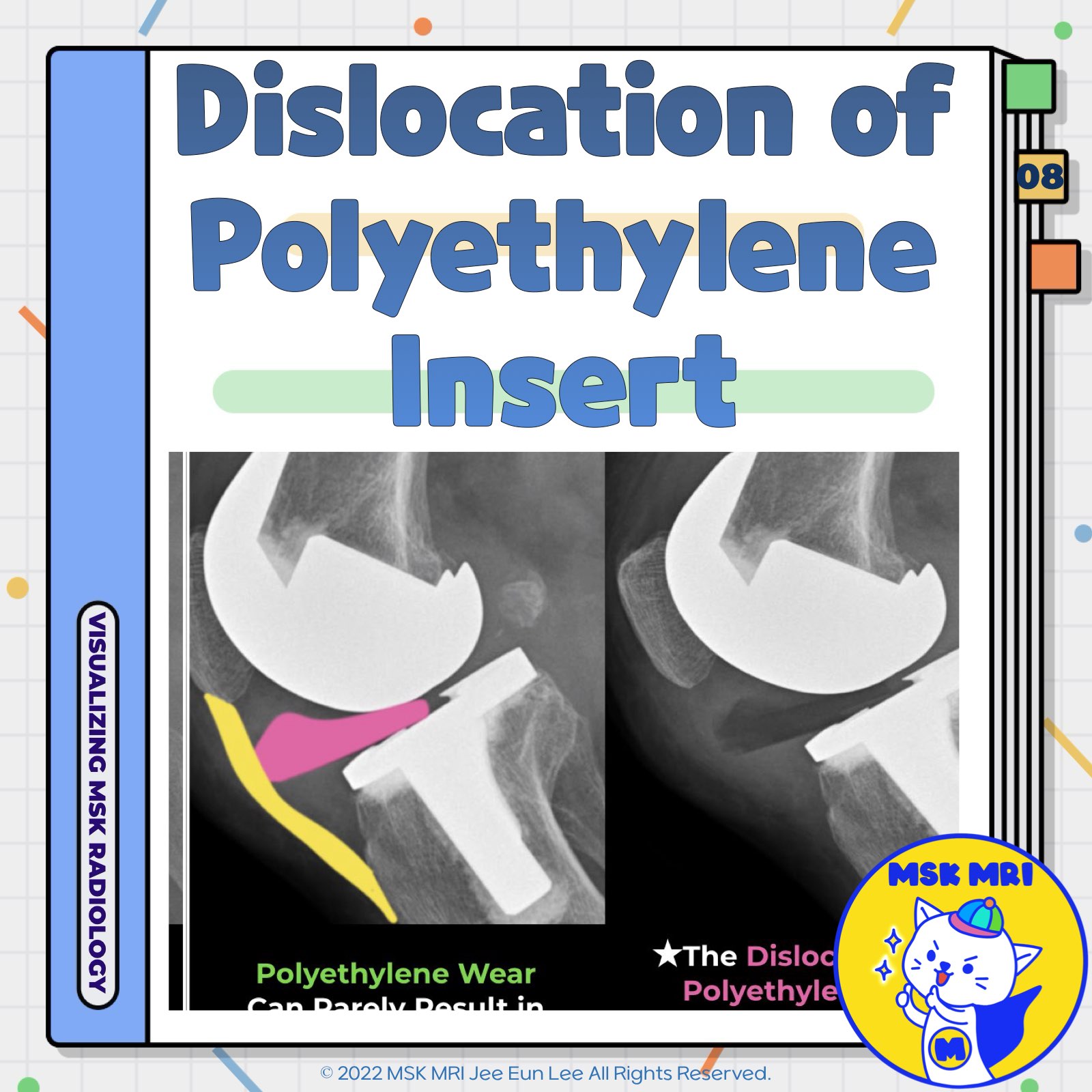
📌 Dissociation of the Polyethylene Tibial Insert in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Dissociation of the polyethylene tibial insert from the tibial baseplate is a rare complication after Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA).
- Dissociation of the polyethylene tibial insert can occur due to dislodgement of the locking screw or pin.
✅ MRI Findings
- Linear signal hyperintensity between the polyethylene tibial insert and tibial tray suggests the presence of dissociation.
- An obvious gap between the polyethylene tibial insert and tibial tray, along with thinning of the polyethylene tibial insert, indicates:
✅ Clinical Implications
- The dislocated polyethylene insert can cause significant damage to the patellar tendon.
- Dissociation should be considered in the differential diagnosis for patients with:
References
- AJR 2016; 206:1264–1271
- J Arthroplasty. 2011 Feb;26(2):339.e1-4
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#TotalKneeArthroplasty, #PolyethyleneTibialInsert, #Dissociation, #TKAInsert, #tibialinsert, #PatellarTendon, #KneeProsthesis, #OrthopedicImaging, #JointReplacement, #PolyethyleneInsert
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5CD. Cartilage Repair and TKA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-D.10) Aseptic Loosening (0) | 2024.07.19 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-D.09) Specific Zone Numbers of Periprosthetic Lucency after TKA (0) | 2024.07.19 |
| (Fig 5-D.07) Polyethylene Wear-Induced Synovitis and Osteolysis (0) | 2024.07.19 |
| (Fig 5-D.06) Polyethylene Wear–Induced Synovitis (0) | 2024.07.19 |
| (Fig 5-D.05) Radiographic Findings of Polyethylene Wear and Fracture (0) | 2024.07.19 |