https://youtube.com/shorts/Fm-lp01MQRg

Coalition by MSKMRI JEE EUN LEE.pdf
6.67MB
- Mechanism
-
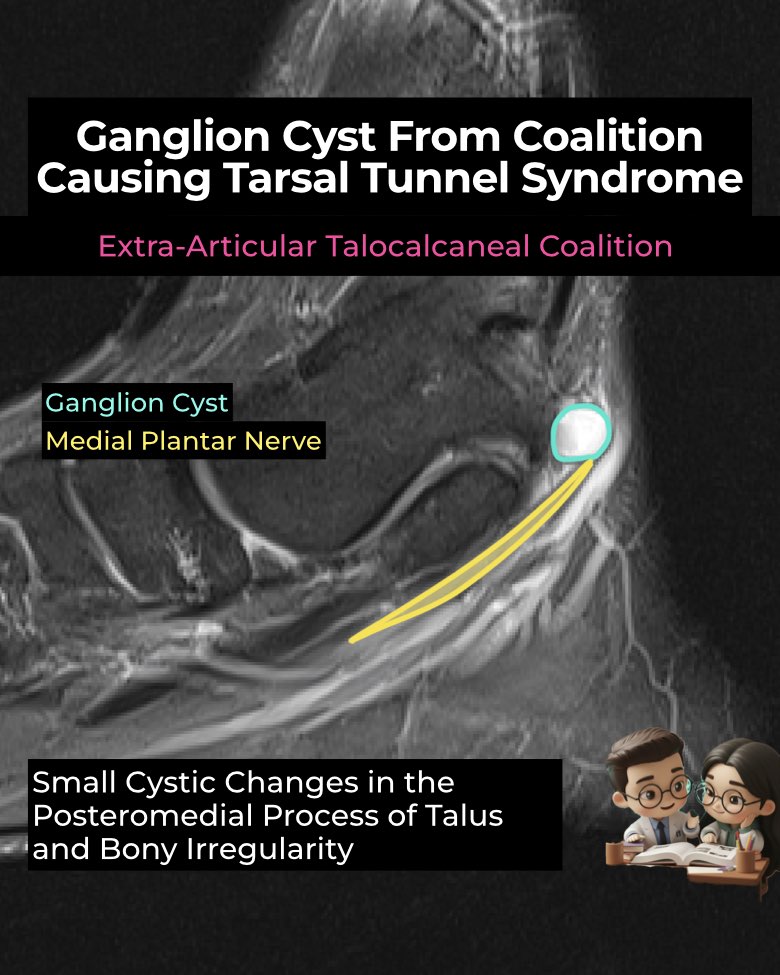
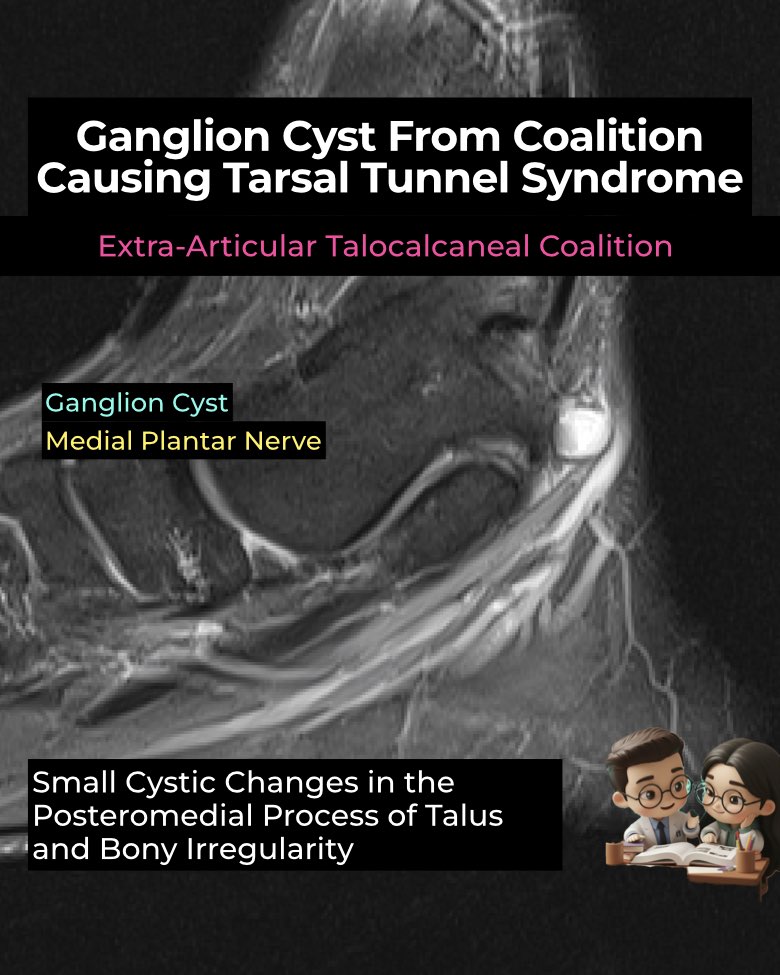
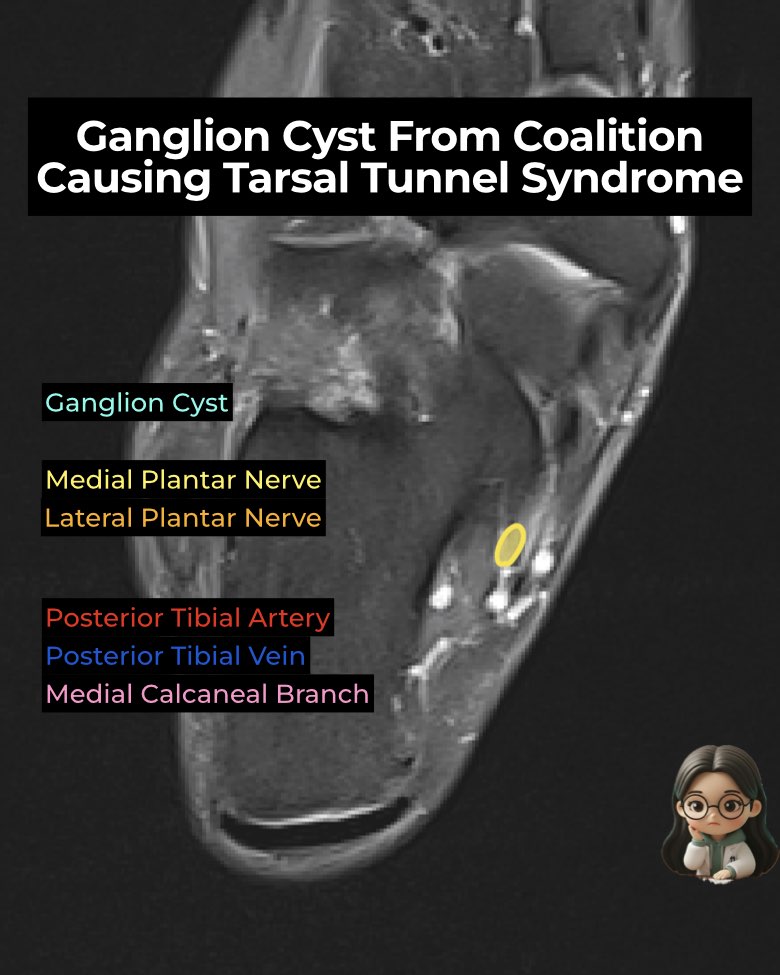
- Coalition mass effect: Non-osseous TCC (fibrous, cartilaginous) often shows bony excrescences or a dysmorphic sustentaculum tali encroaching into the tarsal tunnel.
-
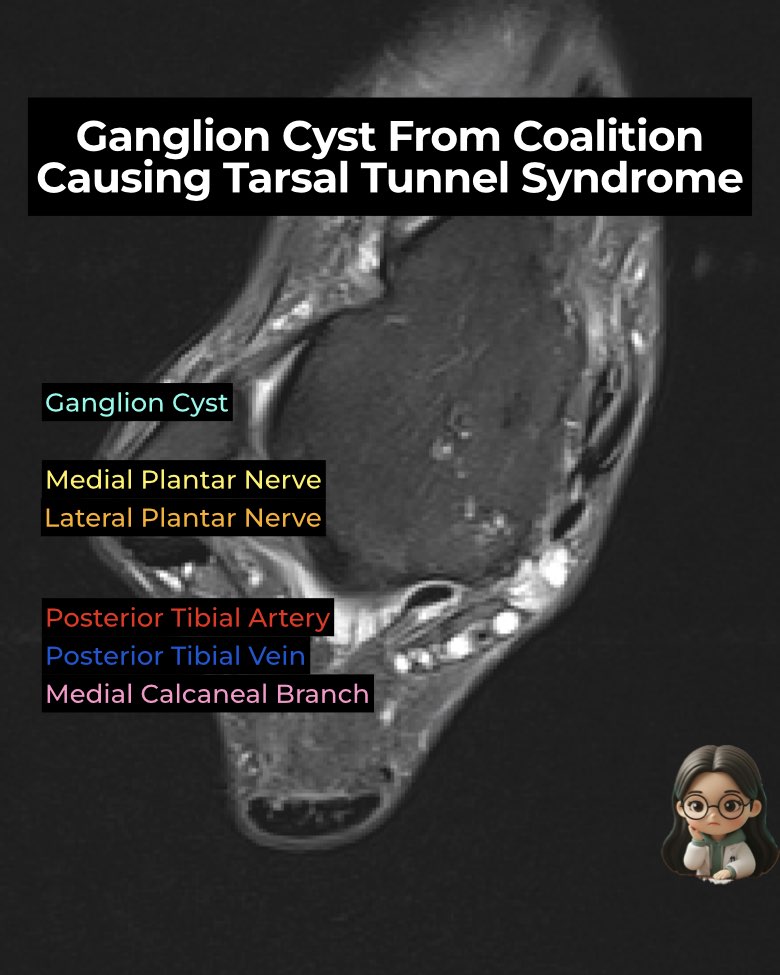
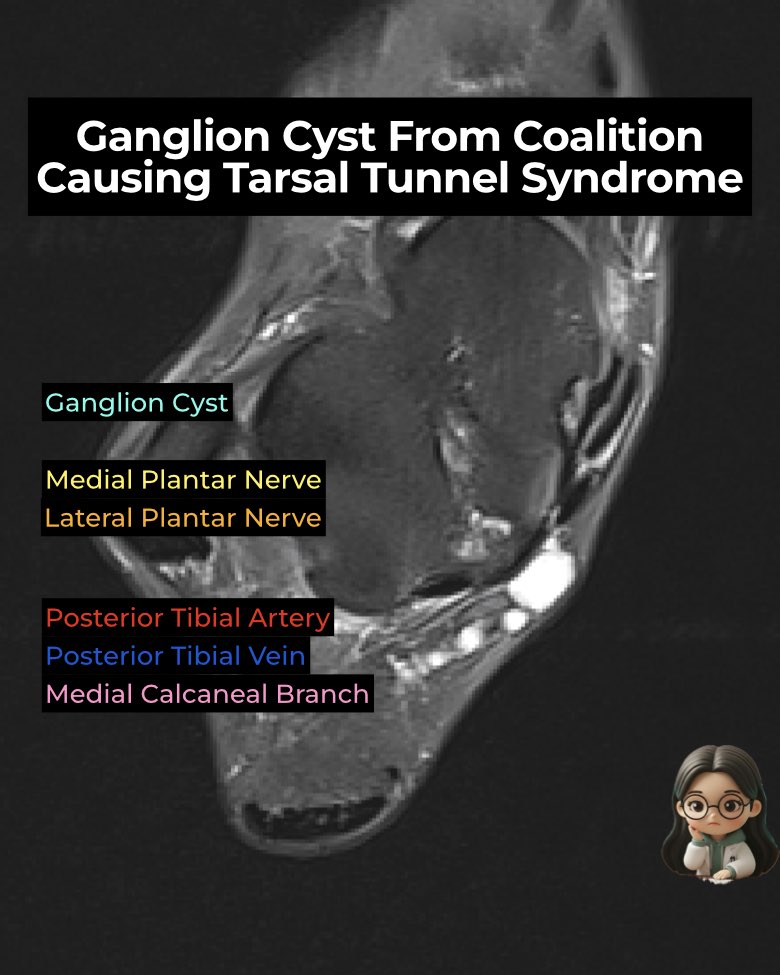
- Ganglion cysts: May arise from the fibrocartilaginous synchondrosis, decompress into the tarsal tunnel, and directly compress the tibial nerve and branches.
- Nerve Involvement
-
- Most affected: Medial plantar nerve (MPN) → stretched or displaced along FHL.
-
- Others: Lateral plantar nerve, calcaneal branches.
-
- Imaging may show neuritis: nerve enlargement and increased T2 signal.
- Tendon Involvement
-
- FHL and FDL most commonly impinged → tenosynovitis, tendinosis, split tears.
- MRI Findings
-
- Coalition: Irregular margins, marrow edema, pseudarthrosis.
-
- Ganglion cyst: Well-defined, fluid-intensity mass protruding into tunnel.
-
- Nerve changes: Hyperintense, thickened MPN ± displacement.
-
- Denervation: Edema or fatty atrophy in plantar muscles in chronic cases.
#Radiology #MSKMRI #TarsalCoalition #TarsalTunnelSyndrome #FootMRI #OrthopedicImaging #MRIDiagnosis #RadiologyEducation #Neuroradiology #MedicalEducation
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.