Type 4 lesions involve a complete longitudinal vertical tear in the posterior horn of the meniscus, leading to meniscotibial ligament instability.
There are two different subtypes of type 4 lesions in order to account for the instability pattern.
The subtype 4A is a complete longitudinal vertical tear of the red-red zone of the meniscus,
The second pattern (subtype 4B) involves a complete tear of the junction itself where the meniscocapsular and meniscotibial fibers attach to the posterior horn.
Edema and irregularity of the meniscocapsular junction of the posterior horn is the most frequent finding.
A fluid signal cleft at the meniscocapsular junction is most specific for making the diagnosis.
MRI shows edema at the meniscocapsular junction which replaces the typical fat signal. Although a discrete fluid-filled cleft is not identified, this appearance is suggestive of a meniscocapsular tear.
A small bone bruise is present in the subjacent posterior aspect of the medial tibia.
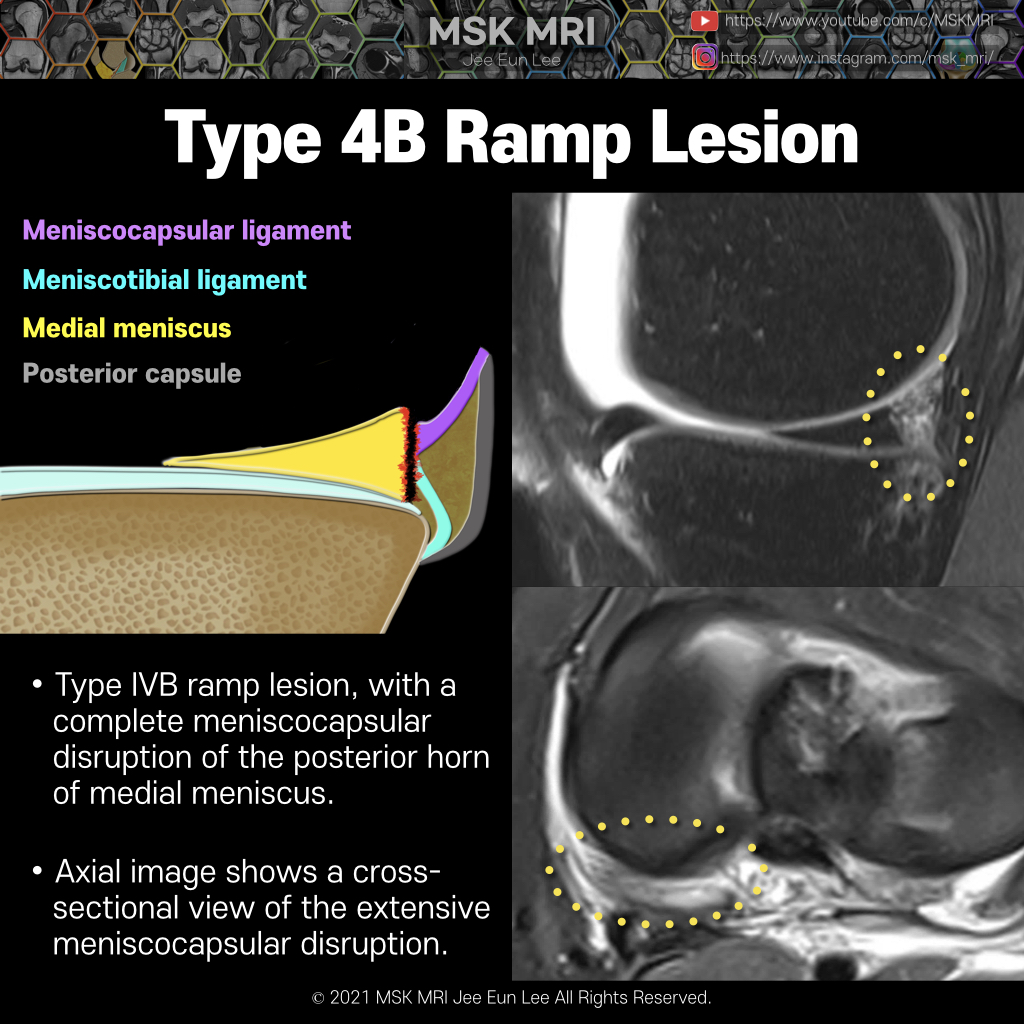


Axial image shows a cross-sectional view of the extensive meniscocapsular disruption.
© 2021 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
You may not distribute or commercially exploit the content. Nor may you transmit it or store it on any other website or other forms of the electronic retrieval system.
If you would like to use an image or video for anything other than personal use, please contact me.
(jamaisvu1977@gmail.com)


#MSKMRI, #virtualMRI, #radiologist, #Knee_MRI, #MSKMRI_Knee, #Knee_anatomy, #Knee_meniscus, #meniscus, #Virtual_MRI, #MRI_illustrator, #medialmeniscus, #MM, #meniscustear, #medialmeniscustear, #Ramplesion, #longitudinaltear, #ACLtear,#meniscocapsularseparation