

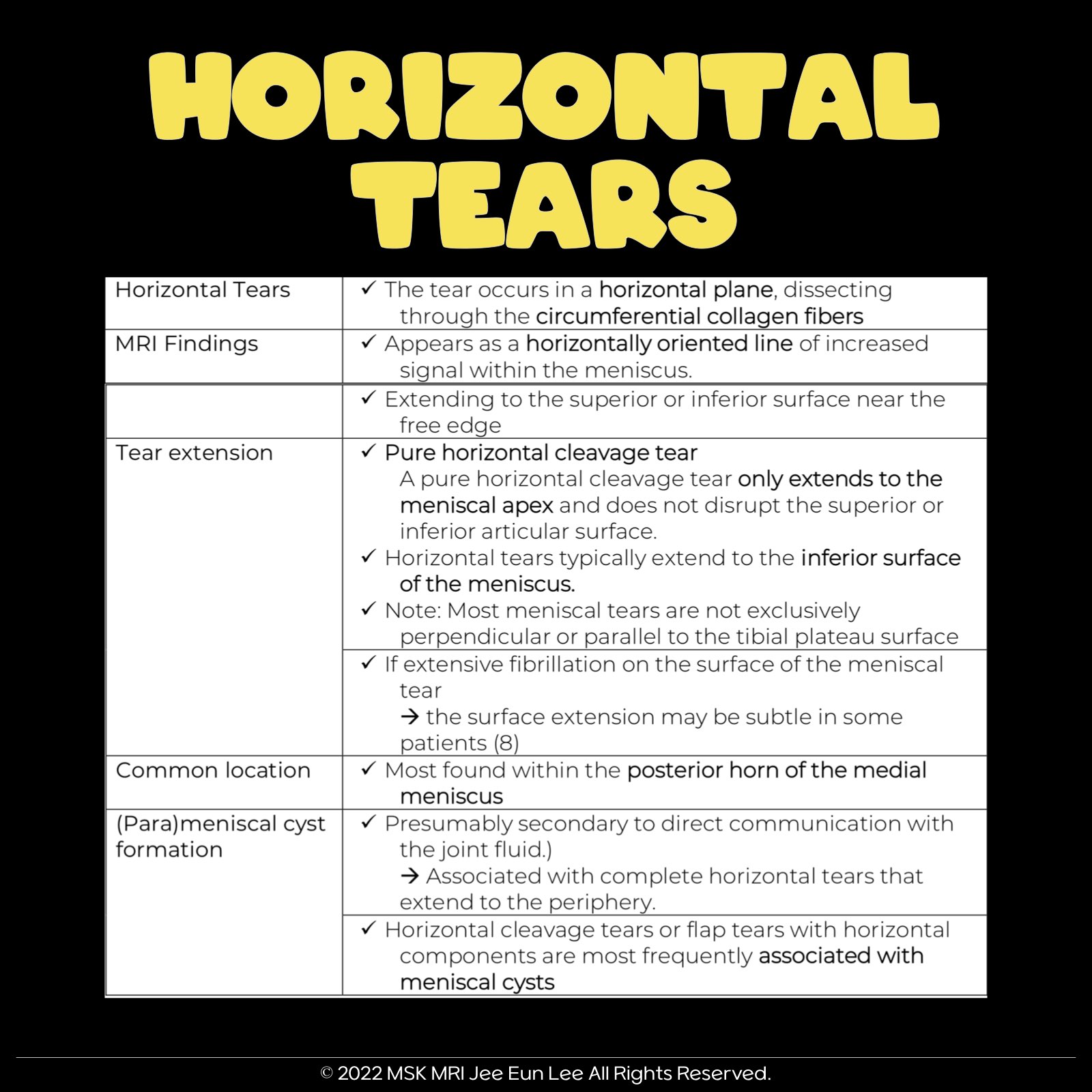
| Horizontal Tear | Meniscal tear in horizontal plane, dissecting through circumferential collagen fibers. |
| MRI Appearance of Tear | Appears as a horizontally oriented line of increased intrameniscal signal extending to the superior or inferior surface of the meniscus, typically near the free edge. |
| Common Location | Most common within the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. |
| Characteristics of Tear | A pure horizontal cleavage tear extends only to the meniscal apex without superior or inferior articular surface disruption. |
| Parameniscal Cysts | Appear as lobulated lesions with increased signal adjacent to the meniscus. A high-signal-intensity fluid collection either directly overlying or adjacent to the meniscus. |
| Secondary Signs of Tear | Common secondary or indirect signs include parameniscal cyst, meniscal extrusion, and subchondral marrow edema. Horizontal cleavage or flap tears with horizontal components are often associated with meniscal cysts. |
#MeniscalTears #Horizontaltear #VisualizingMSK
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 1. Meniscus' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 1-B.04) Longitudinal-Vertical Meniscal Tears with ACL tear (1) | 2024.01.19 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 1-B.03) Longitudinal-Vertical Meniscal Tears (0) | 2024.01.18 |
| (Fig 1-A.18) anterior meniscofemoral ligament of the medial meniscus, infrapatellar plica (1) | 2024.01.16 |
| (Fig 1-A.17) Oblique meniscomeniscal ligament (0) | 2024.01.15 |
| (Fig 1-A.16) Anterior intermeniscal ligament (0) | 2024.01.14 |