Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
1️⃣ Graft Impingement Overview
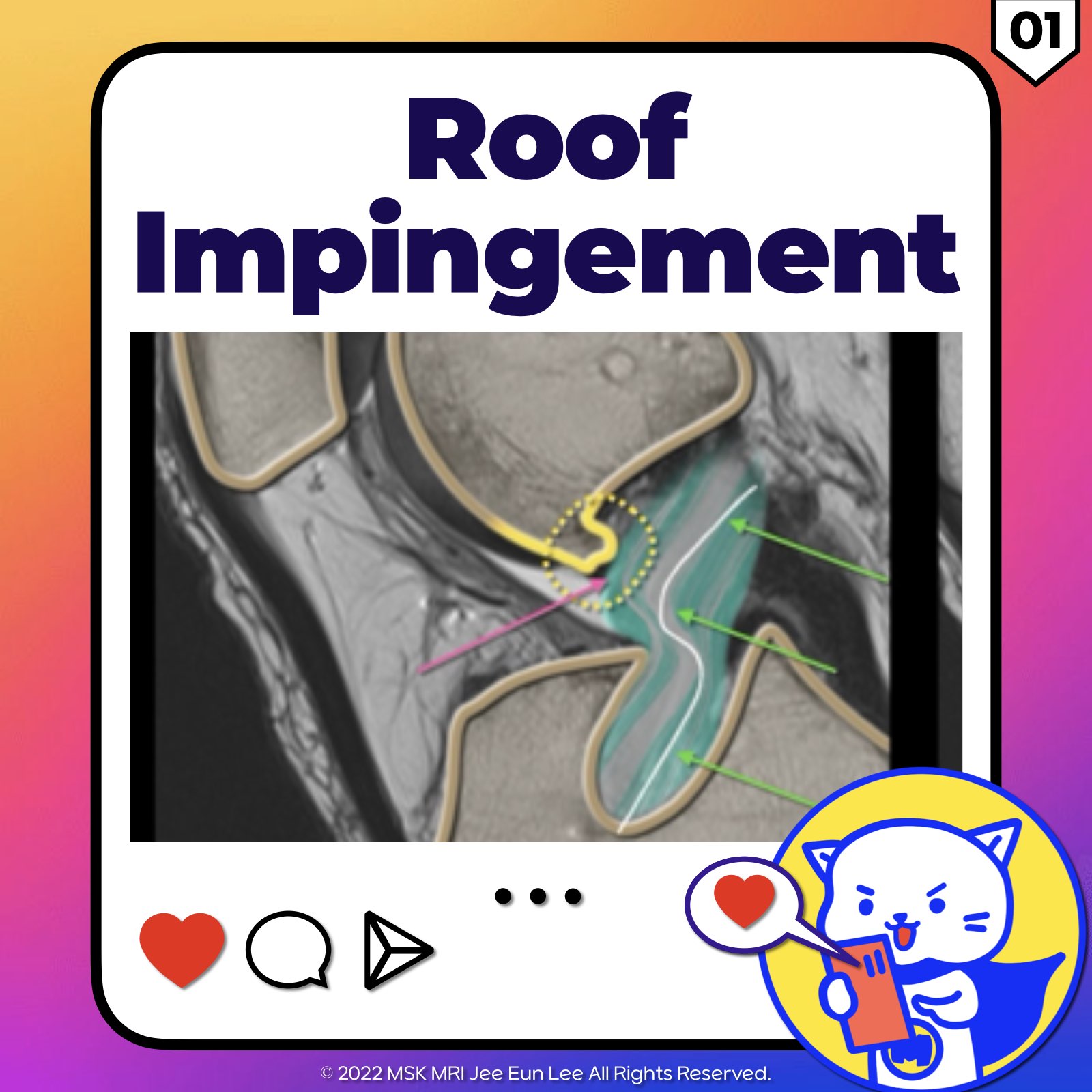
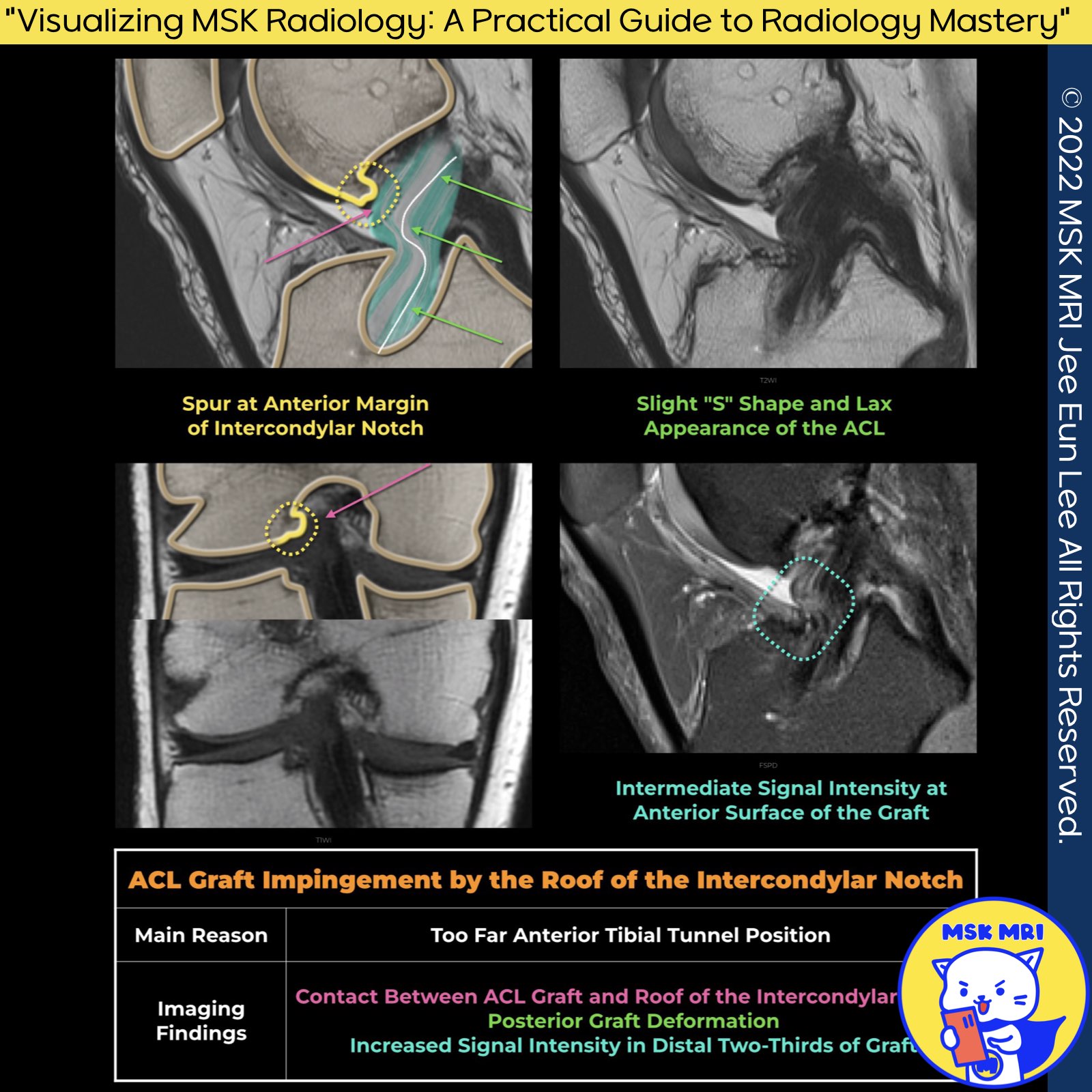
- Graft impingement is identified by the graft's repeated or constant friction against the intercondylar notch roof.
- Patients experiencing graft impingement often report a decrease in their range of motion, particularly in achieving full extension.
- This condition may increase the risk of graft tearing.
2️⃣ Common Causes and Mechanisms
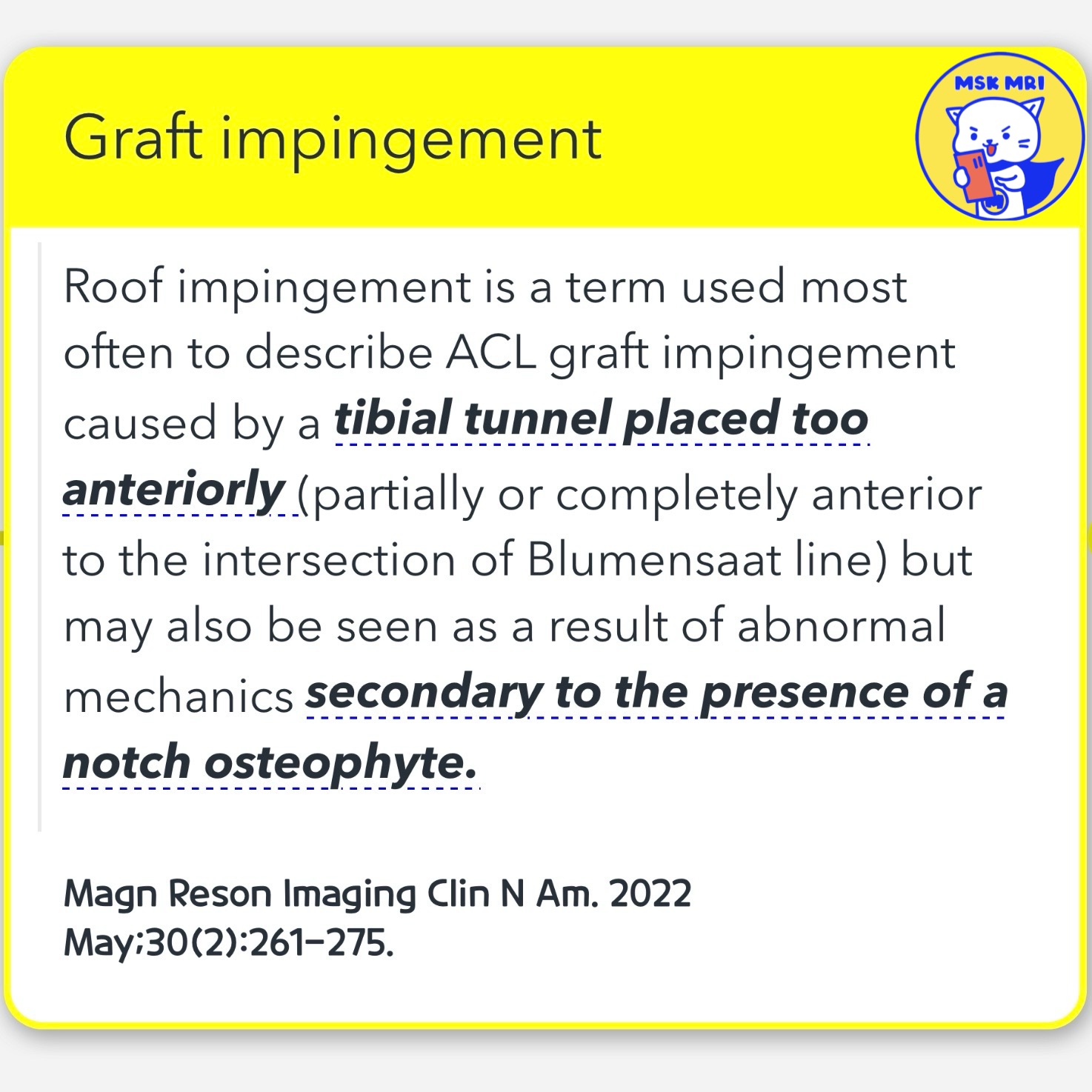
- mainly due to the anterior positioning of the tibial attachment site(either partially or completely in front of the Blumensaat line intersection) or the presence of bony spurs within the intercondylar notch.
- Anterior misplacement of the tibial tunnel may prevent full joint extension due to graft impingement. Additionally, intercondylar bony spurs may exacerbate graft rupture progression through graft shearing.
3️⃣ MRI Findings
- MR imaging reveals direct contact between the ACL graft's anterior aspect and the intercondylar notch's roof,
- Potentially leading to the graft's posterior deformation by the anterior inferior edge of the intercondylar roof.
- There's often an increased signal intensity observed within the distal two-thirds of the graft.
- Increased graft's signal intensity, often focal and selectively involving the anterior two-thirds of the graft.
→ This increase in signal intensity can persist beyond one year, distinguishing it from changes attributed to graft incorporation.
4️⃣ Importance of Avoiding Roof Impingement
- Some research underscores that preventing roof impingement is crucial for graft success, surpassing the need for perfect isometry—maintaining the graft's ideal length and tension through the knee's full range of motion.
- Skeletal Radiol. 2005;34:431–52
Skeletal Radiol. 2022 Jul;51(7):1347-1364
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2022 May;30(2):261-275.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved. #VisualizingMSK #ACLinjuries #KneeMRI #ACLtear #aclreconstructionprocedure #aclr #roofimpingement #aclgraft You may not distribute or commercially exploit the content. Nor may you transmit it or store it on any other website or other forms of the electronic retrieval system.
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 2.ACL and PCL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 2-D.03) Sidewall impingement with ACL Graft tear (0) | 2024.03.09 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 2-D.02) Sidewall impingement ACL reconstruction (0) | 2024.03.09 |
| (Fig 2-C.13) MRI Characteristics of Different Graft Type (0) | 2024.03.03 |
| (Fig 2-C.12) ACL Graft Ligamentization (0) | 2024.03.03 |
| (Fig 2-C.10) Amis and Jacob’s method, ACL tibial tunnel (0) | 2024.03.02 |