==============================================
⬇️✨⬇️🎉⬇️🔥⬇️📚⬇️
Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
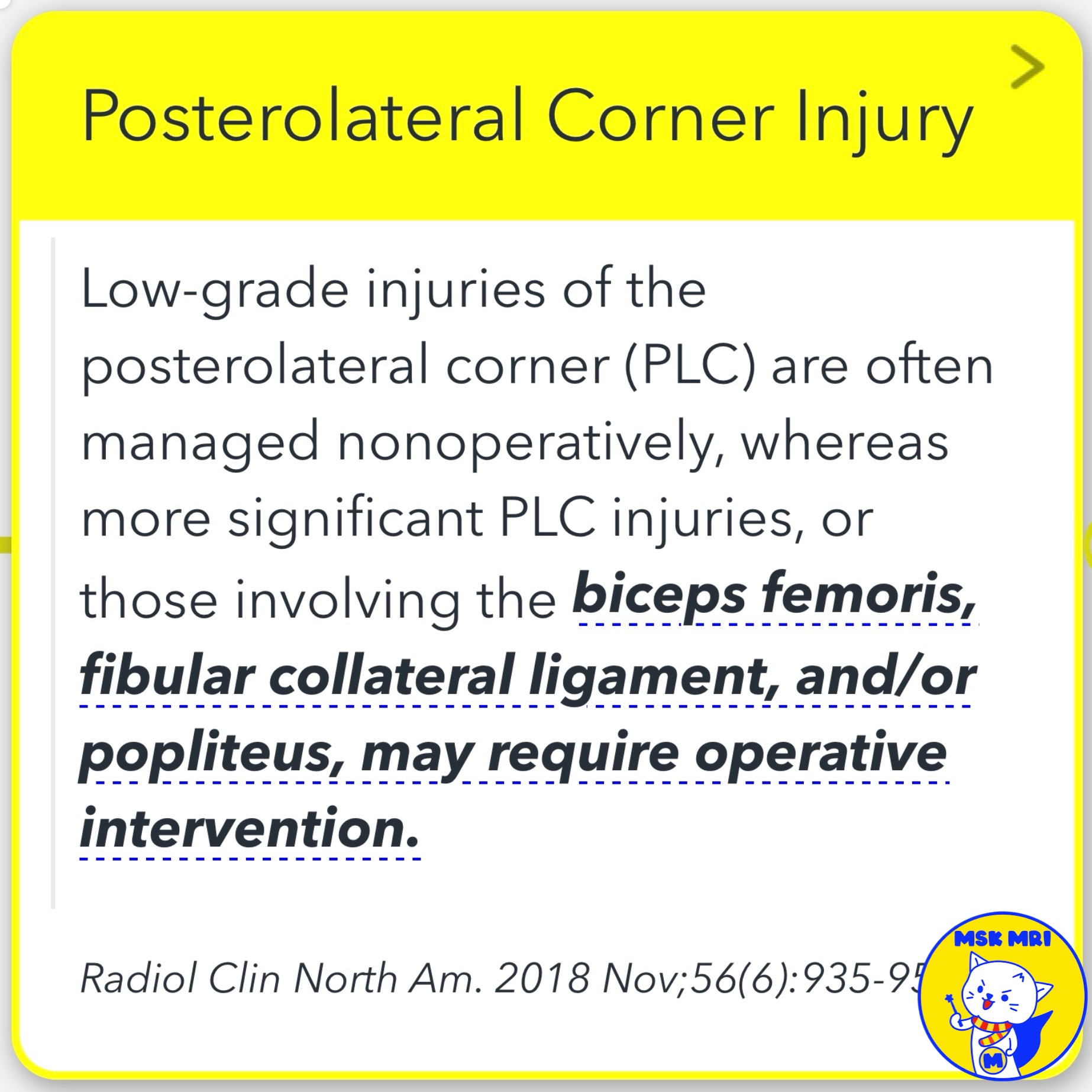
📌 Posterolateral Corner (PLC) Injury Treatment
✅ Treatment Overview
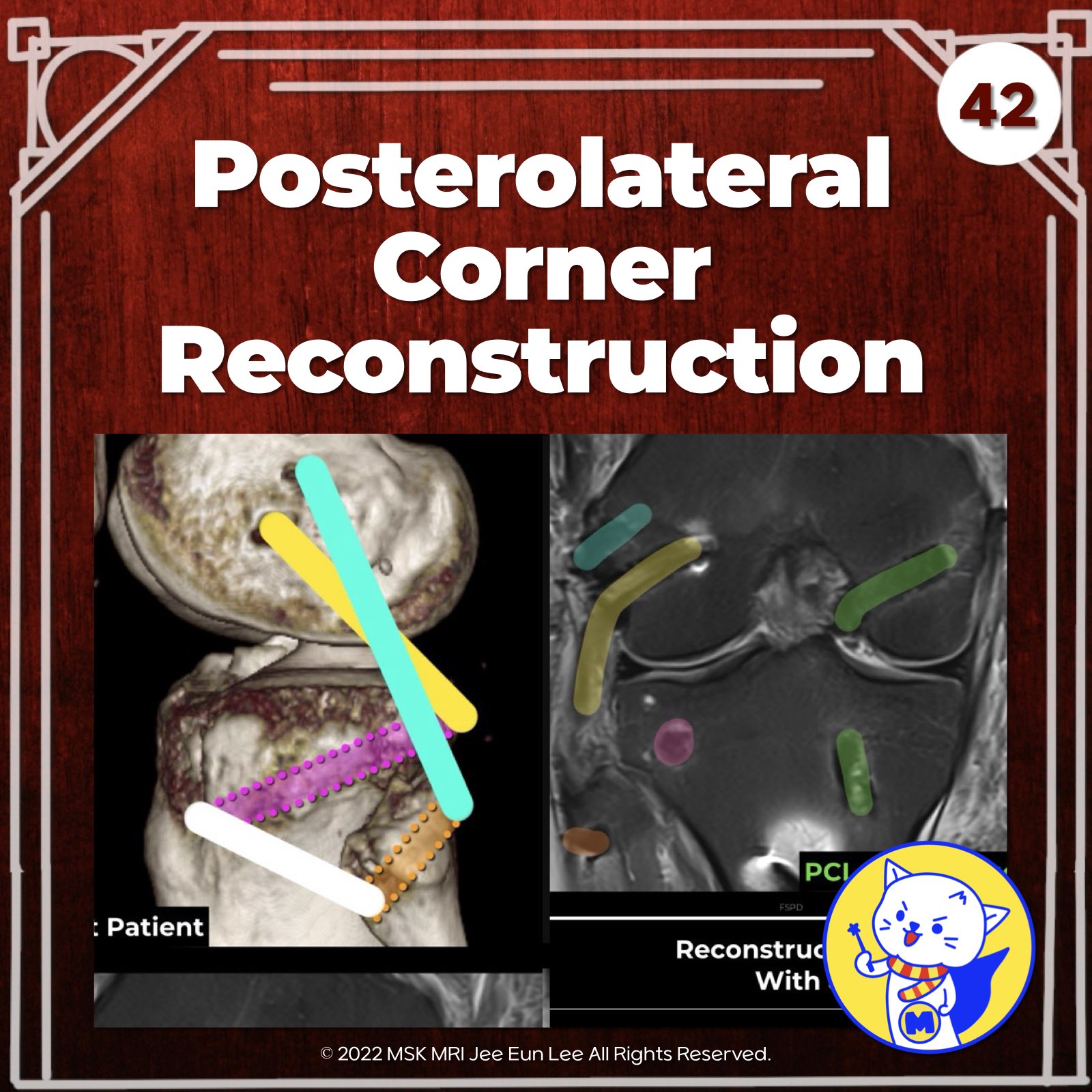
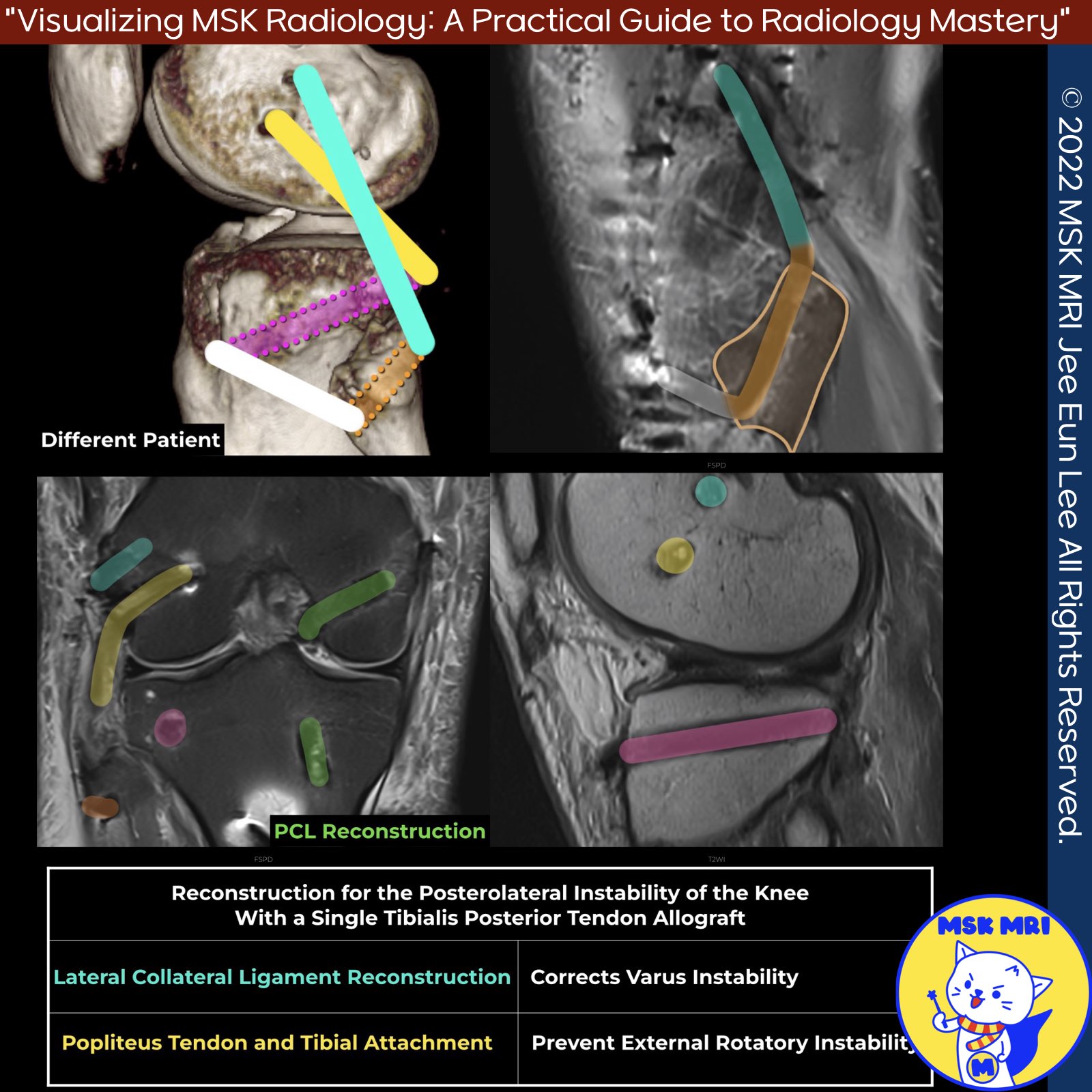
- High-grade PLC injuries are best treated with reconstruction rather than repair.
- The lateral collateral ligament (LCL), popliteus tendon (PT), and popliteofibular ligament (PFL) are key reconstruction focus areas.
✅ Acute Injury Management
- Grade I and II: Use a knee brace in extension for 4-6 weeks, followed by physical therapy. Delayed ACL or PCL reconstruction may follow once knee mobility is restored.
- Grade III: Prompt reconstruction of cruciate ligaments and PLC structures. Avulsion injuries are repaired directly to bone, and primary repairs of LCL and PT avulsions without midsubstance tears are done within 2-3 weeks post-injury.
✅ Chronic Injury Management
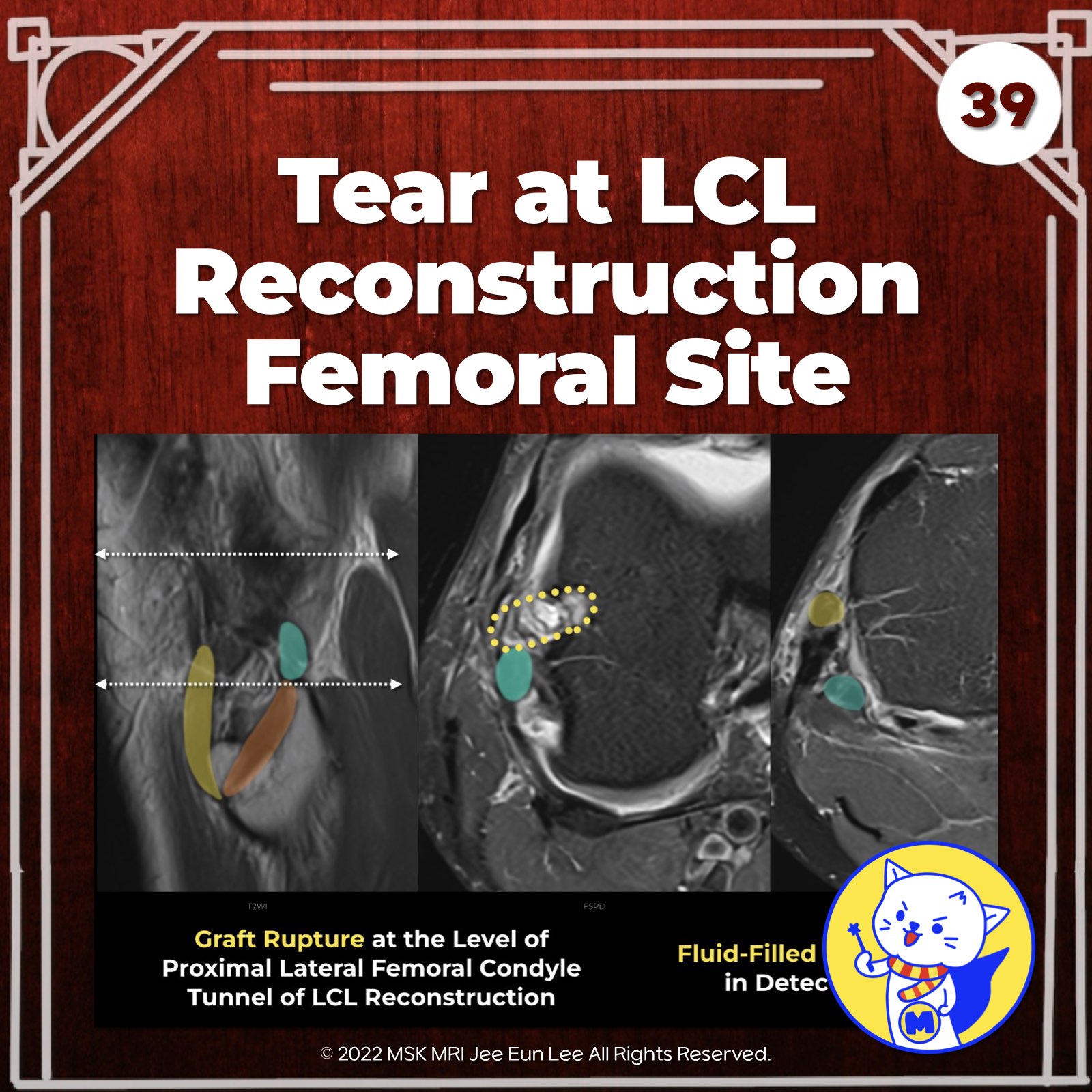
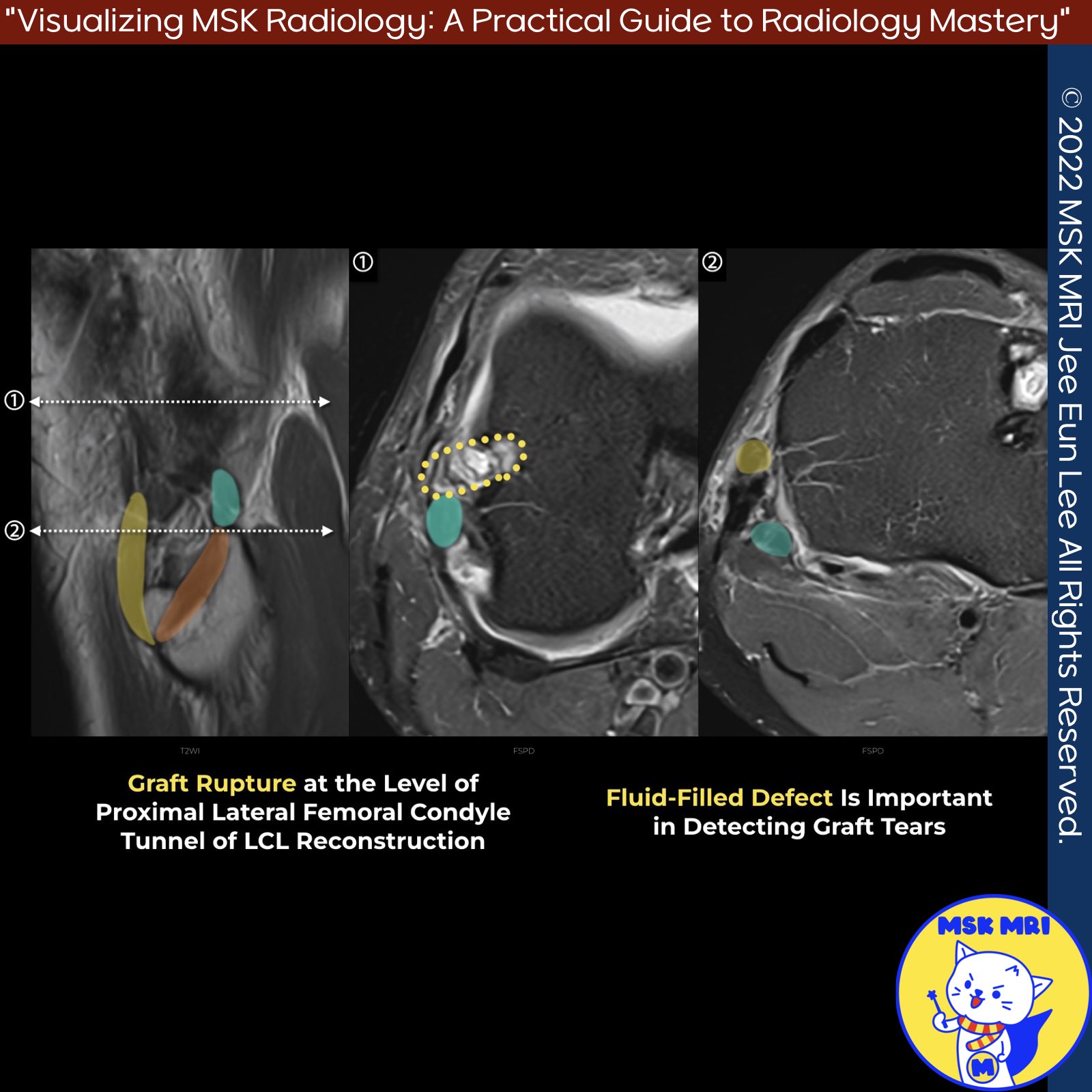
- Chronic injuries often require ligamentous reconstruction and correction of varus deformity via high tibial medial open osteotomy.
✅ Nonanatomical: These techniques do not place tunnels at the native ligament footprints.
- Clancy Procedure: Tenodesis of the distal biceps tendon to mimic the LCL.
- Larson Procedure: Uses a vertical graft limb from the fibular head to the lateral femoral condyle and an oblique graft limb from the posterior fibular head to the femoral condyle.
- Modified Larson (Fanelli): Uses a washer lock and a figure-of-eight graft configuration.
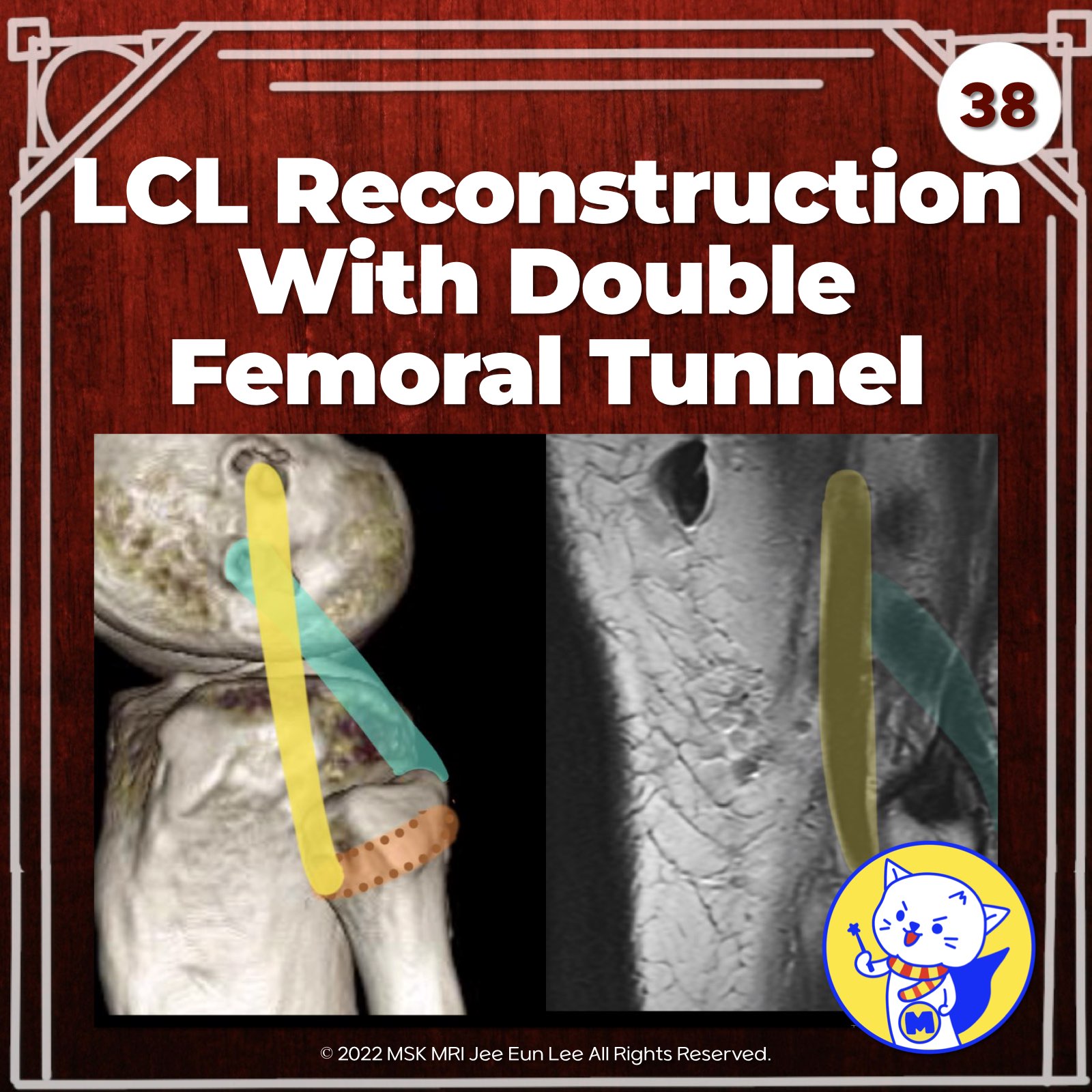
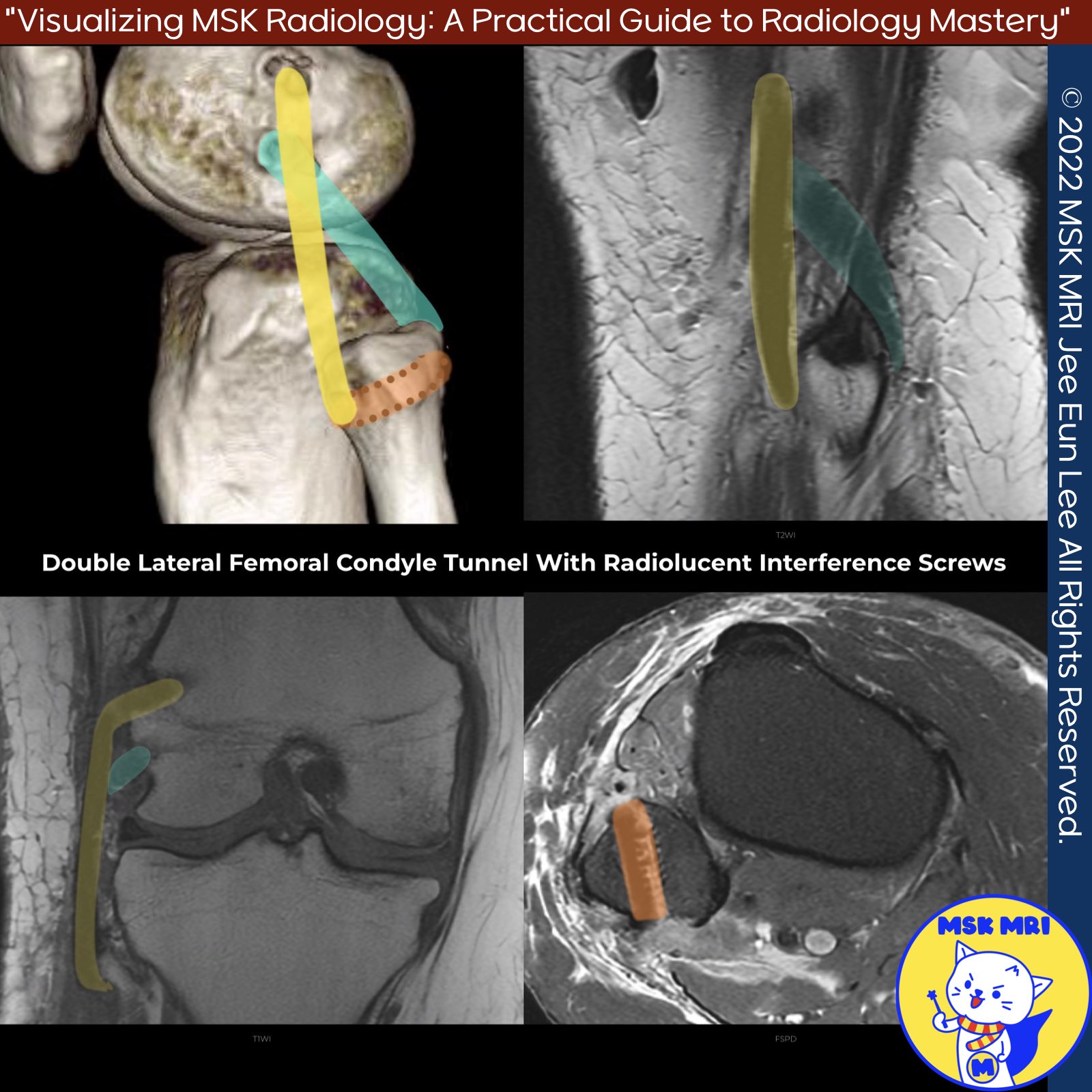
- Modified Larson (Arciero): Involves two femoral drill holes to reconstruct the PT and LCL footprints.
- Stannard’s Technique: Uses anterior or posterior tibial allografts (minimum 2.4 cm) to reconstruct the LCL, PT, and PFL.
✅ Anatomical: These techniques place grafts in the native anatomical positions.
- LaPrade’s Technique: Reconstruction of the LCL, PT, and PFL with two femoral tunnels, one tibial tunnel, and one fibular tunnel. Preferred graft is a split Achilles allograft.
References
- Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2016 Feb;20(1):52-64.
- Arthroscopy. 2004 Jul;20 Suppl 2:195-200.
- Radiol Clin North Am. 2018 Nov;56(6):935-951.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#PLCInjury, #KneeReconstruction, #OrthopedicSurgery, #LigamentReconstruction, #SportsMedicine, #KneeInjuryTreatment, #LCLReconstruction, #PopliteusTendon, #OrthopedicResearch, #KneeSurgery
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 3.Collateral Ligaments' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Segond Fracture: Key Indicator of ACL Injury You Shouldn’t Miss (0) | 2025.01.15 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 3-B.40, 41) Anterolateral Ligament Reconstruction (0) | 2024.05.25 |
| (Fig 3-B.37) Anterior Medial Tibial Plateau Rim Fracture (0) | 2024.05.24 |
| (Fig 3-B.36) Fibular Head Avulsion Fractures (0) | 2024.05.24 |
| (Fig 3-B.35) Fibula Head Attachments Anatomy (0) | 2024.05.24 |