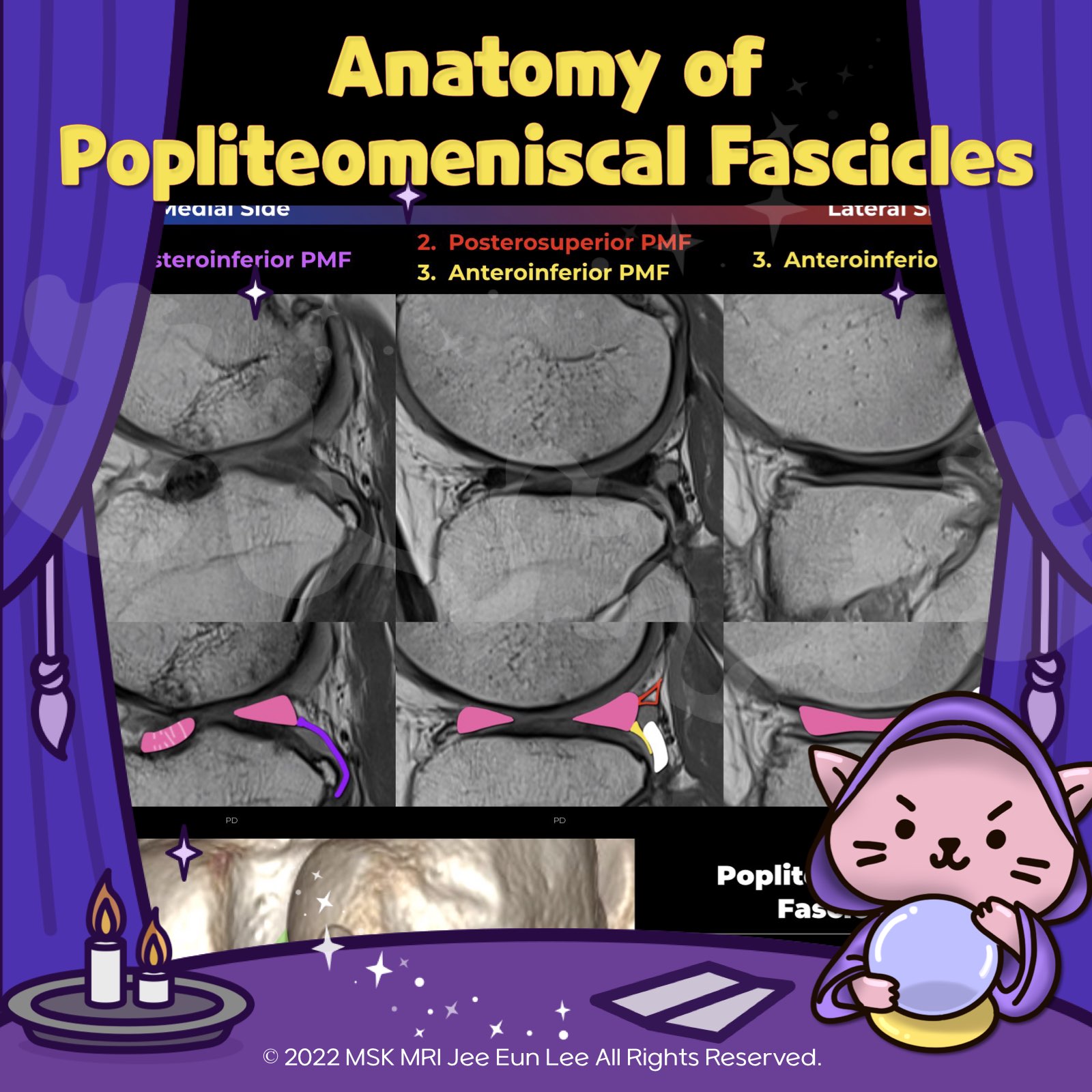
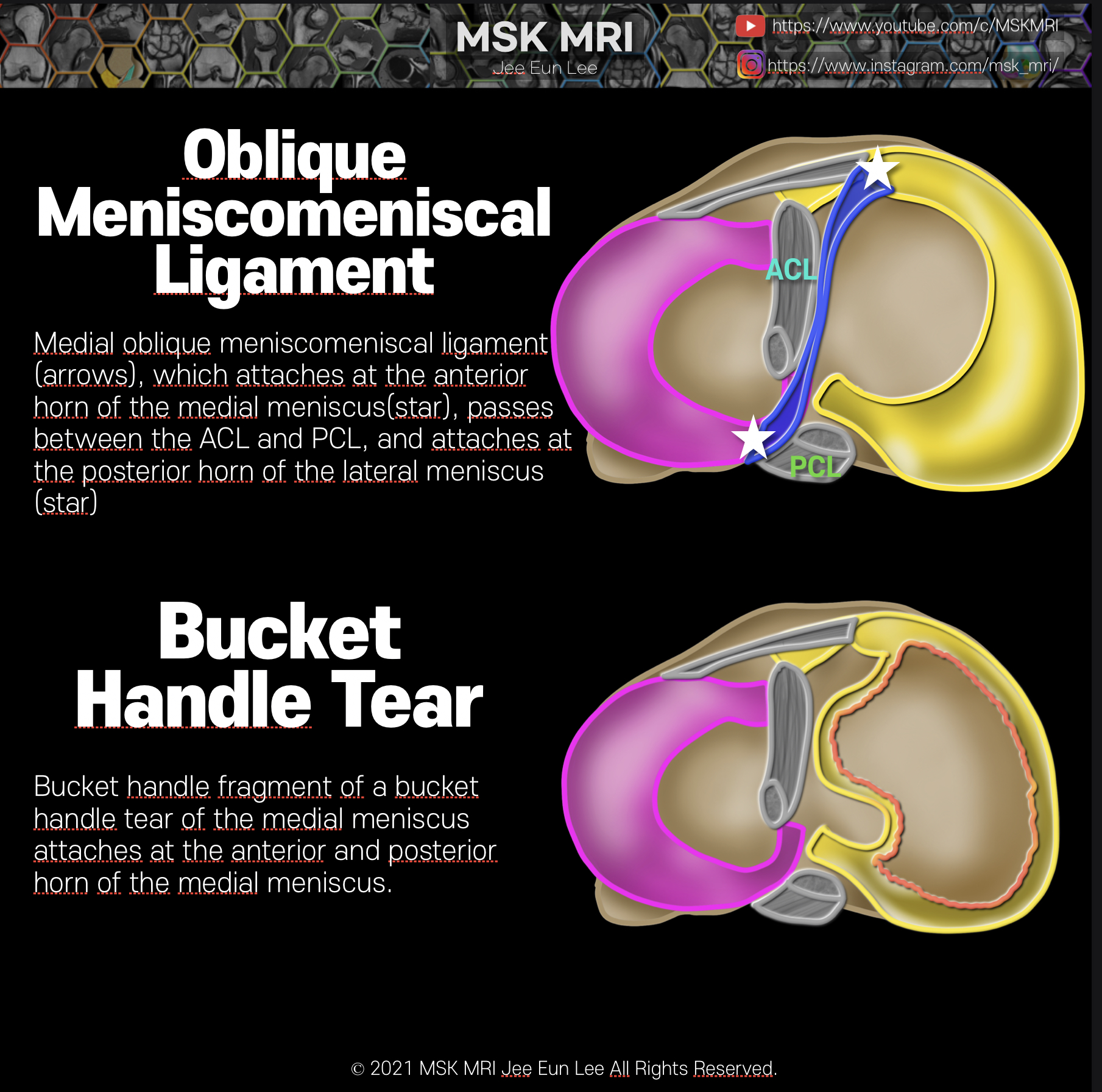
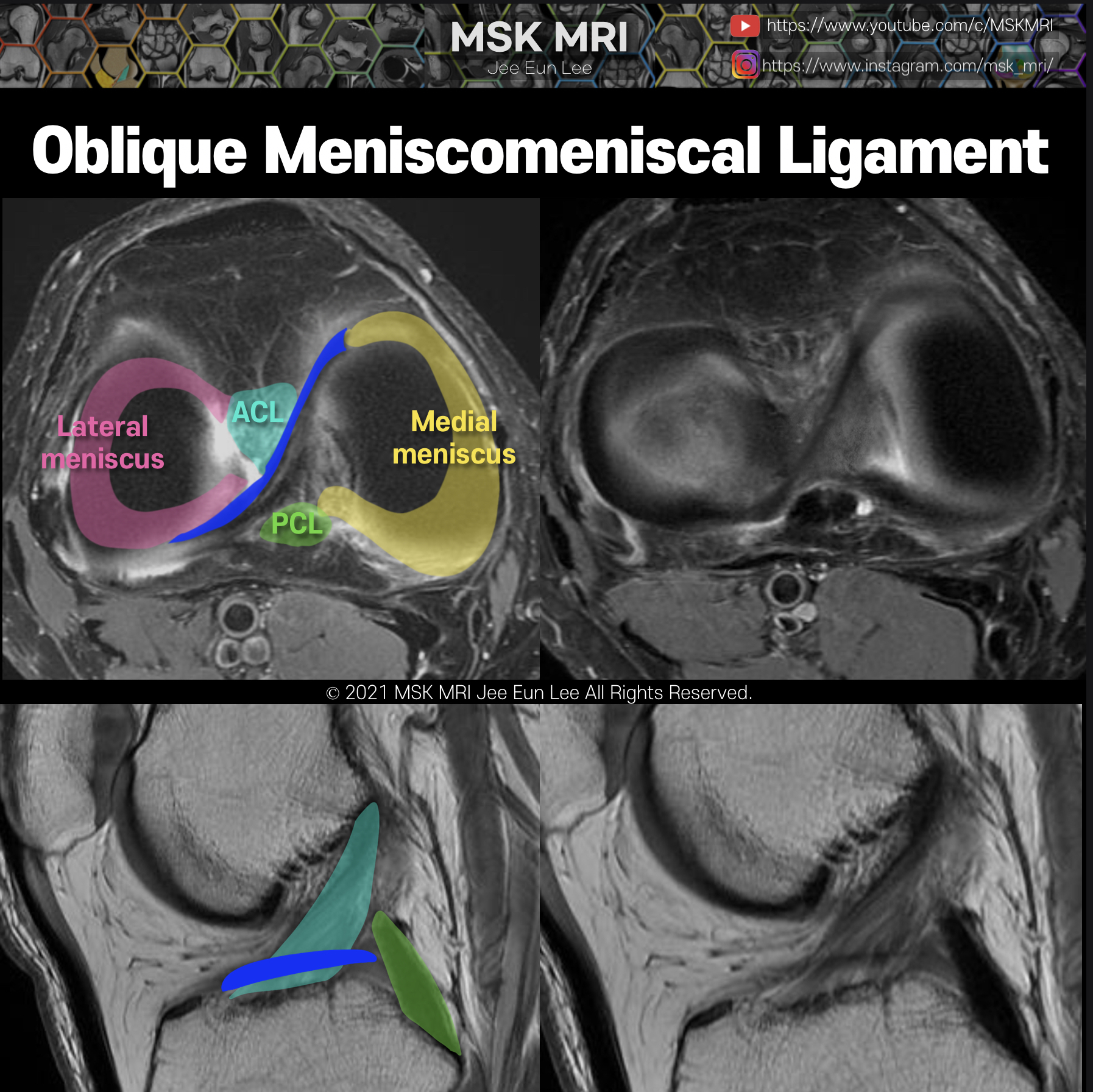
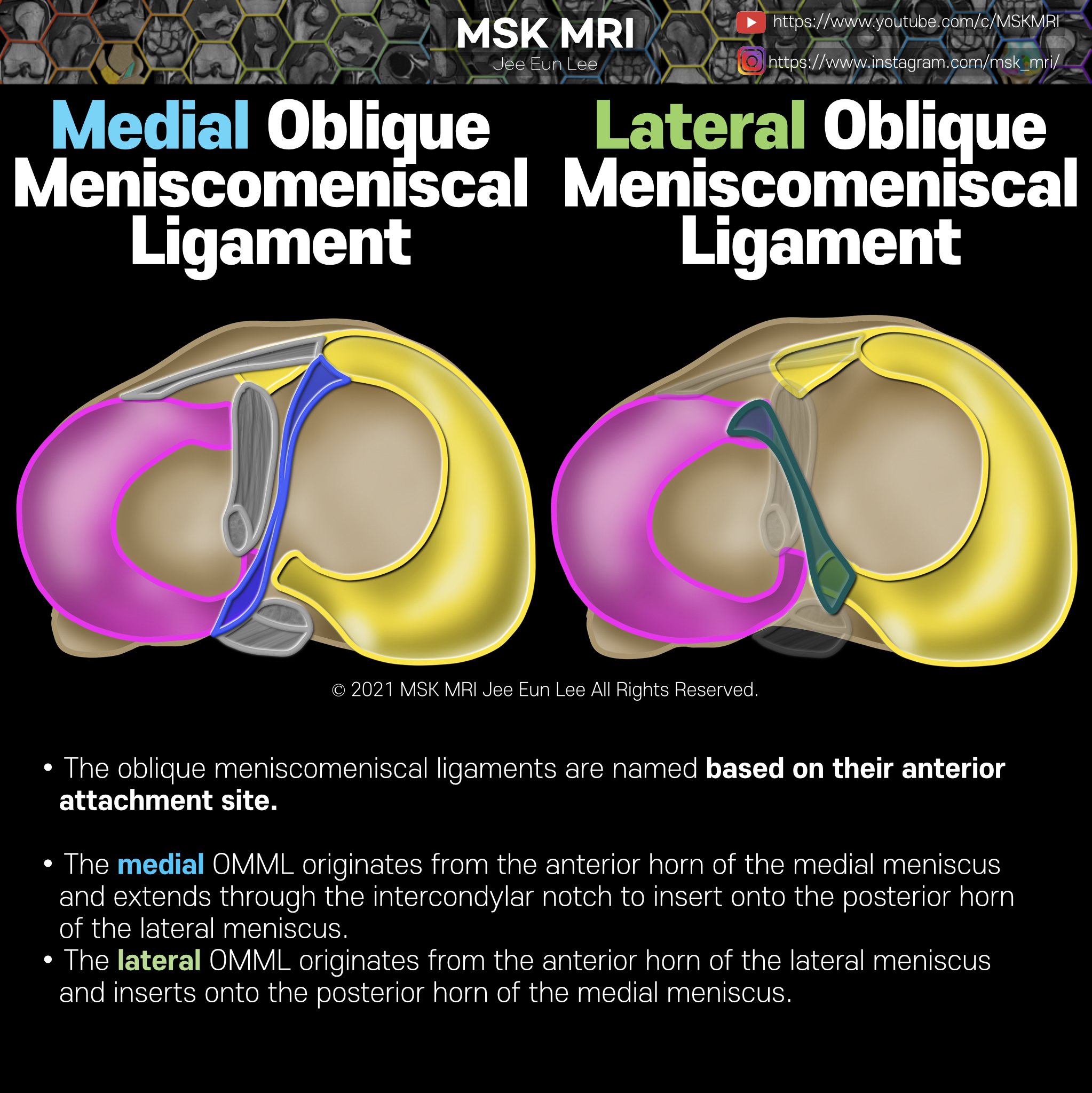
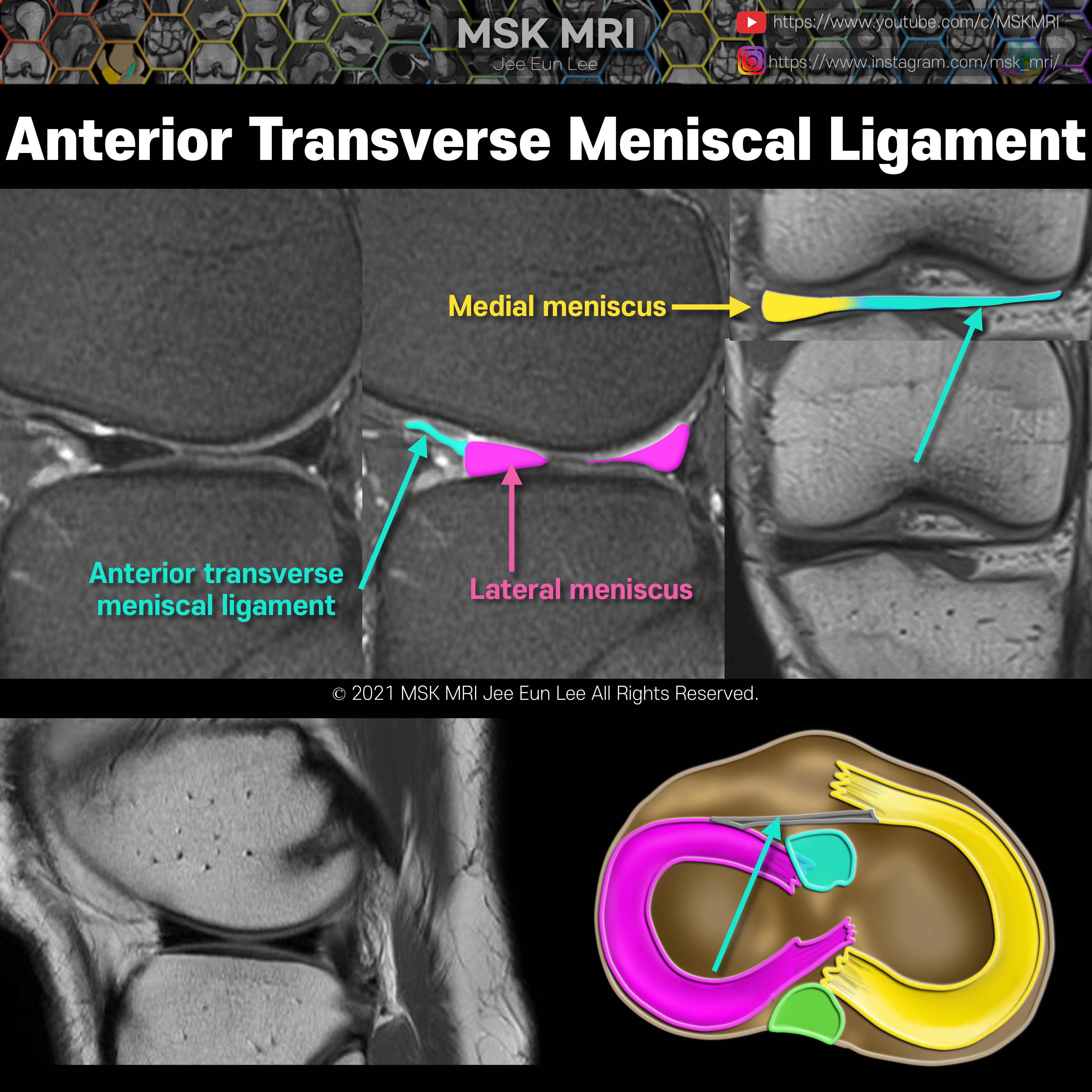
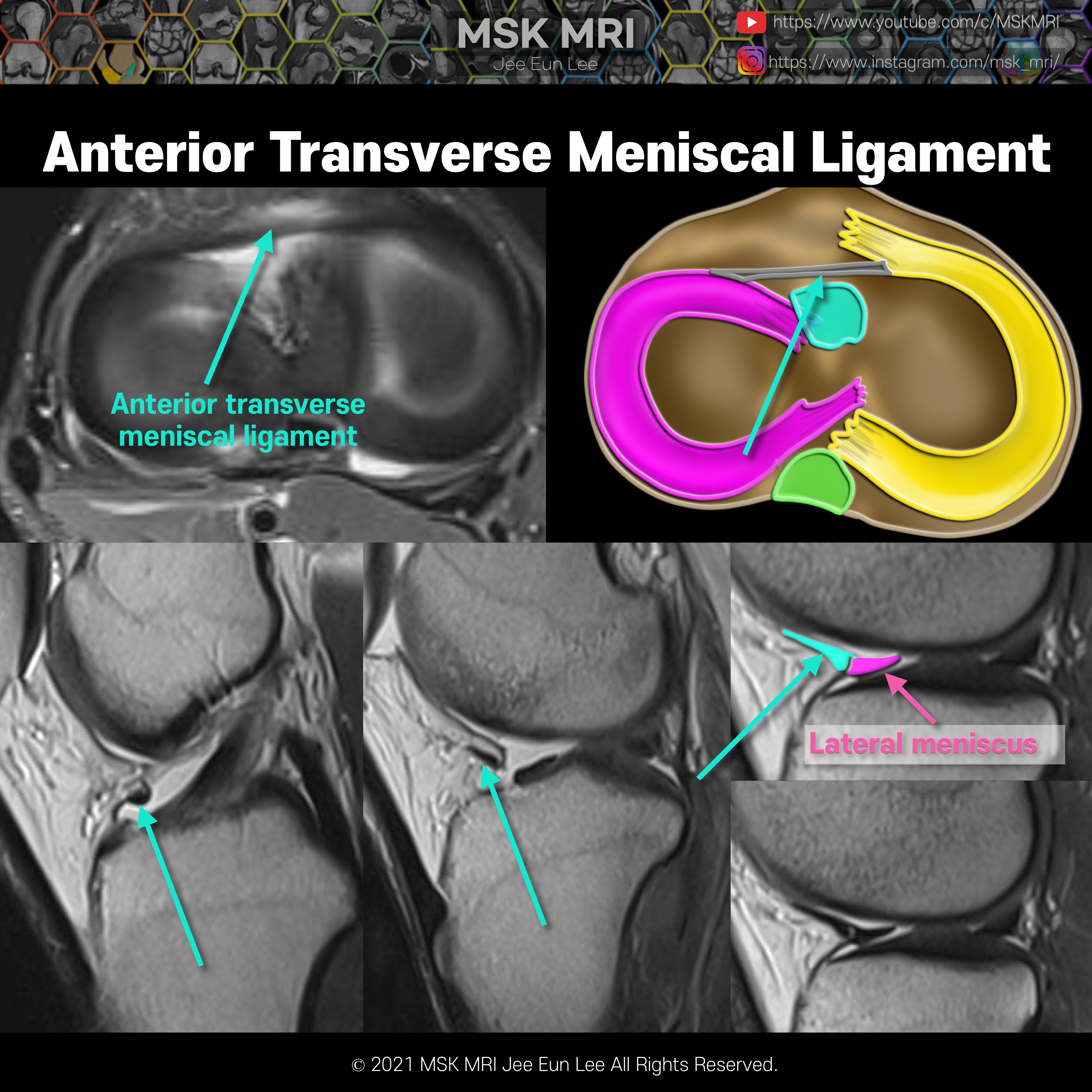
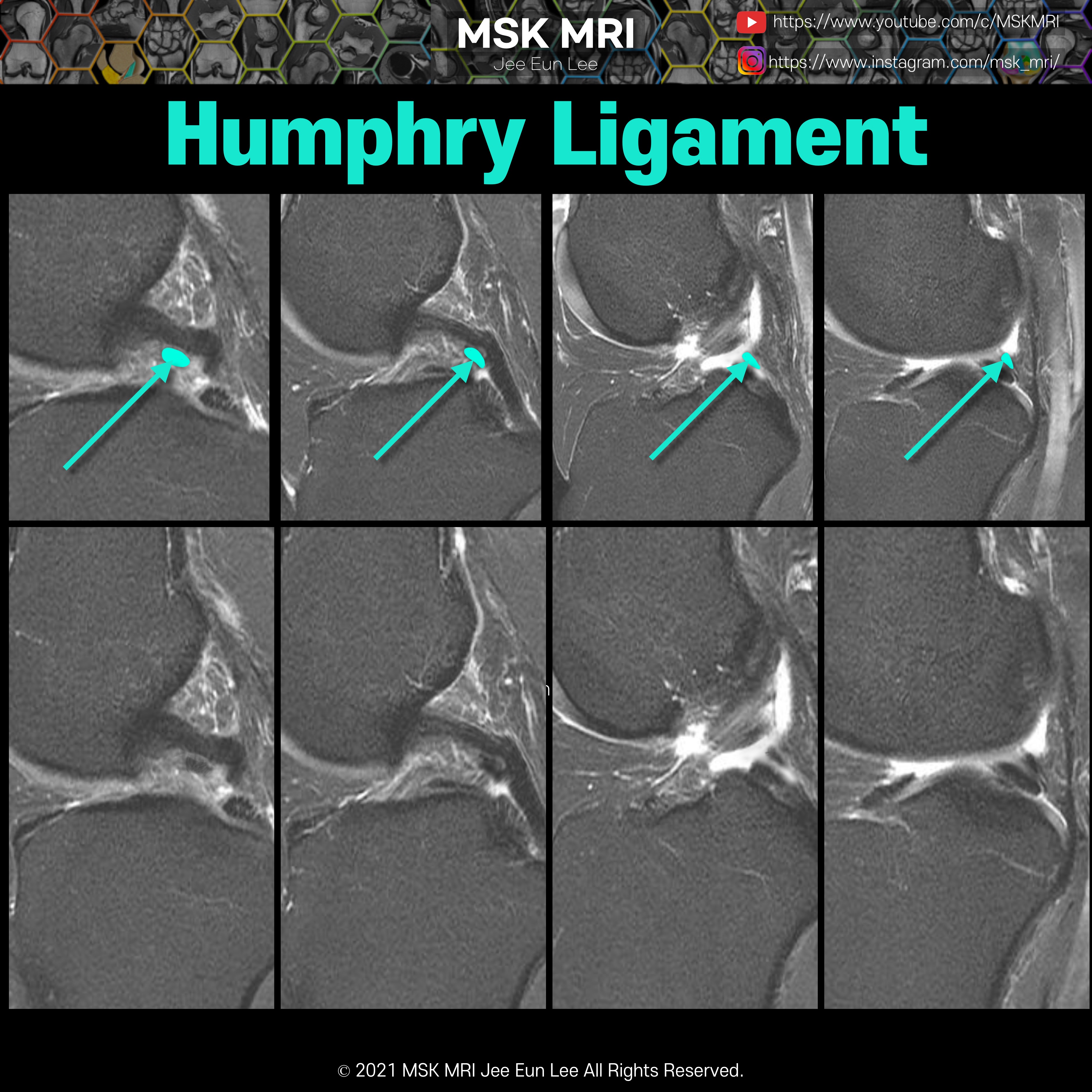
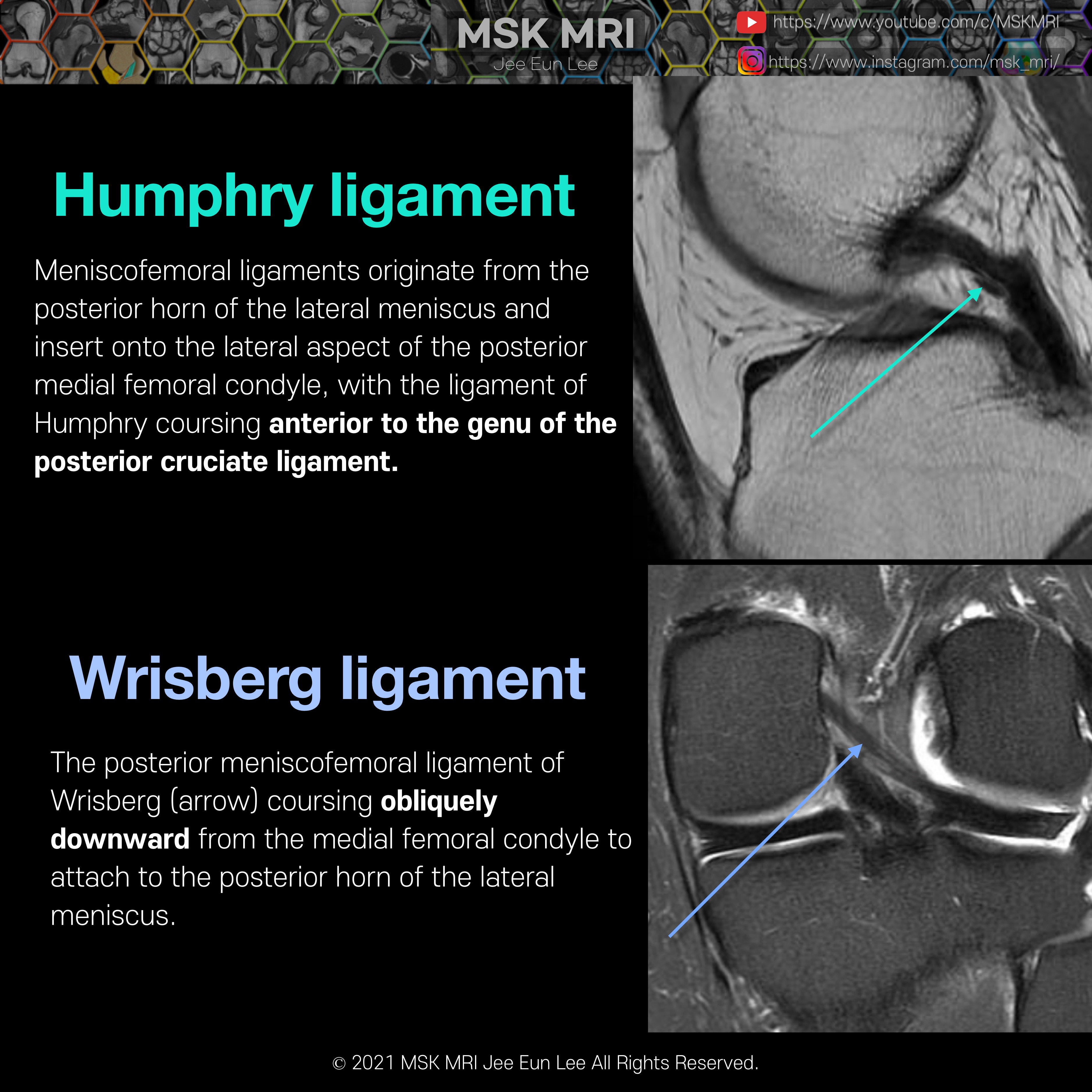
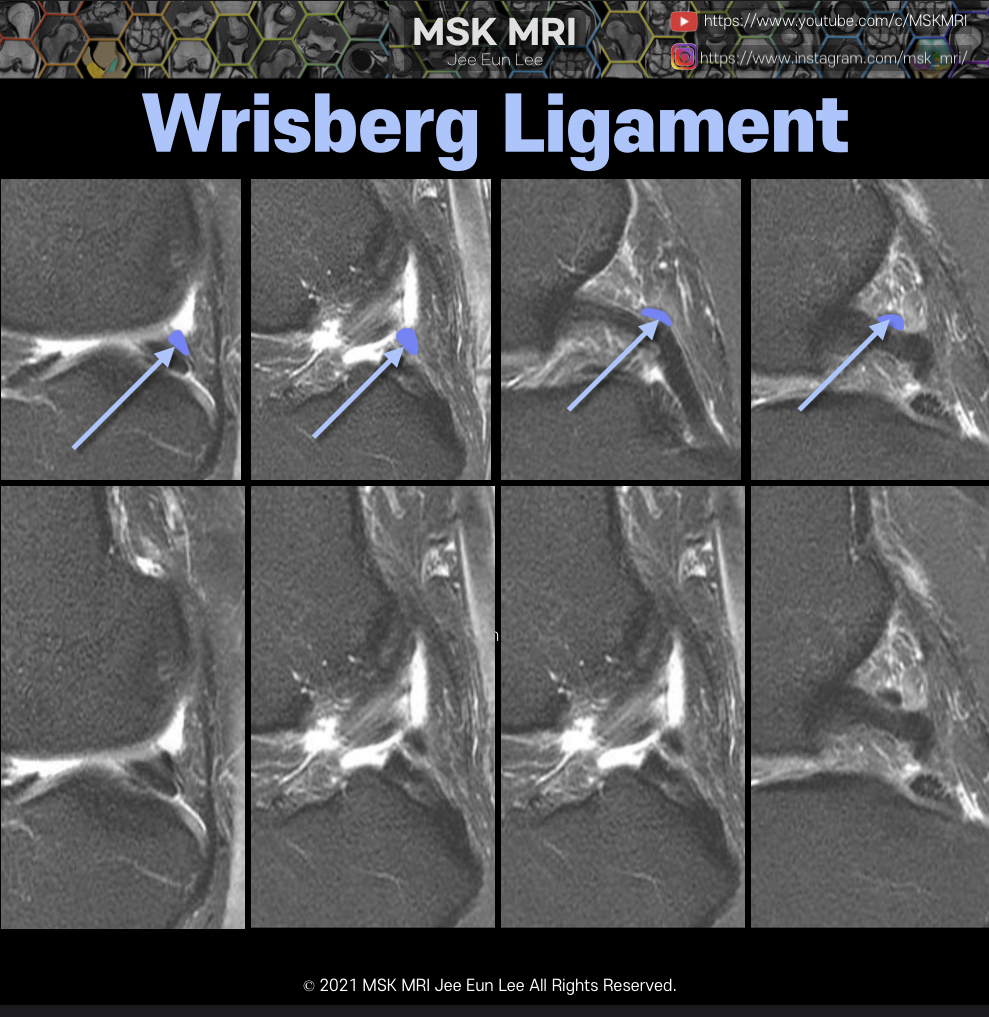
https://youtu.be/GYwJcbKhxbY Fascicle Location and Appearance Anteroinferior Popliteomeniscal Fascicle Visible on sagittal slices near the fibular head; extends posteroinferiorly from the lateral side of the lateral meniscus (LM) and merges with the popliteus tendon; conjoined attachment with the popliteofibular ligament at the fibula’s styloid process; variable appearance. Posterosuperior Popli..