Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
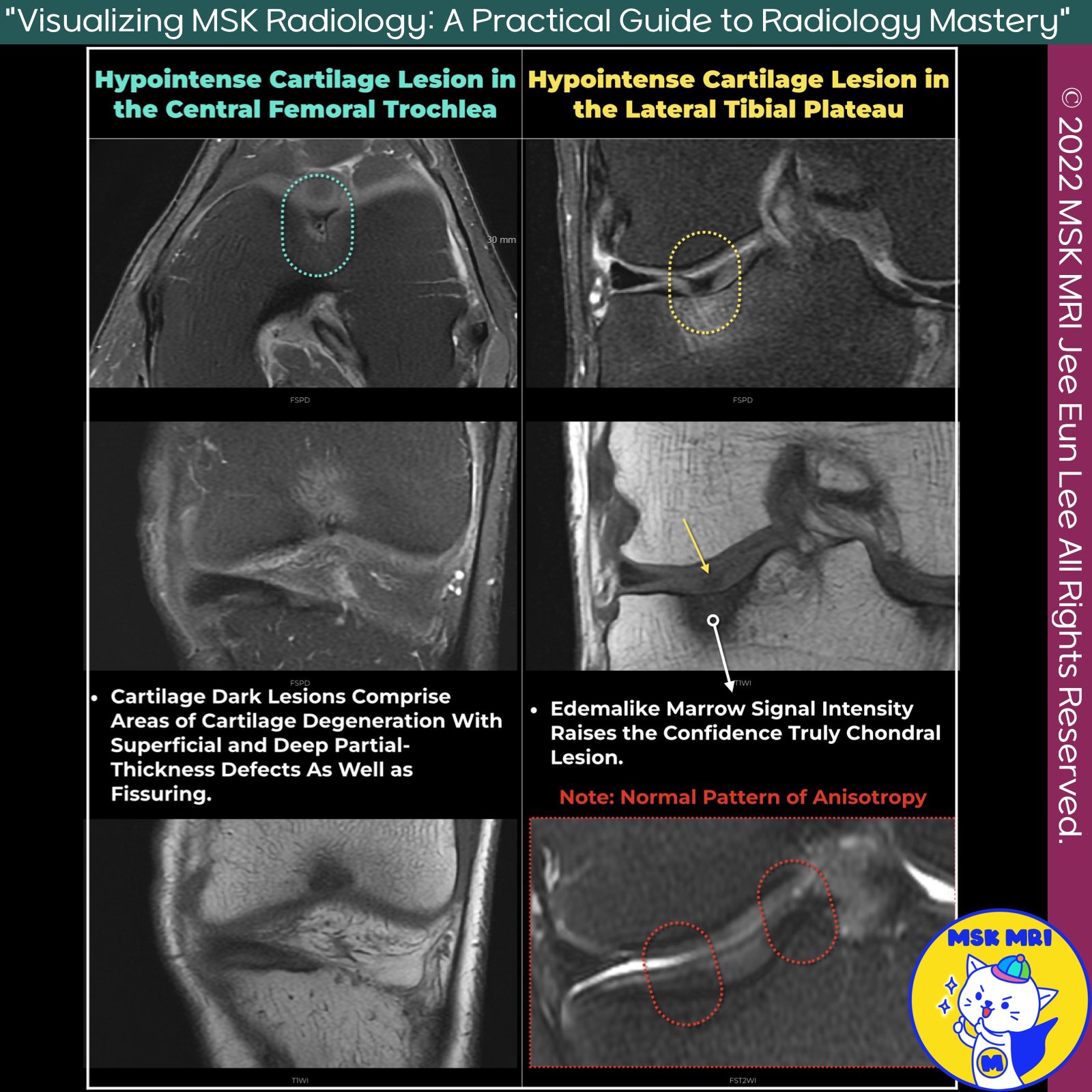
📌Hypointense Lesion in Cartilage
- Hypointense lesions in cartilage, known as cartilage dark lesions, are focal areas seen as low signal intensity on MRI.
- They are significant indicators of cartilage degeneration, often observed during knee arthroscopy.
✅ Characteristics and Detection
- Morphologically Normal Cartilage: These lesions have a 64% positive predictive value for degeneration detection at knee arthroscopy.
- Location and Appearance: Typically found in the middle zone, they can be linear or globular and are commonly associated with fibrillation or fissuring.
- Common Sites: Most commonly involve the femoral trochlea, lateral femoral condyle, and retropatellar areas.
- Arthroscopic Findings: Cartilage Degeneration: Represents areas with superficial and deep partial-thickness defects and fissuring.
✅ Composition and Signal Intensity
- Proteoglycan Concentration: Lesions are softer due to lower proteoglycan concentration and water content, seen in the central aspect of the trochlea.
- Chondrocalcinosis: Calcium pyrophosphate deposition may cause scattered, punctate, hypointense signal foci, best detected with gradient-echo MRI sequences.
✅ Mechanisms and Factors
- Tissue Anisotropy Disruption: Caused by increased exposure of "bound" protons on disrupted collagen to bulk water or mature fibrocartilage.
- Magic Angle Effect: Focal cartilage degeneration leads to losing the magic angle effect and more rapid T2 decay due to altered collagen fiber orientation.
✅ Pitfall
- Distinguishing from Normal Anisotropy: Radiologists must distinguish these areas from normal anisotropy patterns.
References
- RadioGraphics 2022; 42:1457–1473
- Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2021 Oct;25(5):690-699
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#CartilageLesion #MRI #ChondralDegeneration #KneeArthroscopy #CartilageFissuring #TissueAnisotropy #Chondrocalcinosis #Proteoglycan #MagicAngleEffect #RadiologyResearch
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5AB. Chondral and osteochondral' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-A.13) Fissure with Chondral Flap (0) | 2024.07.05 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-A.12) Fissure or Fissuring in Cartilage (0) | 2024.07.05 |
| (Fig 5-A.10) Cartilage Damage Terminology (0) | 2024.07.04 |
| (Fig 5-A.09) Summary of MRI Findings in Cartilage Damage (1) | 2024.07.04 |
| (Fig 5-A.08) International Cartilage Repair Society grade 3 and 4 (0) | 2024.07.04 |