👉 Click the link below and request access—I’ll approve it for you shortly!
https://www.notion.so/MSKMRI-KNEE-b6cbb1e1bc4741b681ecf6a40159a531?pvs=4
==============================================
✨ Join the channel to enjoy the benefits! 🚀
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4bw7o0l2rhxn1GJZGDmT9w/join
==============================================
👉 "Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚"
[Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery]
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS
==============================================
MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee
📚 Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery Now! 🌟 Available on Amazon, eBay, and Rain Collectibles! 💻 Ebook coming soon – stay tuned! ⏳ 🔗 https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0DJGMHMFS 🔗 https://www.ebay.com/itm/3875004193
www.youtube.com
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
www.amazon.com
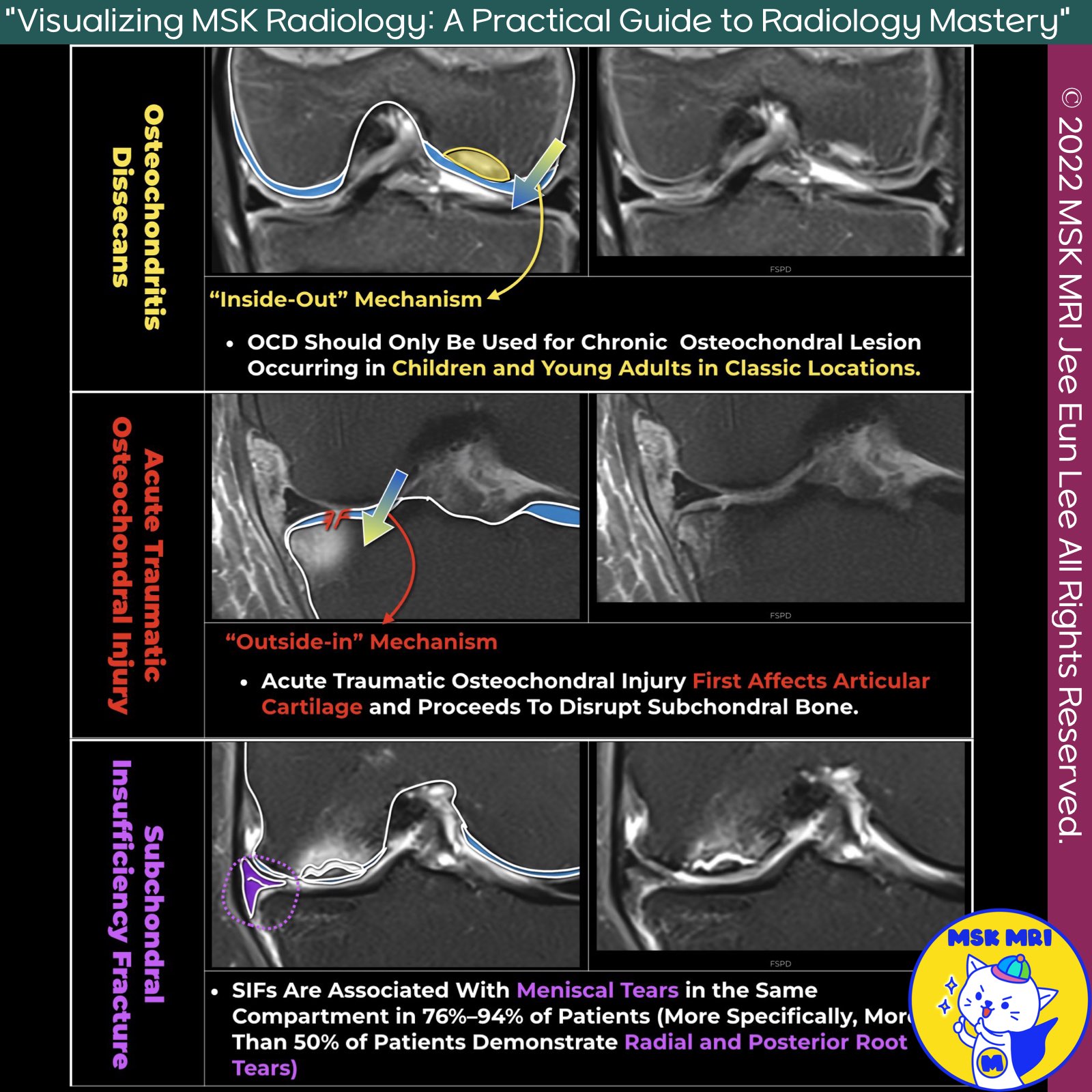
📌 Signs of Osteochondral Lesion Instability in Juveniles
- Two critical factors guide our approach to prognosis and treatment strategies for OCD: the patient's skeletal maturity and the stability of the lesion.
- It's imperative first to determine skeletal maturity, as the MRI criteria for instability differ between adults and juveniles with OCD.
- The MRI criteria for instability in juvenile OCD have been revised, and three secondary signs have been added, all of which showed 100% specificity.
- When combined, these secondary MRI findings have 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity for the detection of unstable juvenile OCD lesions.
✅ Secondary Signs of Instability
1️⃣ High-Signal-Intensity Rim on T2-Weighted Images
- A T2-weighted high-signal-intensity rim surrounding a juvenile OCD lesion indicates instability only if it has the same signal intensity as that of joint fluid.
2️⃣ Outer Rim of Low Signal Intensity on T2-Weighted Images
- A second outer rim of T2-weighted low signal intensity may represent organized fibrous tissue or sclerotic bone at the interface between the OCD lesion and underlying cancellous bone.
- The exact cause of this second outer rim is unknown but is theorized to represent highly organized fibrous tissue or sclerotic bone.
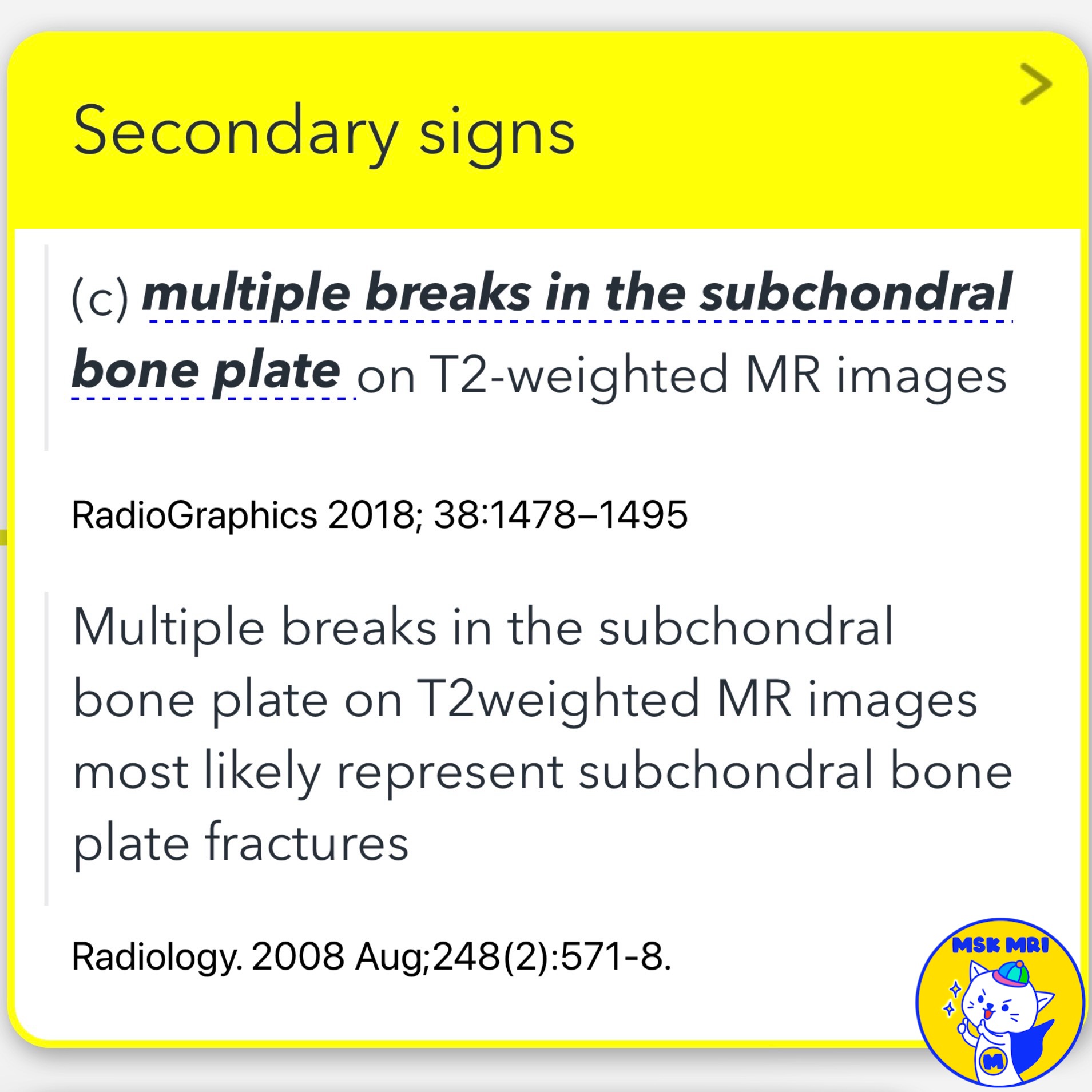
3️⃣ Multiple Breaks in the Subchondral Bone Plate on T2-Weighted MR Images
- Multiple breaks in the subchondral bone plate on T2-weighted MR images most likely represent subchondral bone plate fractures.
✅ Additional Considerations
- The presence of cysts surrounding an OCD lesion is a nonspecific finding in patients with juvenile OCD of the knee. However, the number and size of the cysts may be useful for distinguishing between stable and unstable juvenile OCD lesions.
References
- RadioGraphics 2018; 38:1478–1495
- Radiology. 2008 Aug;248(2):571-8
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#OCD #JuvenileOCD #MRI #Radiology #SkeletalMaturity #LesionStability #HighSignalIntensity #SubchondralBonePlate #FibrousTissue #OCDDiagnosis
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5AB. Chondral and osteochondral' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-B.27) Types of Ossification Variants of the Knee (0) | 2024.07.13 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-B.26) Differential Diagnosis of Osteochondritis Dissecans (0) | 2024.07.13 |
| (Fig 5-B.24) Signs of Osteochondral Lesion Instability in Adults (0) | 2024.07.13 |
| (Fig 5-B.23) ICRS Staging System of Osteochondritis Dissecans (0) | 2024.07.13 |
| (Fig 5-B.22) MRI Findings of Osteochondritis Dissecans (0) | 2024.07.13 |