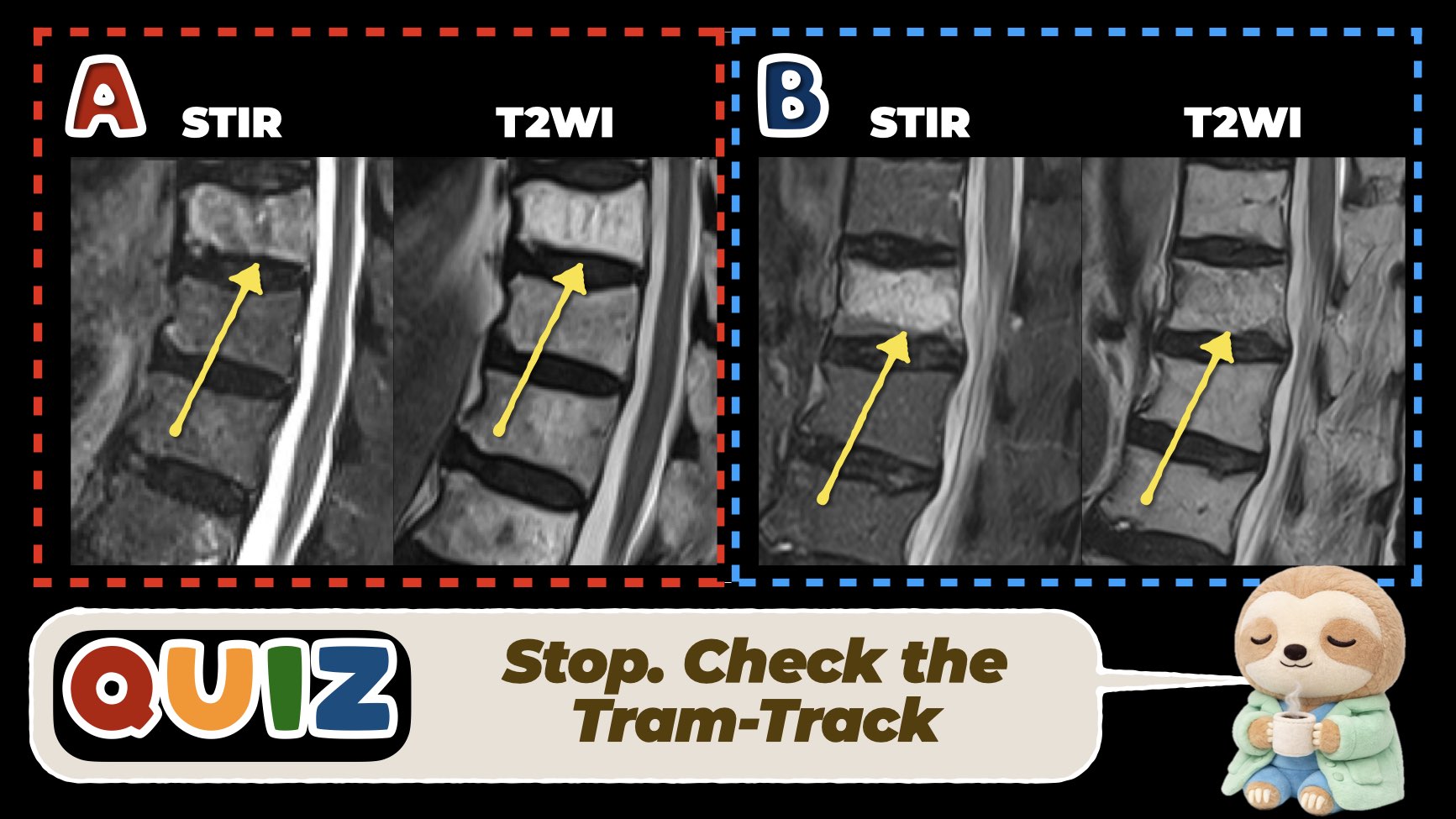
“The fastest way to separate hemangioma from acute fracture.”
https://youtube.com/shorts/mwDwjmVaJuU
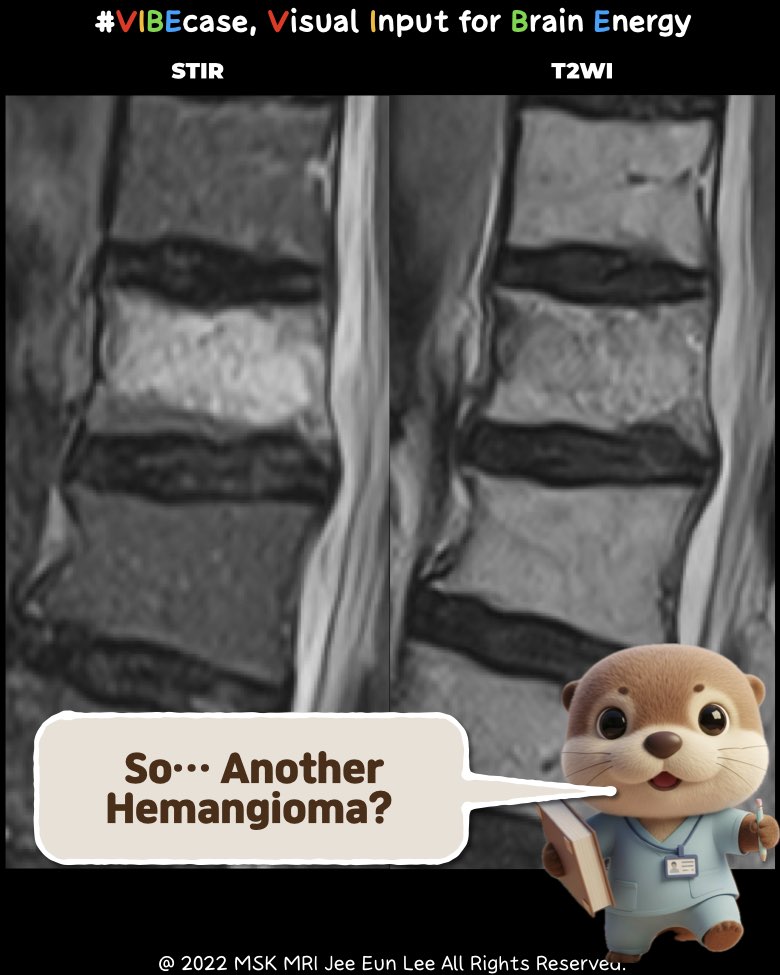
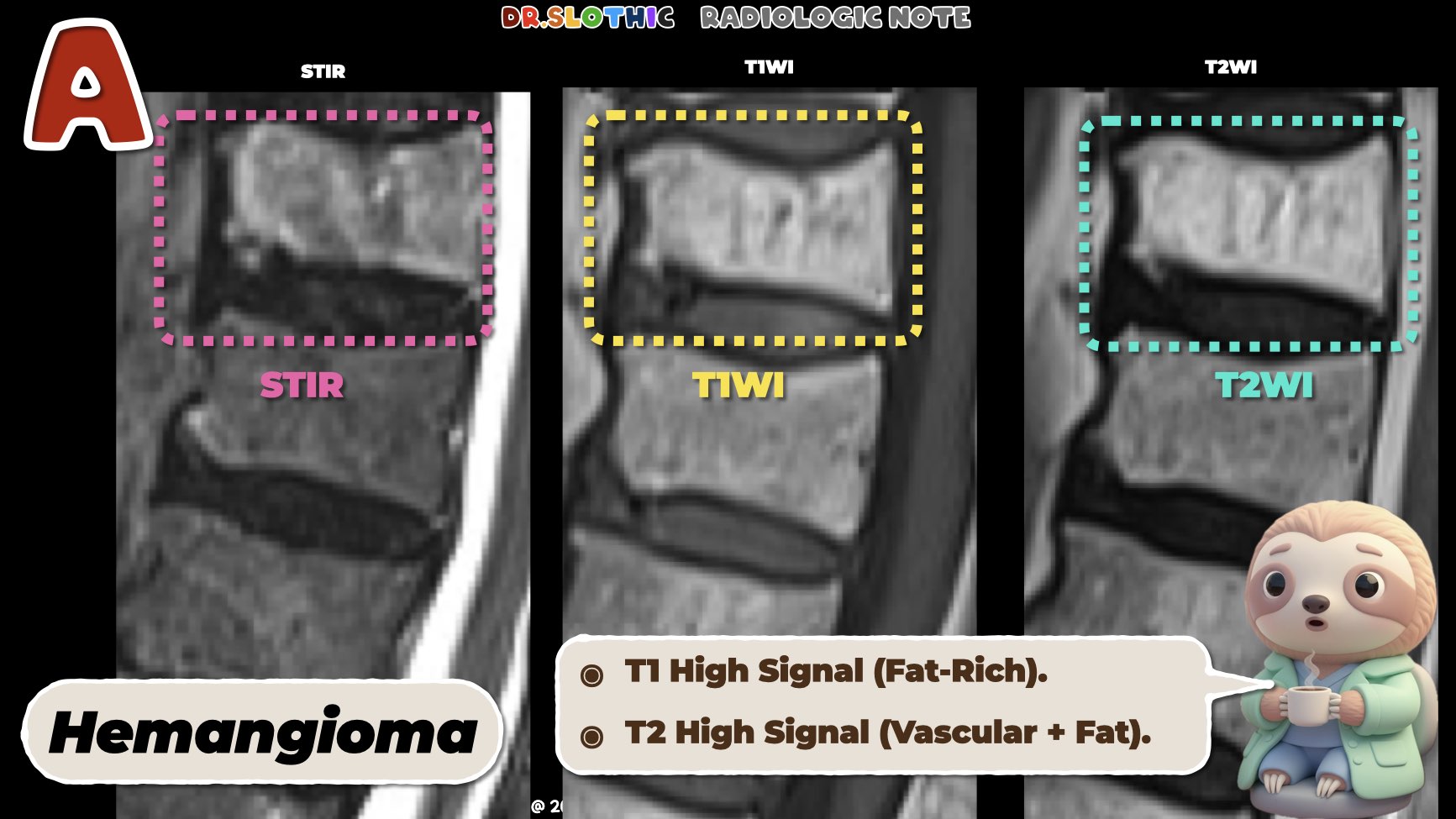
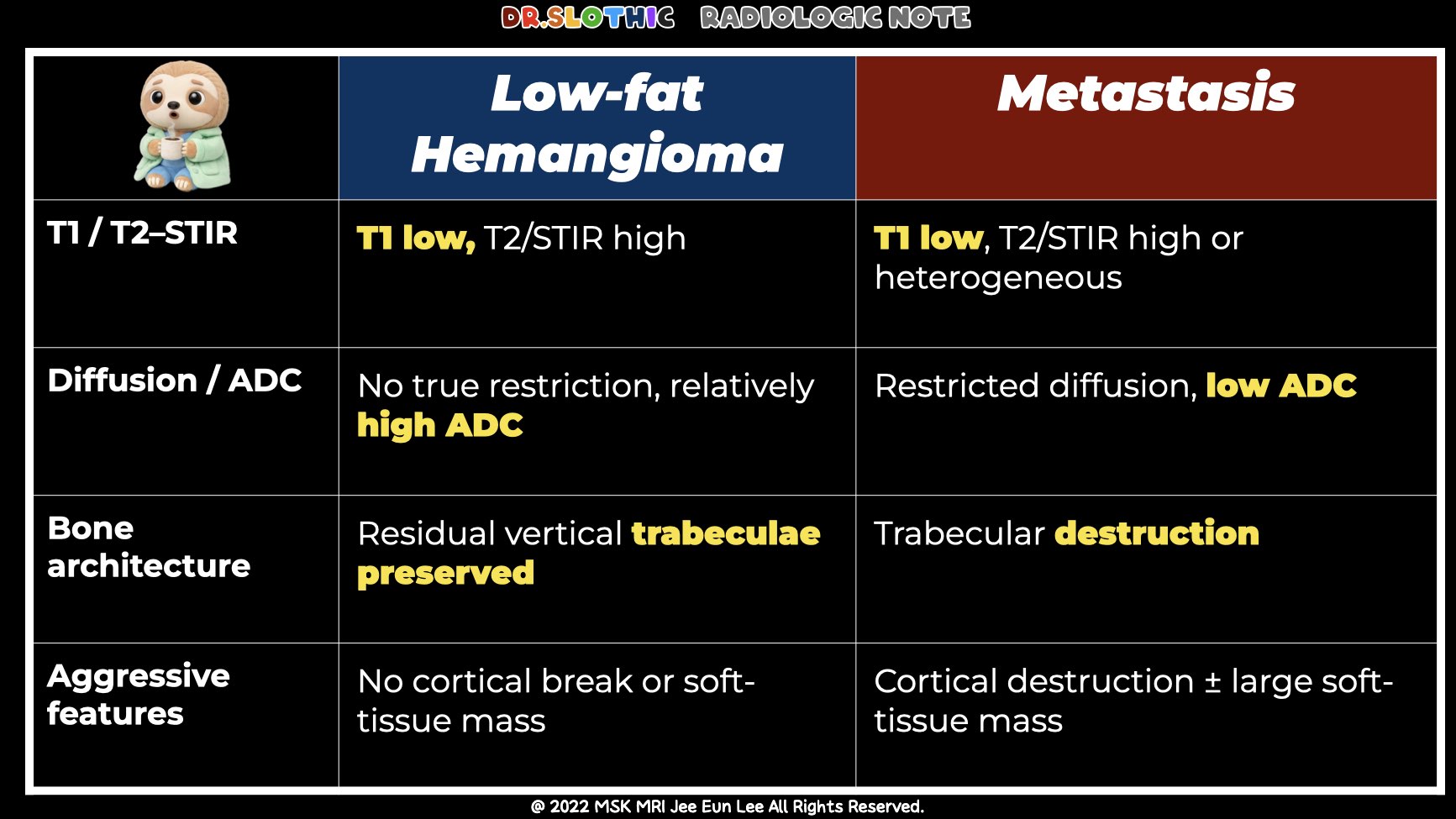
1️⃣ Spinal Hemangioma – MRI Findings
• Location
- Most commonly in the thoracic vertebral body.
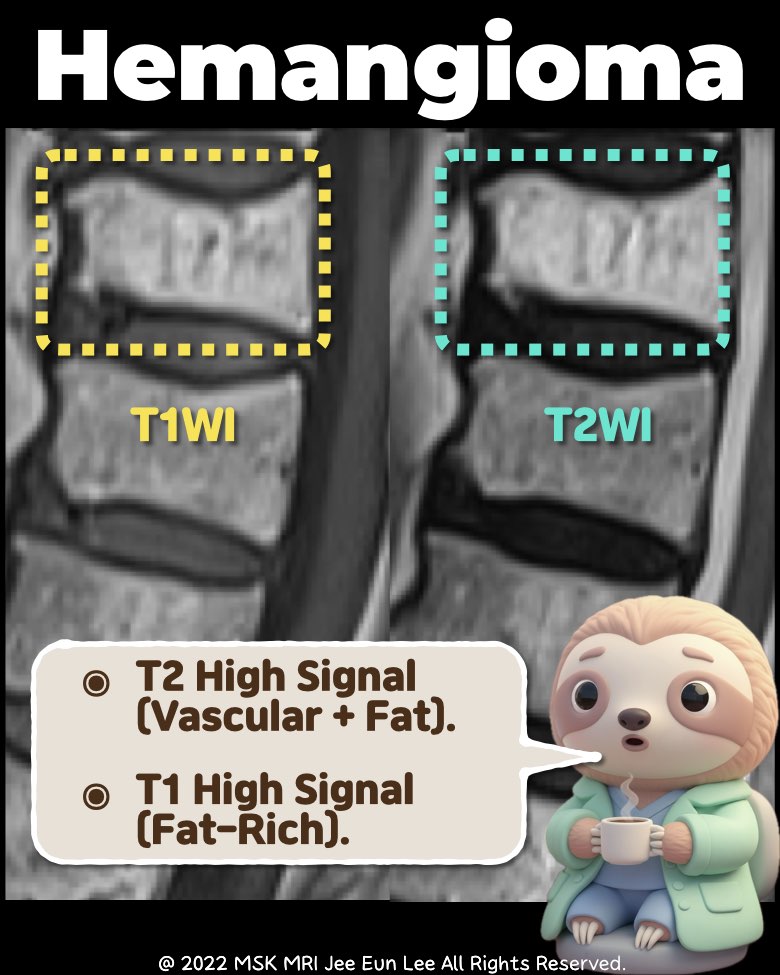
• Signal Characteristics
- T1-weighted: High signal (fat-rich).
- T2-weighted: High signal (vascular + fat).
- Fat-suppressed sequences: Decreased signal.
- Post-contrast: Mild to moderate enhancement.
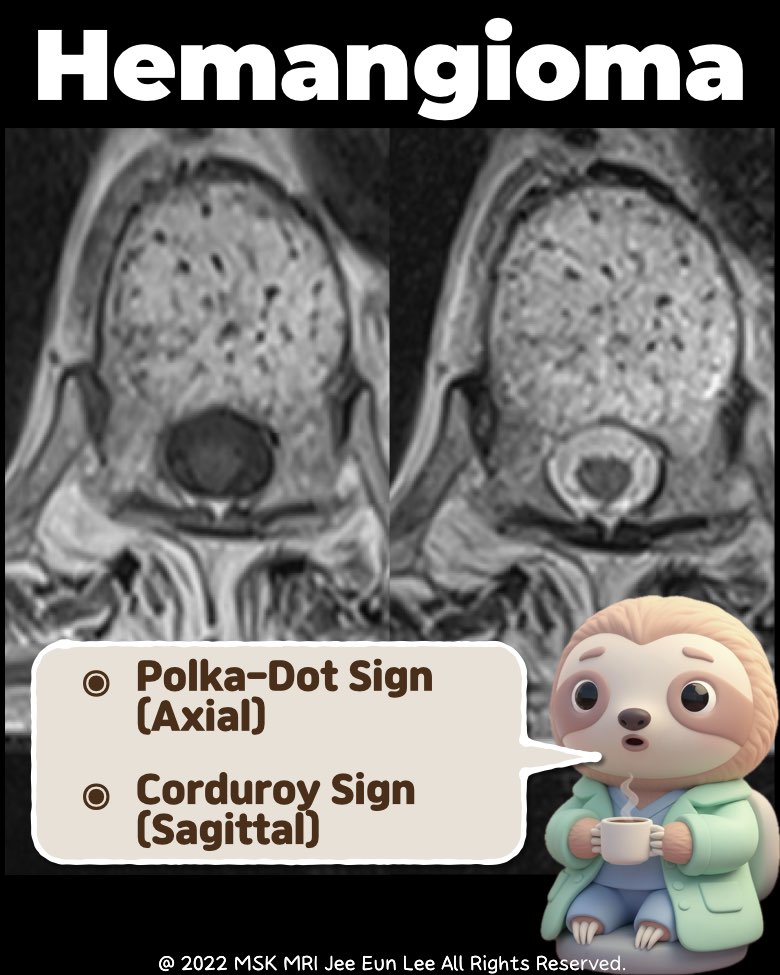
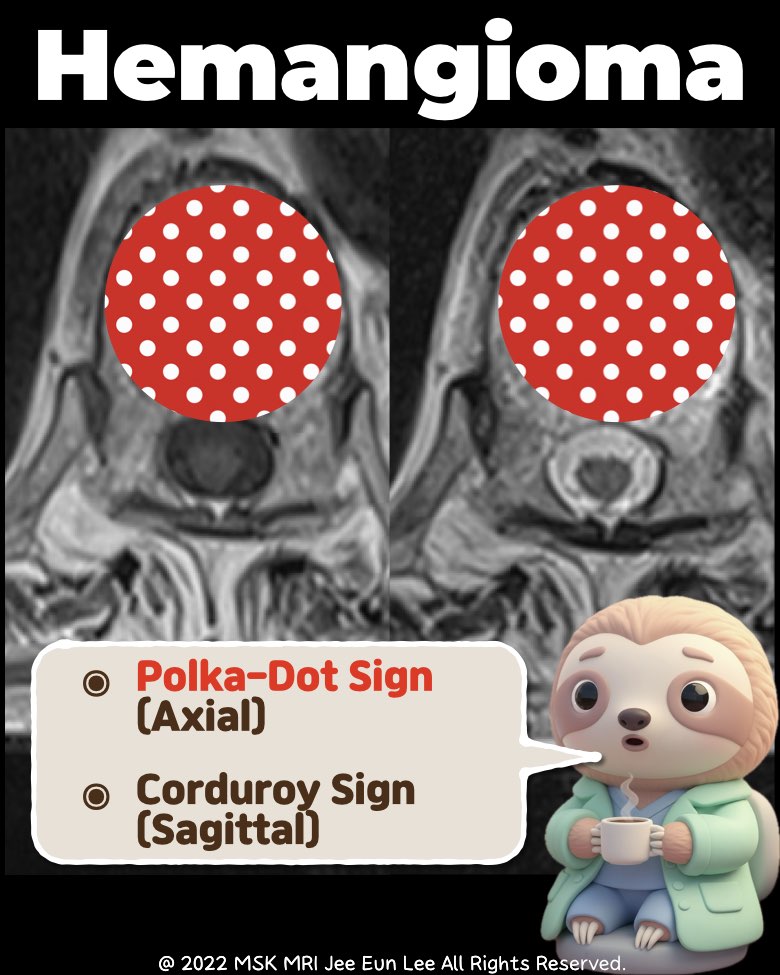
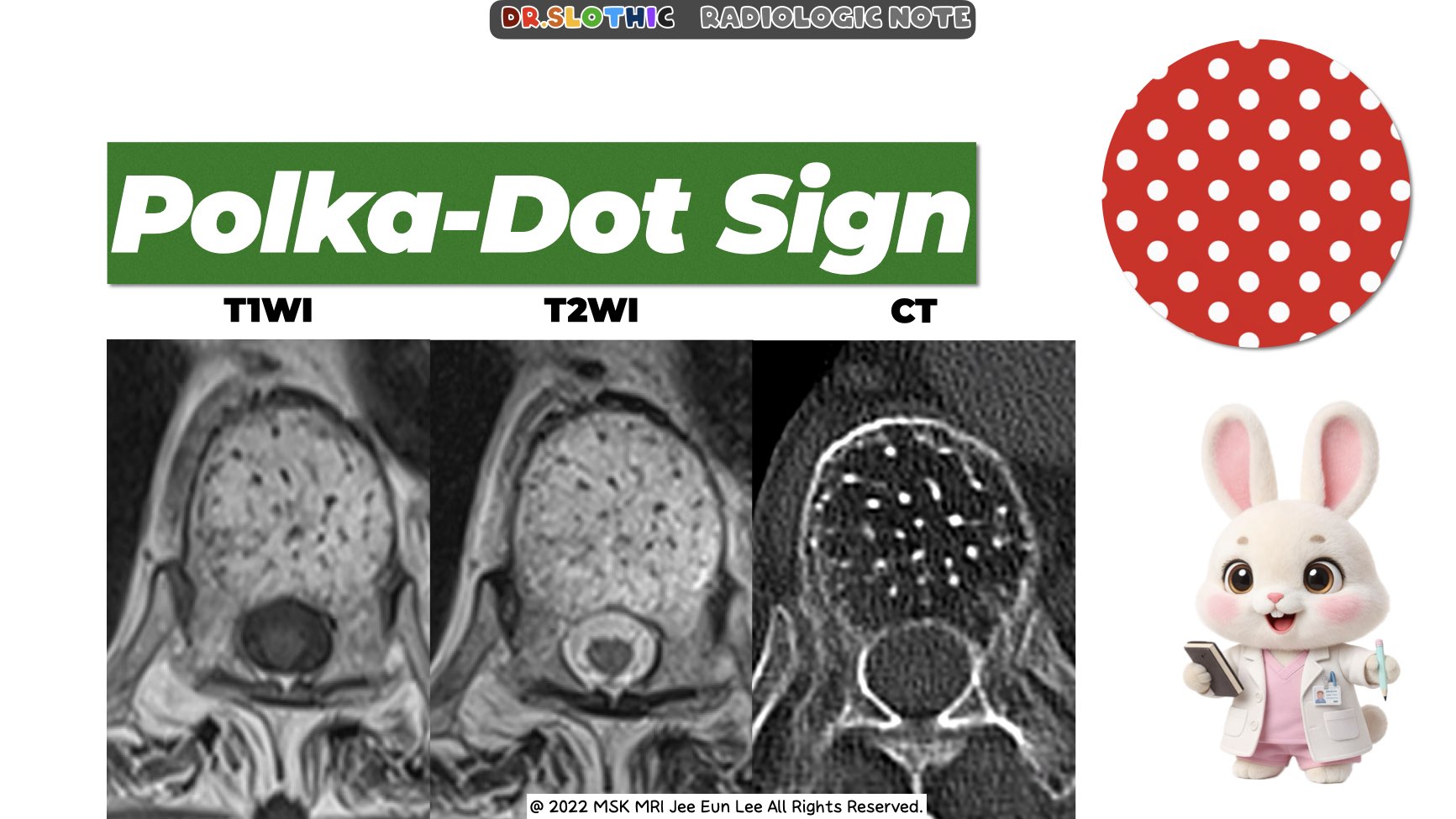
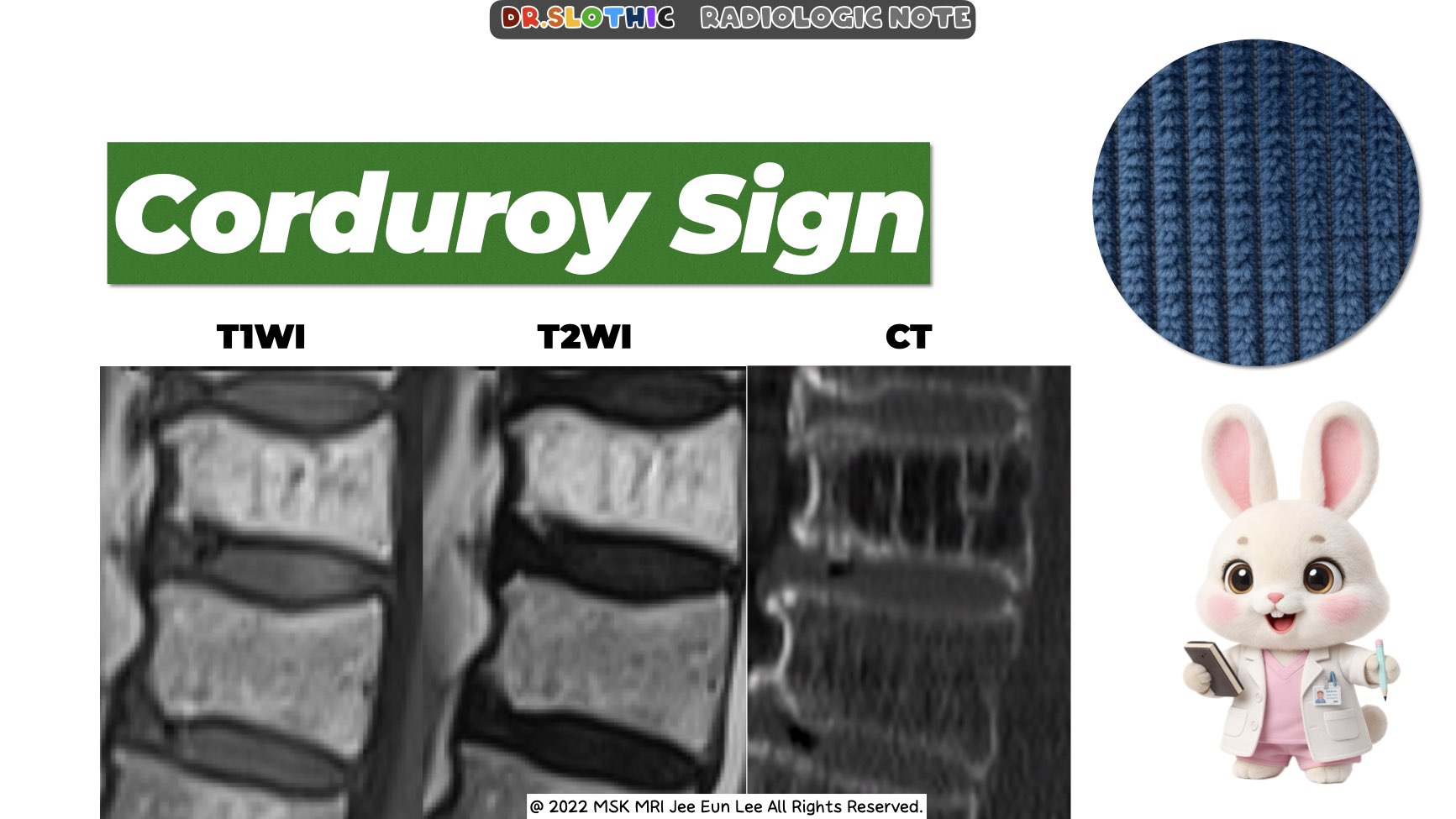
• Morphologic Signs
- Polka-dot sign (axial): Thickened vertical trabeculae.
- Corduroy sign (sagittal): Parallel striated appearance.
- Usually no cortical breach or epidural extension.
• Impression
- Typical benign vertebral hemangioma.
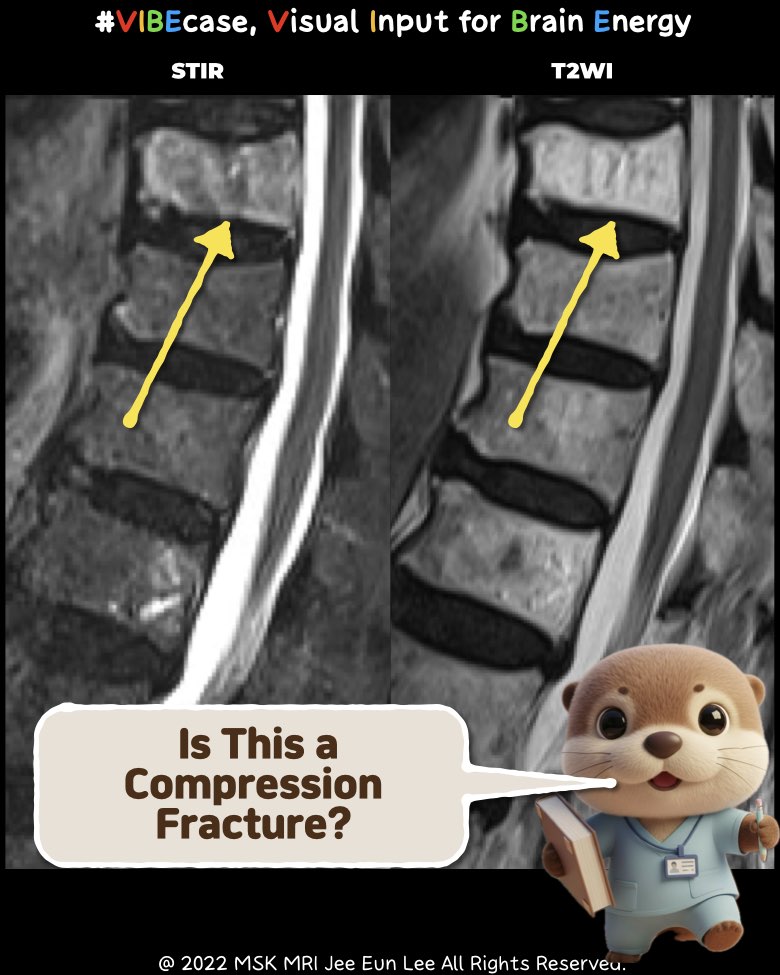
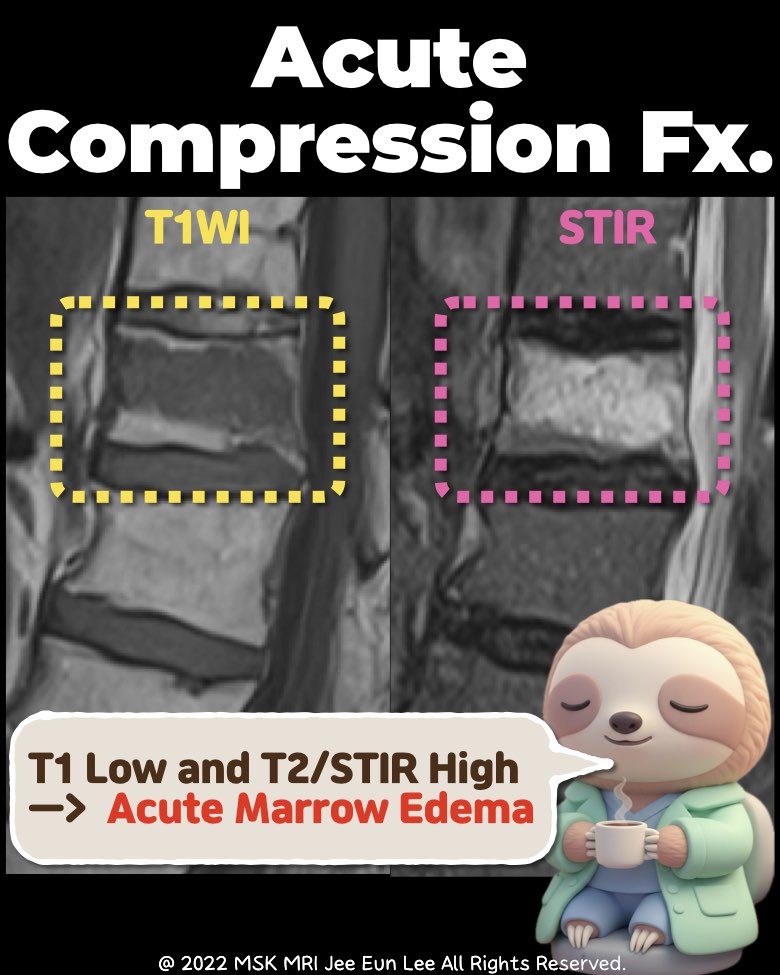
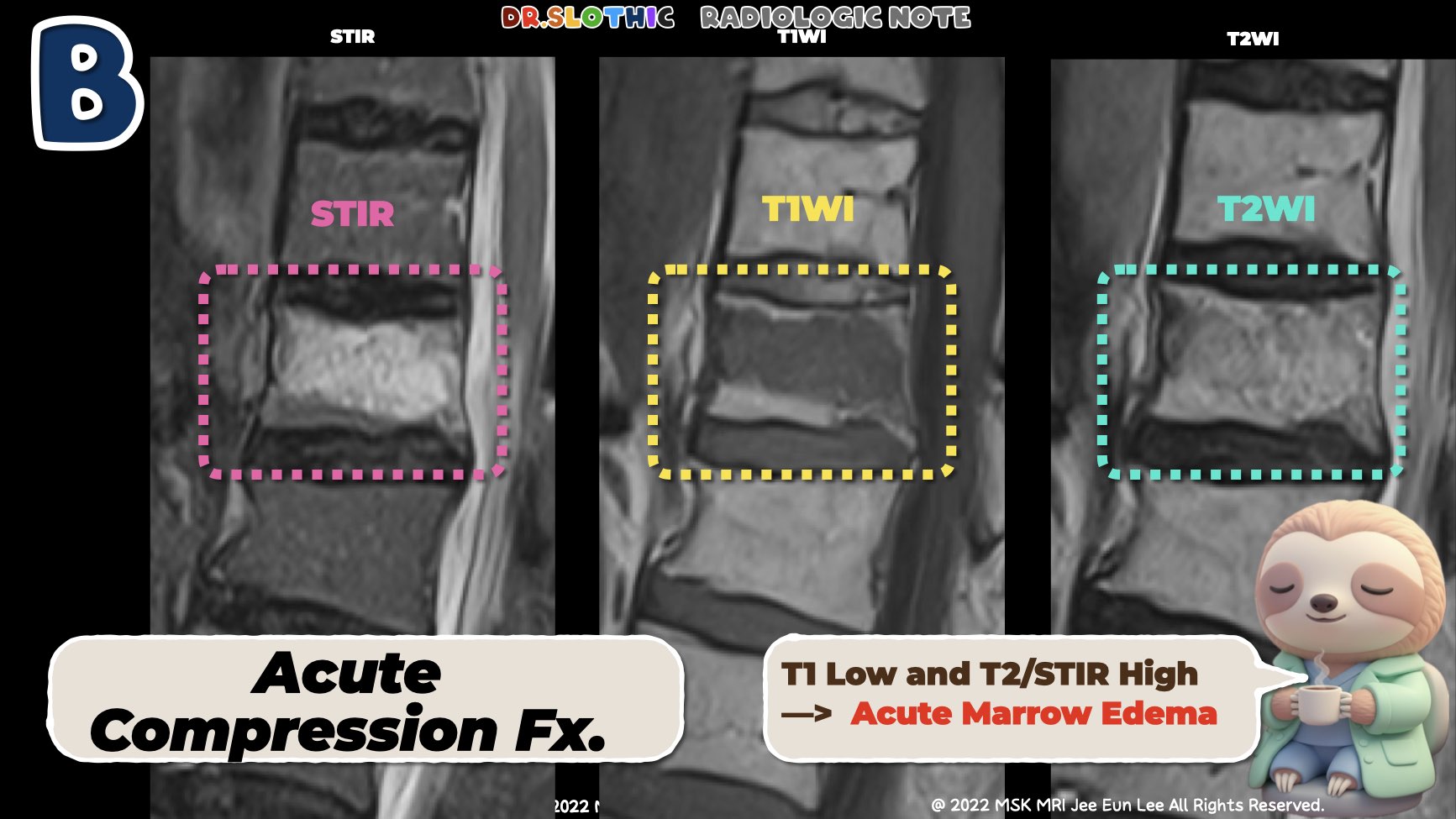
2️⃣ Acute Compression Fracture – MRI Findings
• Signal Characteristics
- T1-weighted: Low signal (acute marrow edema).
- T2 / STIR: High signal (edema).
- Fat-suppressed sequences: Bright high signal.
• Morphology
- Anterior wedge deformity or body height loss.
- Cortical break or endplate irregularity.
- Possible mild retropulsion of the posterior wall.
• Associated Findings
- Paravertebral soft-tissue edema.
- Disc typically intact, no epidural mass.
• Impression
- MRI consistent with acute compression fracture.
#radiology, #mskradiology, #spinemri, #vertebralhemangioma, #compressionfracture, #radiologistlife, #mrieducation, #medstudenttips, #radiologyresident, #drslothic
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.


'✅ Dr. Slothic Notes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 📌 When the MPFL Tears Without Patellar Dislocation (0) | 2025.11.23 |
|---|---|
| 📌 MPFL: It’s Not One Ligament. (0) | 2025.11.23 |
| 📌 Key Imaging Features Suggesting Neurogenic Origin (PNSTs) (0) | 2025.11.23 |
| 📌 Posterior Capsular Recess vs PCL Ganglion — Ultra Short Guide (0) | 2025.11.23 |
| 📌 The Easiest Way to Avoid Misdiagnosing PCL Tears (0) | 2025.11.23 |