https://youtube.com/shorts/Epvpg-EGV1o
Shape, Level, and Position — The Three Keys to Correct Identification
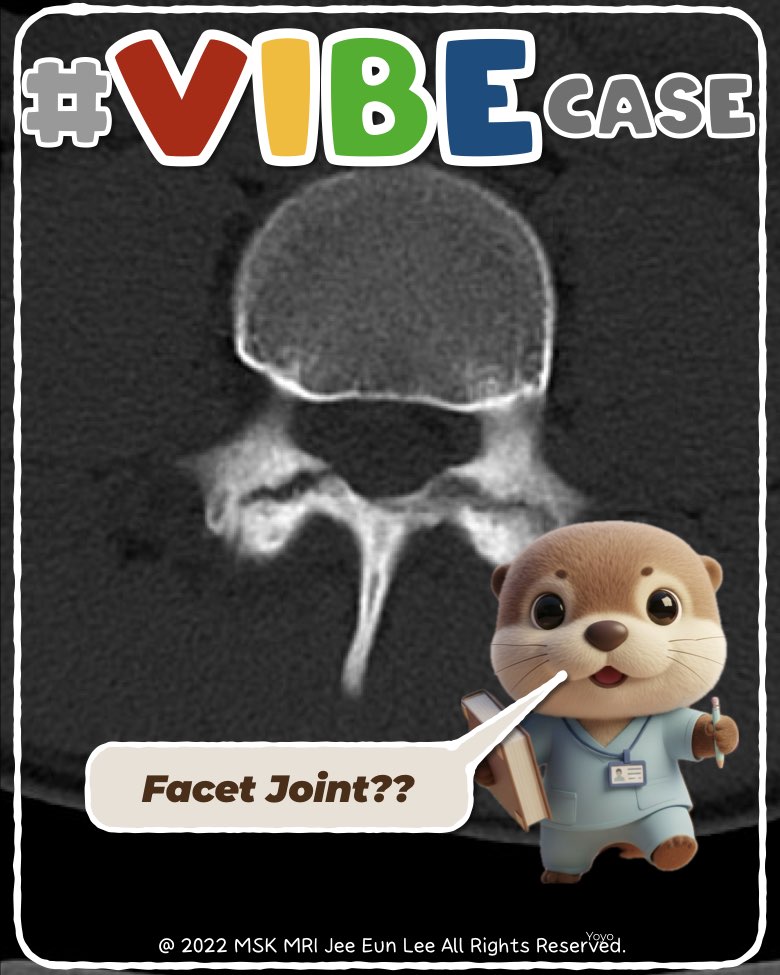
On axial lumbar MRI, a pars defect can mimic the appearance of a facet joint, especially when there is an irregular gap that resembles a joint space. To distinguish them correctly, three criteria must be checked:
1. Level
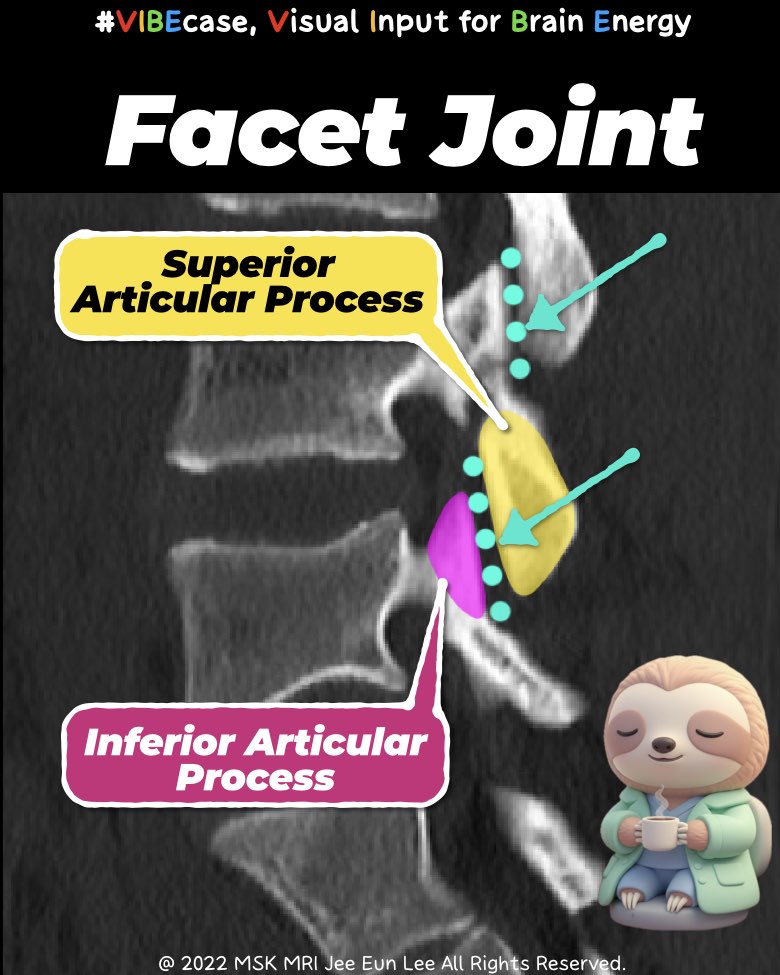
A true facet joint appears only at the level where the superior and inferior articular processes meet.
If the slice is above or below this level, any gap you see is not a facet joint.
2. Position
The facet joint is located posteriorly.
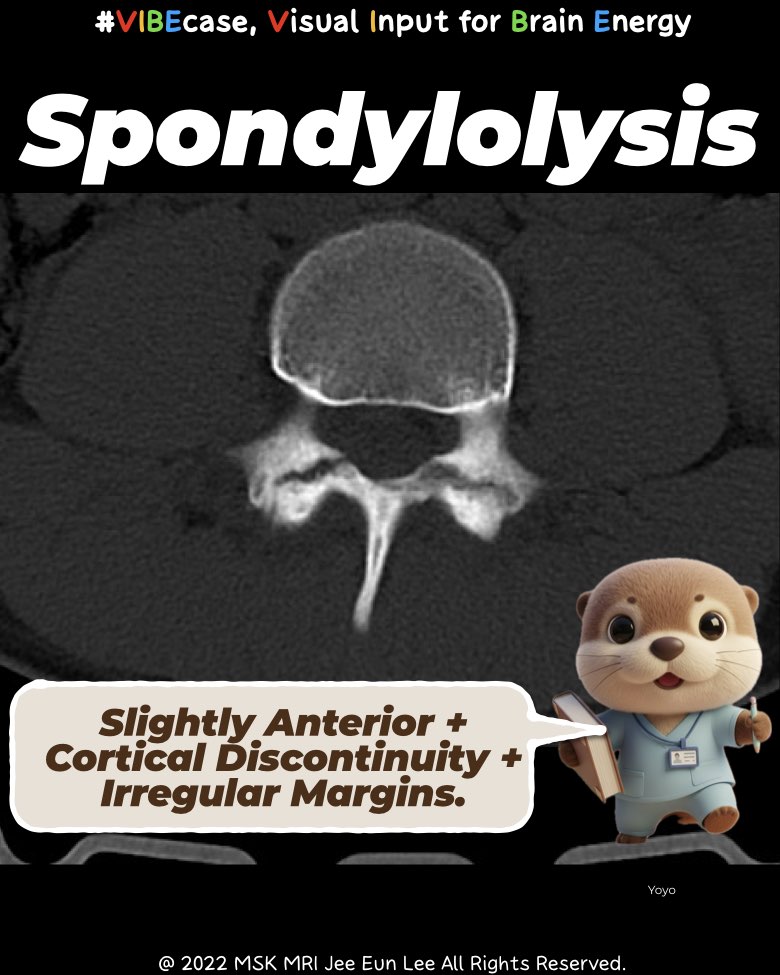
A pars defect lies slightly anterior to the facet joint, at the pars interarticularis level.
3. Shape
Facet joints show a smooth, symmetric V-shaped joint space.
A pars defect shows an irregular cortical break with interrupted cortex, sometimes accompanied by marrow edema.
Putting it together
- Facet joint = posterior + symmetric + articular process level
- Pars defect = anterior + cortical discontinuity + irregular margins
Identify all three, and you can reliably differentiate a pars defect from a facet joint on axial MRI.
#mskradiology, #spineMRI, #spondylolysis, #radiologyeducation, #axialMRI, #facetjoint, #parsdefect, #radiologistlife, #orthoradiology, #medicalimaging, #Vibecase
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.

https://spotifycreators-web.app.link/e/Rg9iH70ASYb
Pars Defect (Spondylolysis) by Dr. Slothic MSK Radiology Podcast
Comprehensive Imaging Findings Across MRI, CT, and Radiography1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)MRI is the most sensitive modality for detecting early pars injuries in adolescents, particularly before cortical disruption becomes visible on radiographs or
spotifycreators-web.app.link