https://youtu.be/vzxclU_34OI?si=B88NykUJHSELzyAC
Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
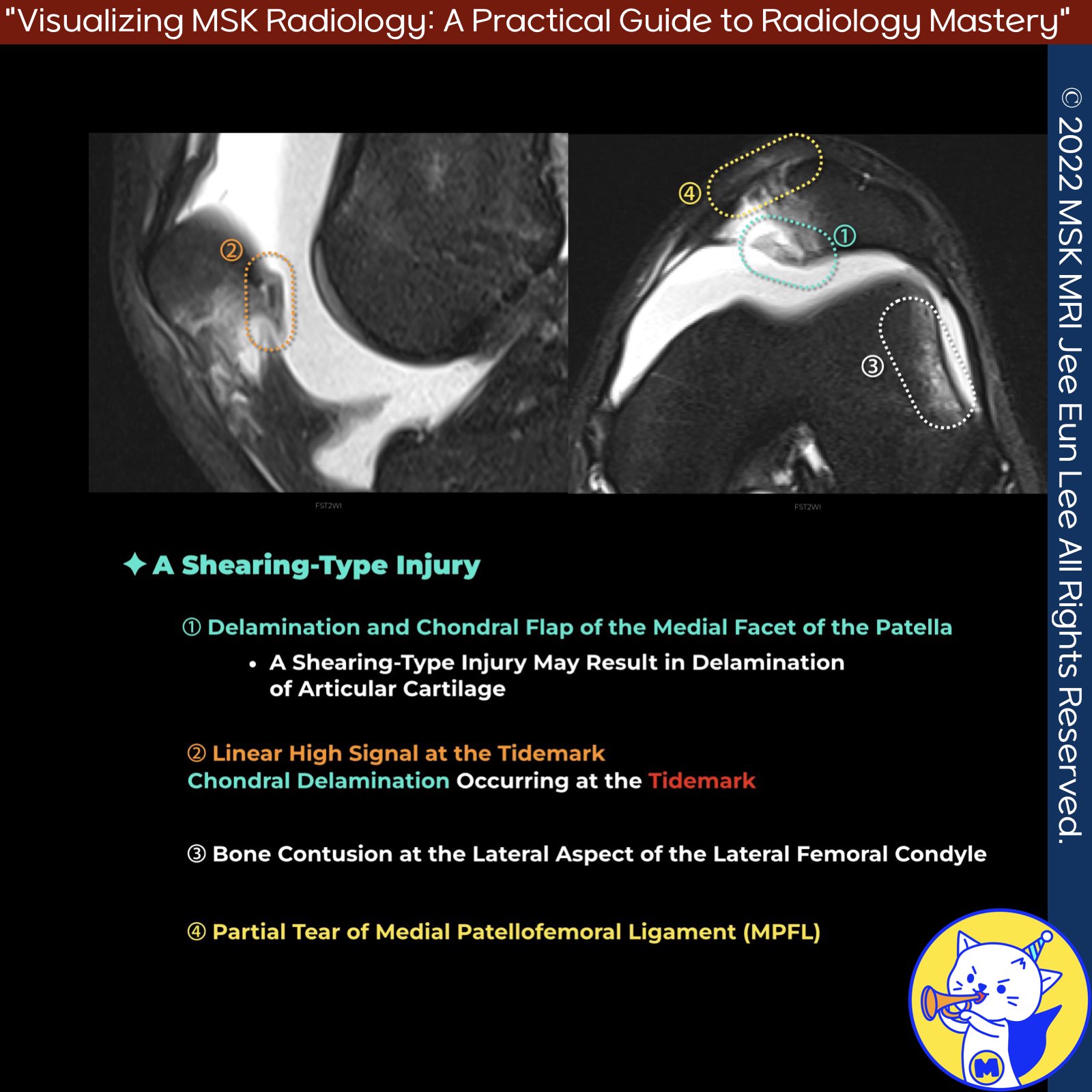
📌 MRI Findings in Shearing-Type Injuries
- Typical appearances of shearing-type injuries are characterized by well-defined, full-thickness, or large partial-thickness defects with acutely angled margins.
- These injuries often include an intra-articular loose body corresponding to the displaced fragment.
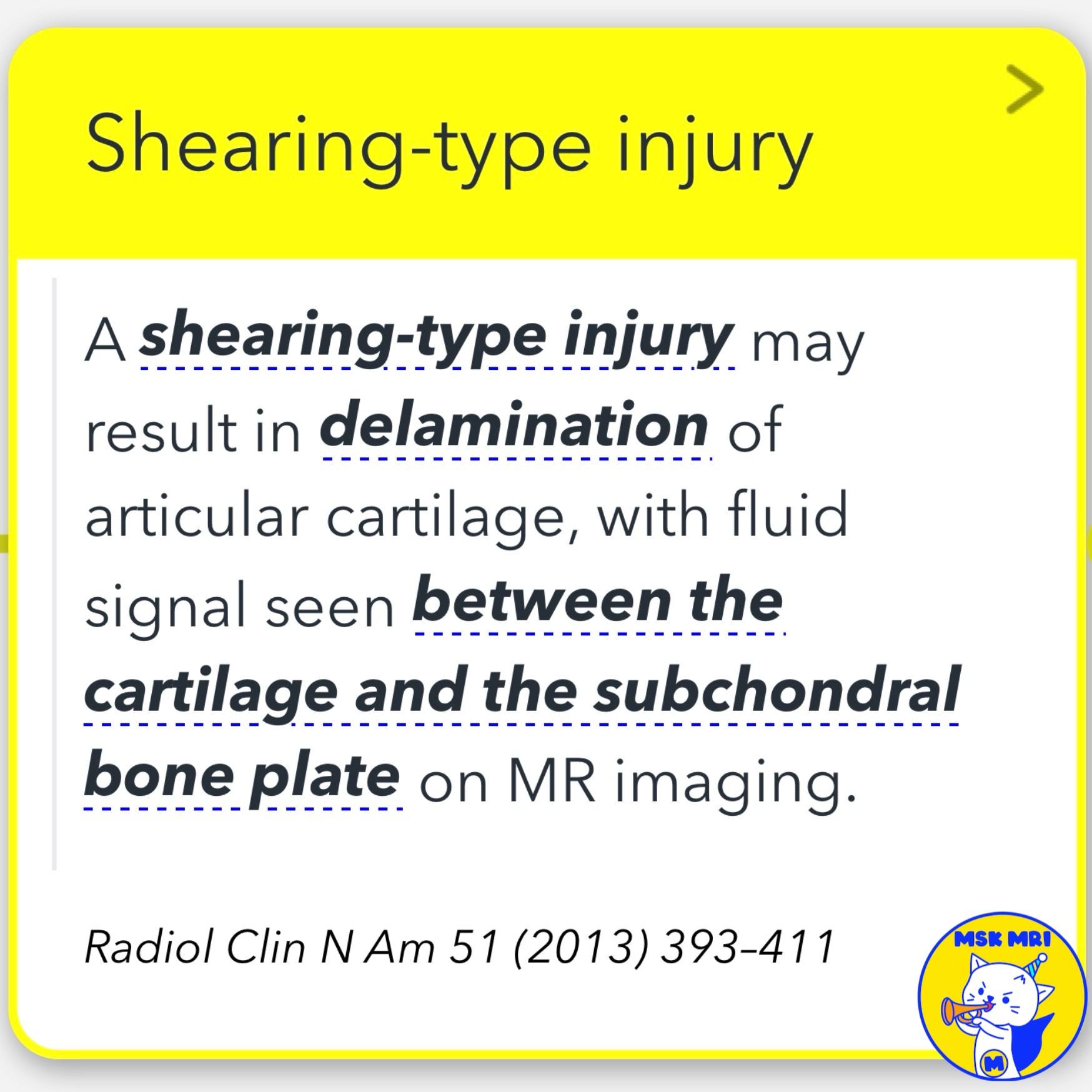
- A shearing-type injury can result in the delamination of articular cartilage, with fluid signal visible between the cartilage and the subchondral bone plate on MRI
(Radiol Clin N Am 51, 2013, 393–411).
✅ Chondral vs. Osteochondral Shearing Injuries
- MRI is crucial for distinguishing between chondral and osteochondral shearing injuries.
- The presence or absence of the underlying subchondral bone plate is a key factor in differentiating these injuries
(Clin Sports Med. 2014 Jul;33(3):413-36).
- Shearing injuries may also involve associated cartilage shearing injury and displaced osteochondral fragments, which can be found within the suprapatellar recess or medial and lateral recesses (Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 22, 2014, 601–620).
✅ Chondral Delamination
- Chondral delamination on MRI usually appears as a thin line of near-fluid signal intensity beneath the deep zone of articular cartilage, at the tidemark.
- This line separates the noncalcified cartilage from the underlying bone and calcified cartilage
(MRI Web Clinic – June 2021 Tissue Delamination).
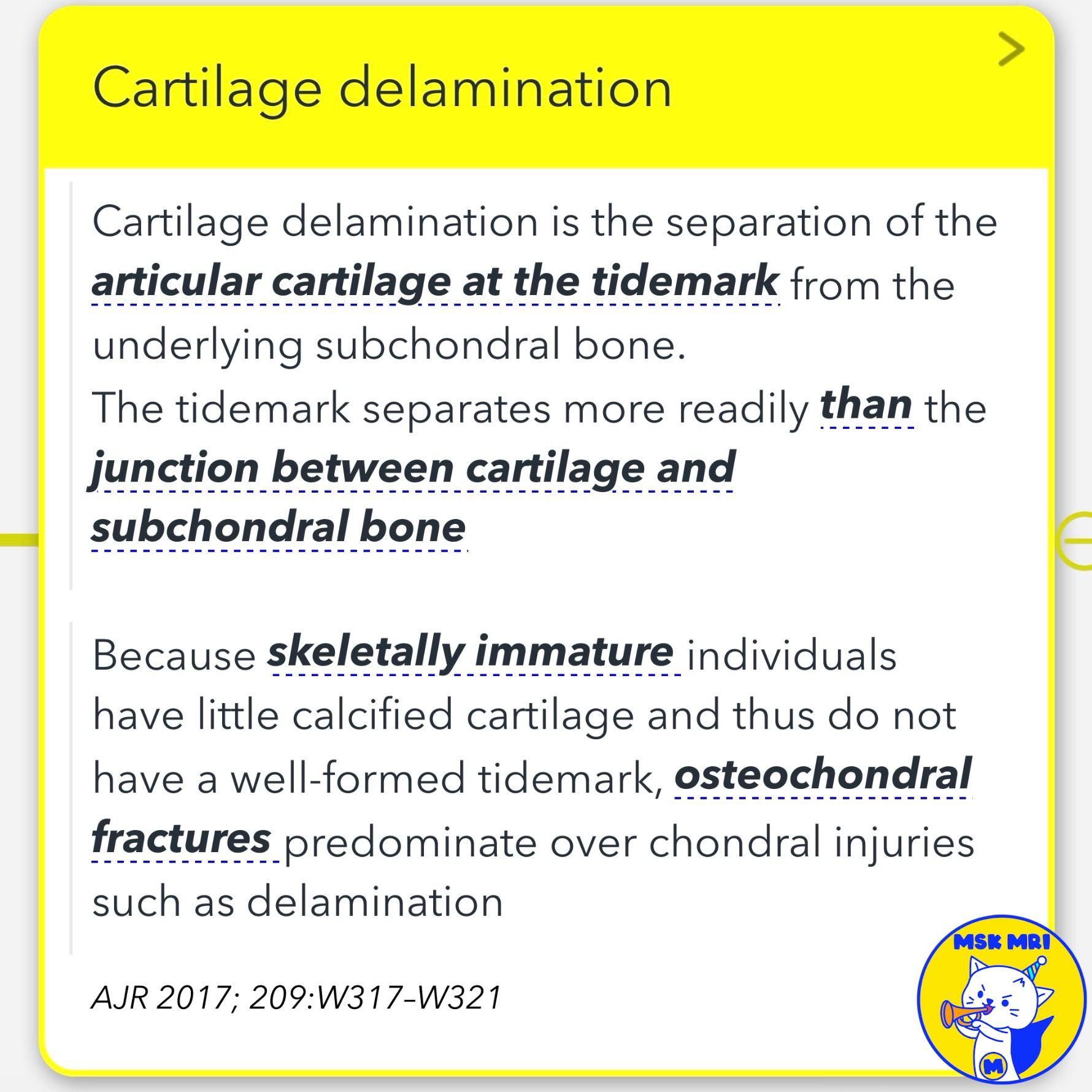
- Cartilage delamination involves the separation of articular cartilage at the tidemark from the underlying subchondral bone.
- This separation occurs more readily at the tidemark than at the junction between cartilage and subchondral bone.
- In skeletally immature individuals, who have little calcified cartilage and thus lack a well-formed tidemark, osteochondral fractures predominate over chondral injuries such as delamination
(AJR 2017; 209–W321).
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#MRI, #ShearingInjuries, #ChondralInjury, #OsteochondralInjury, #CartilageDelamination, #MarrowEdema, #Radiology, #SportsMedicine,