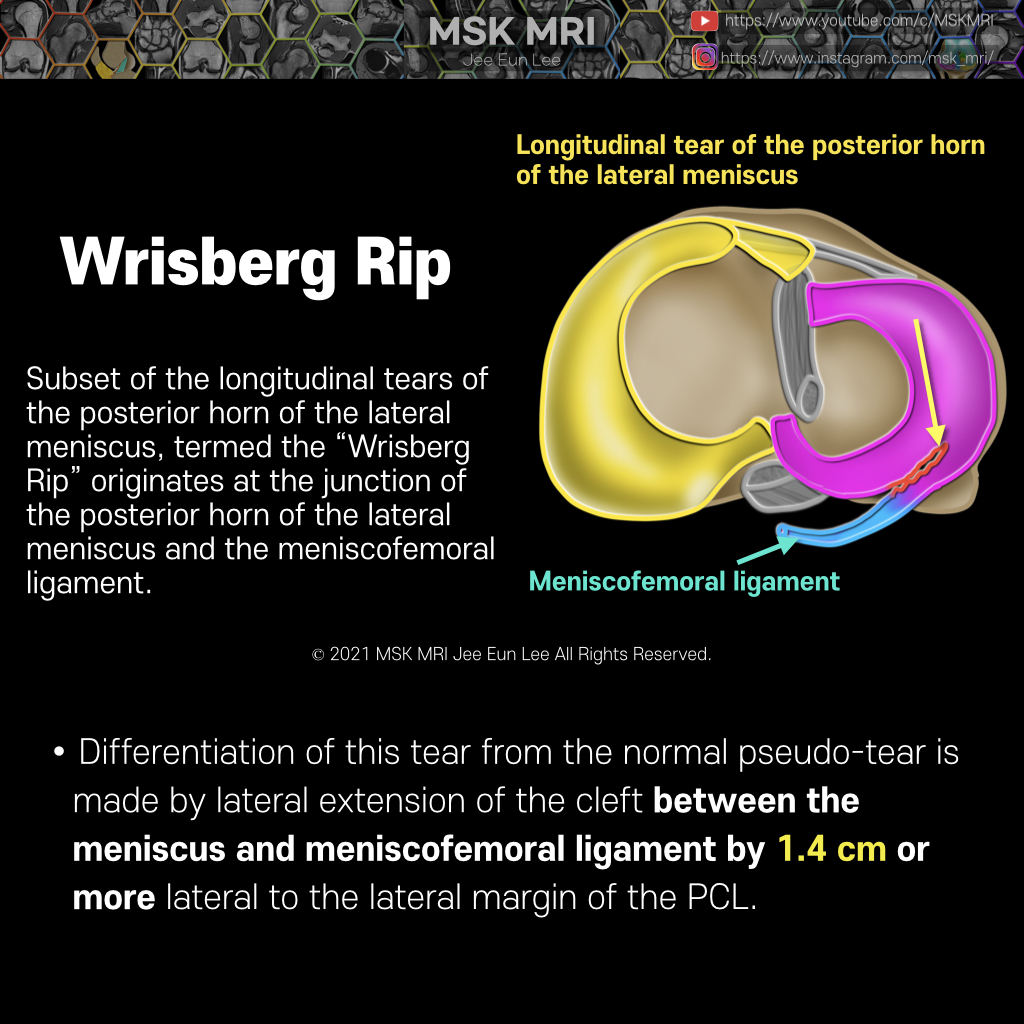
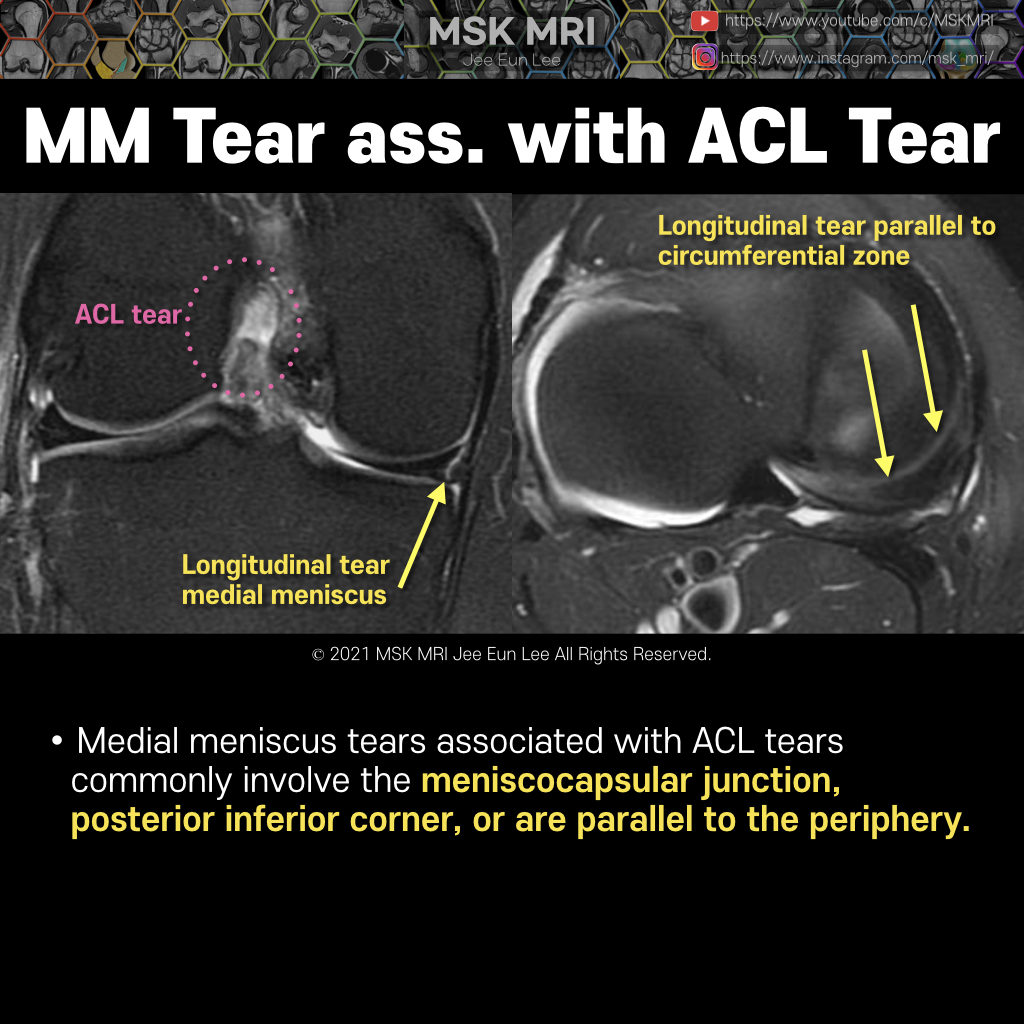
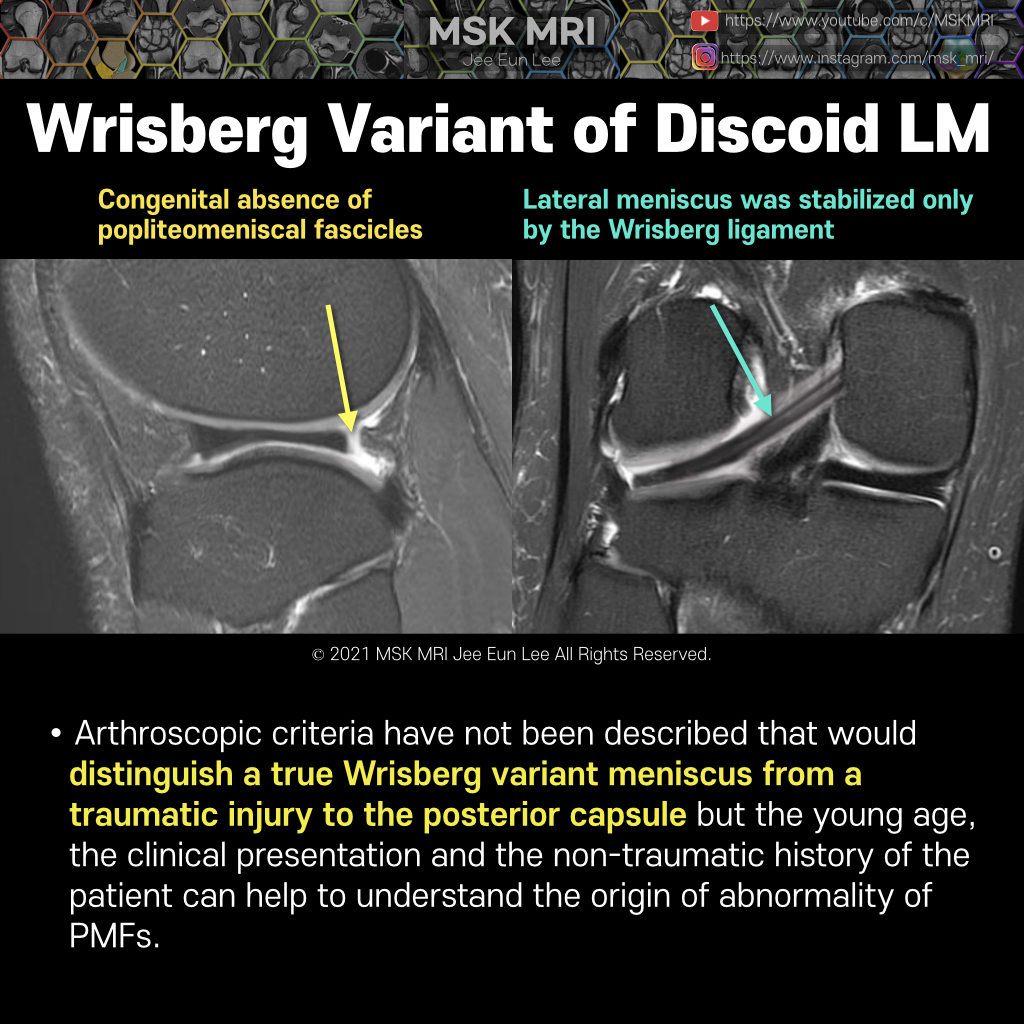
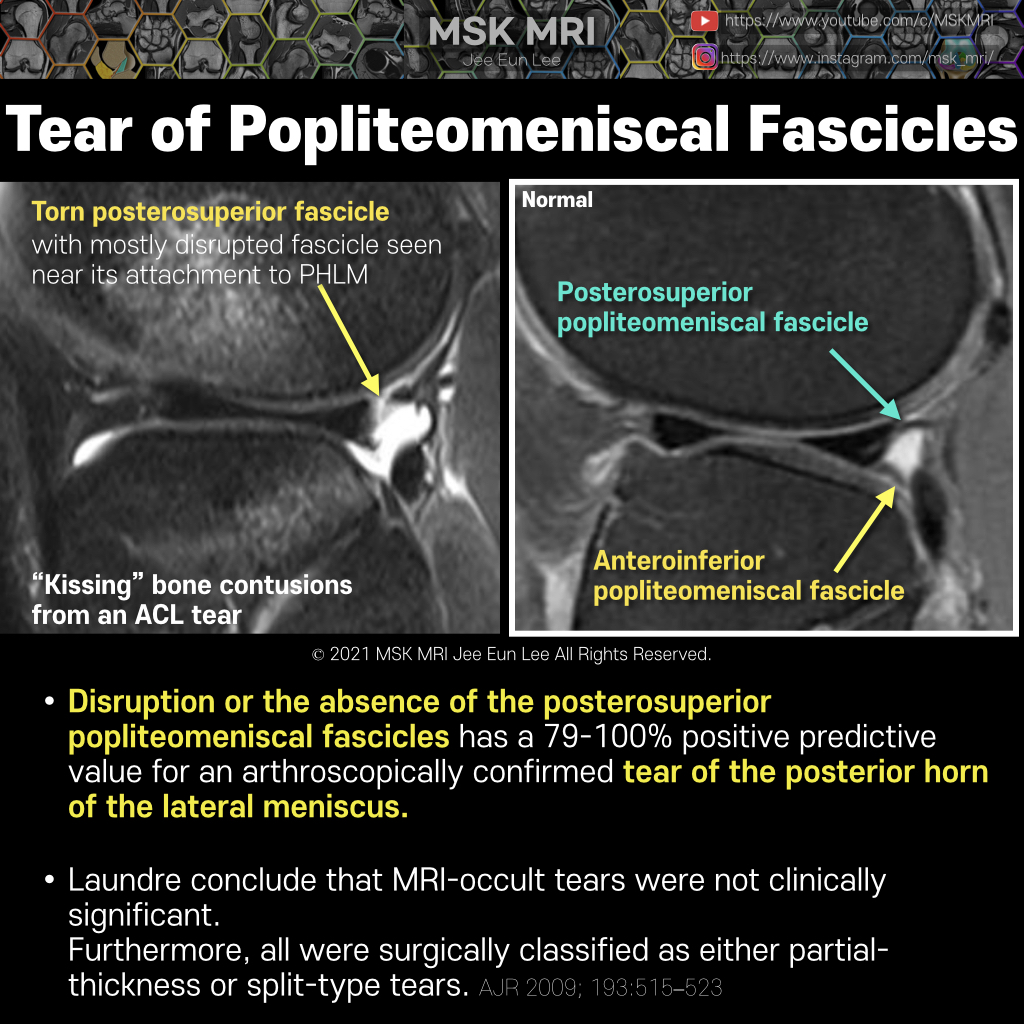
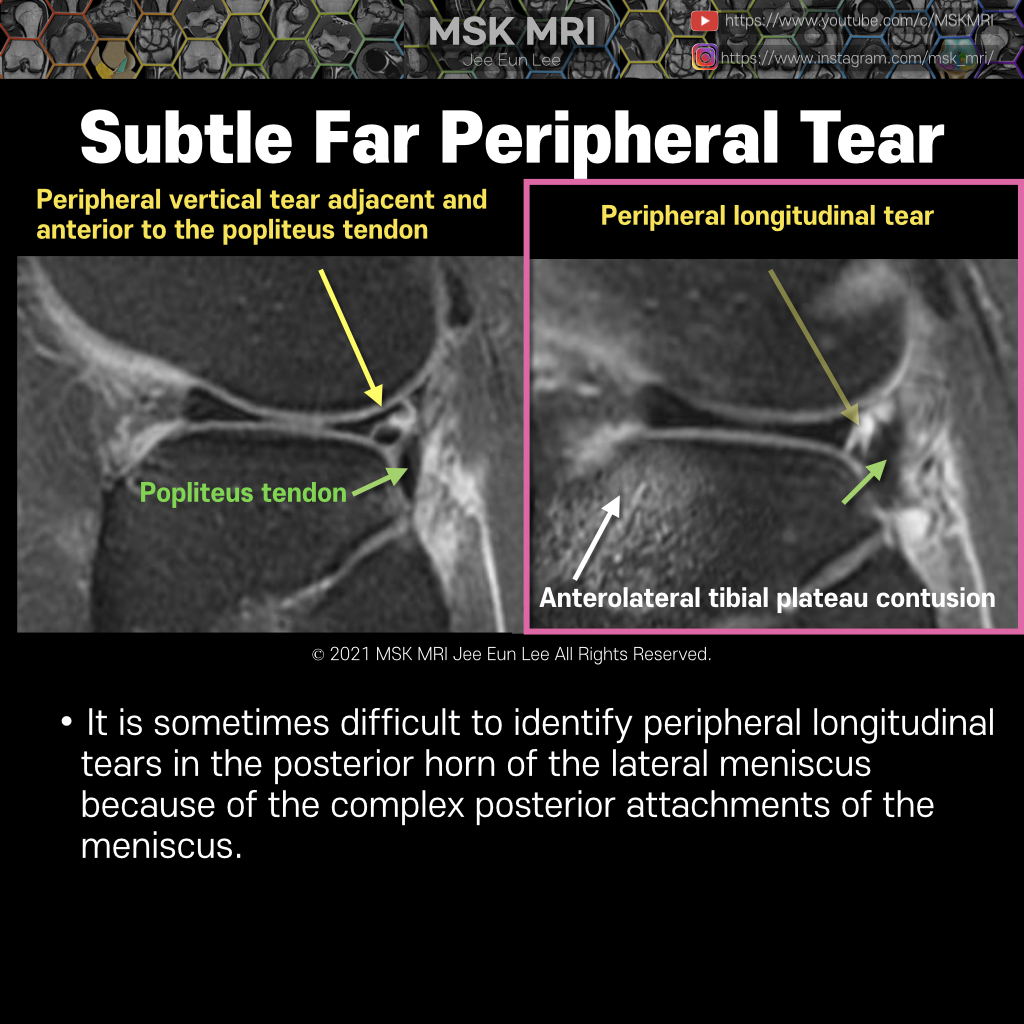
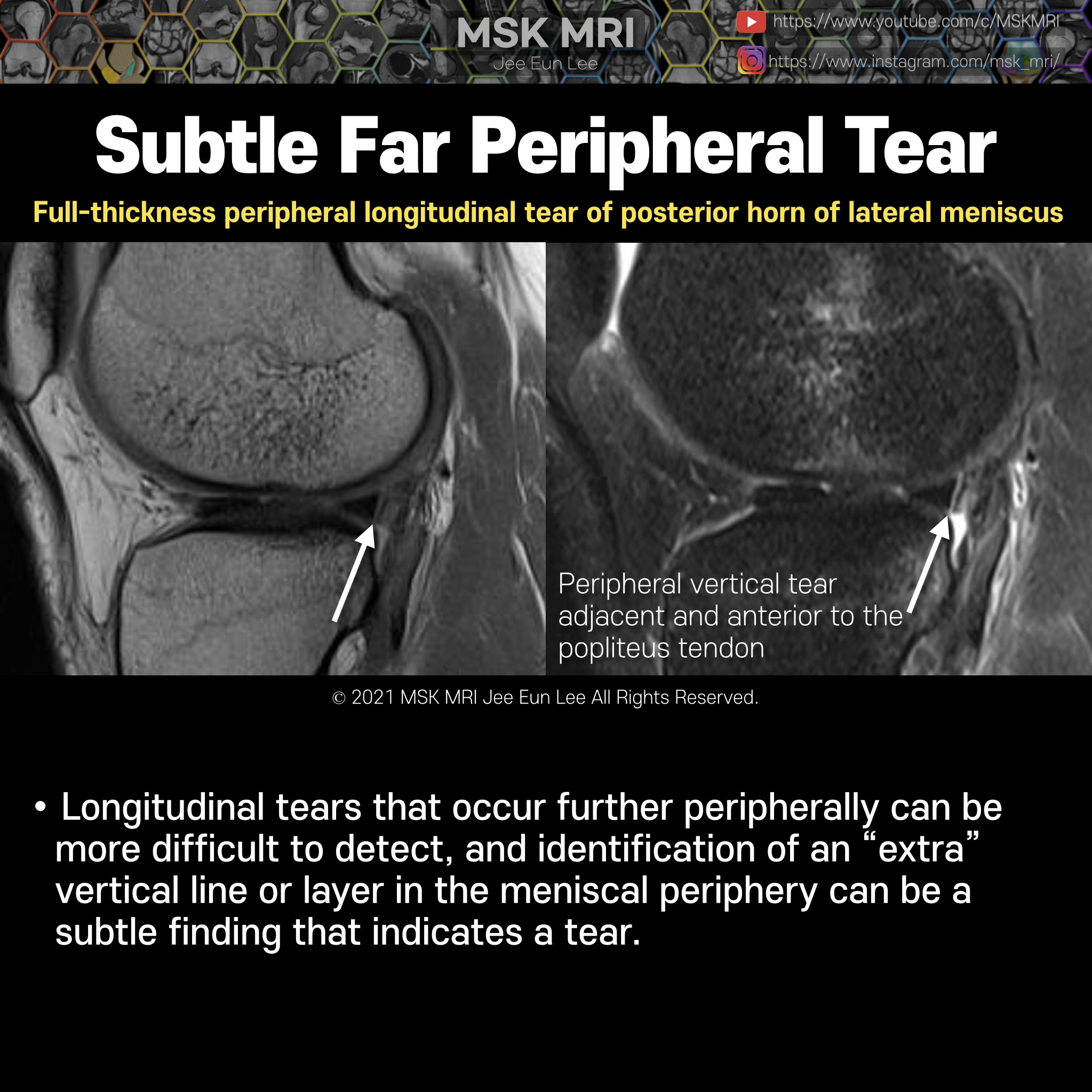
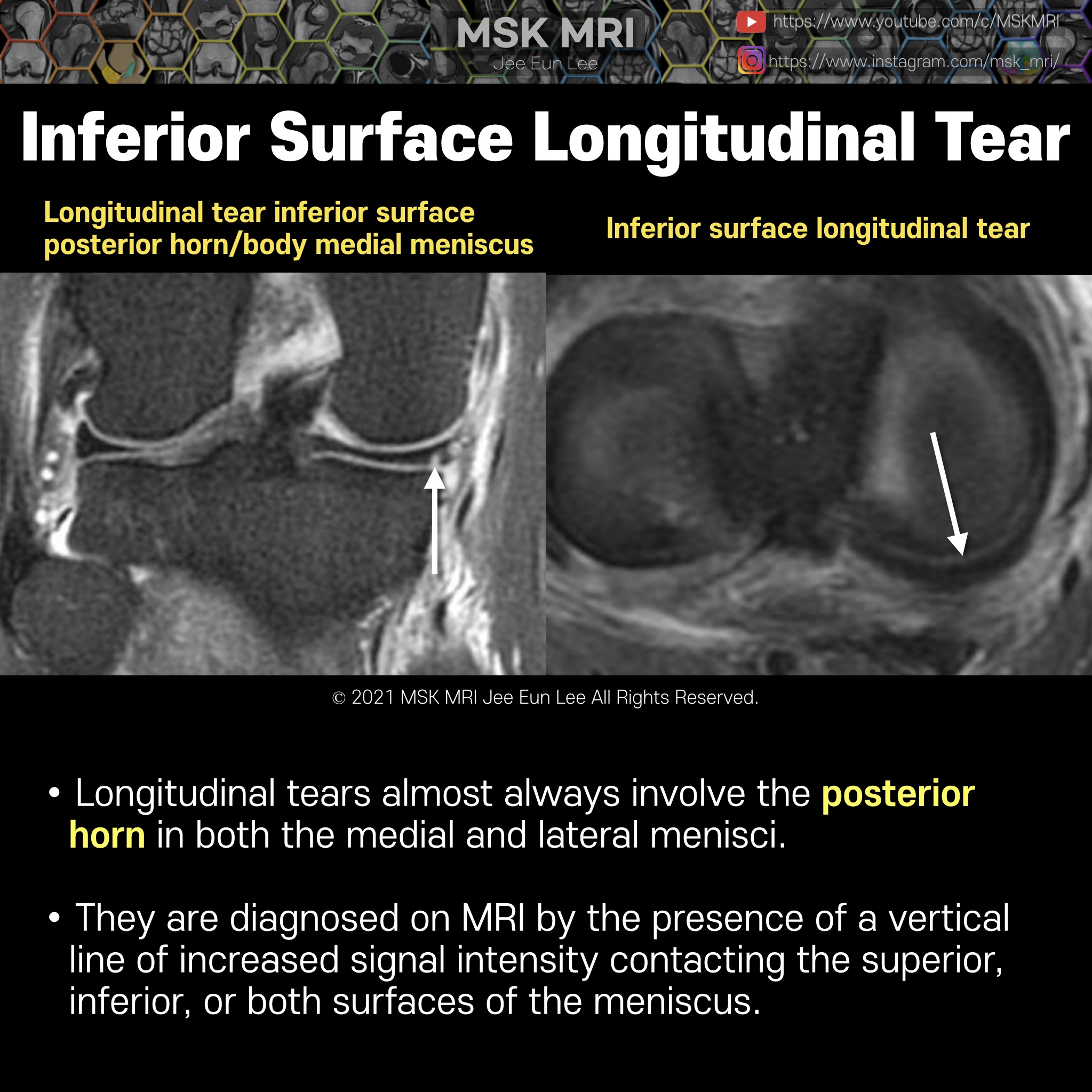
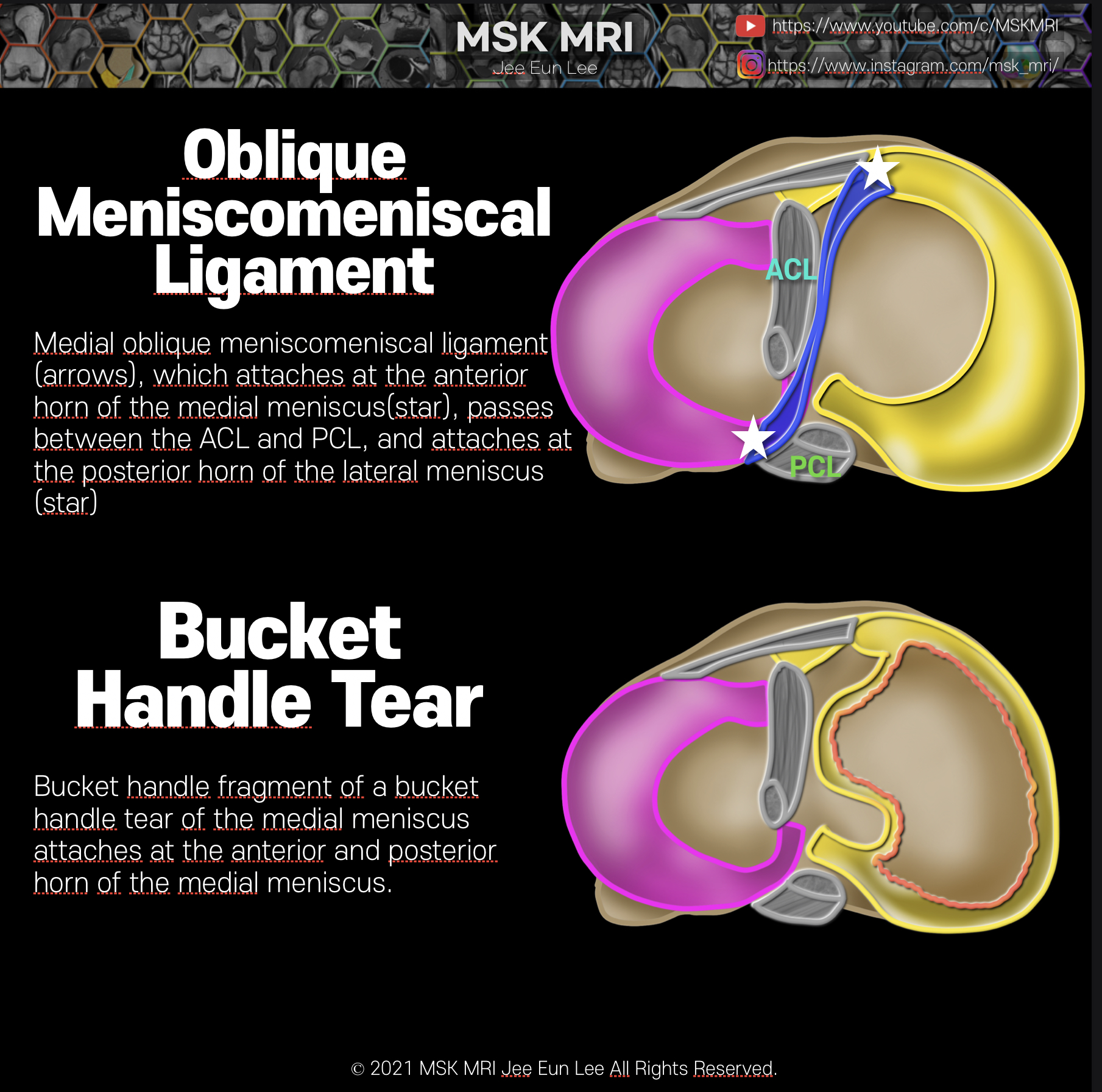
Posterior oblique drawing demonstrates PCL, LM, meniscofemoral ligaments (Humphry ligament and Wrisberg ligament) The meniscofemoral ligaments originate from the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus and insert onto the lateral aspect of the posterior medial femoral condyle, with the Humphry ligament anterior to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) and the Wrisberg ligament posteriorly Wrisber..