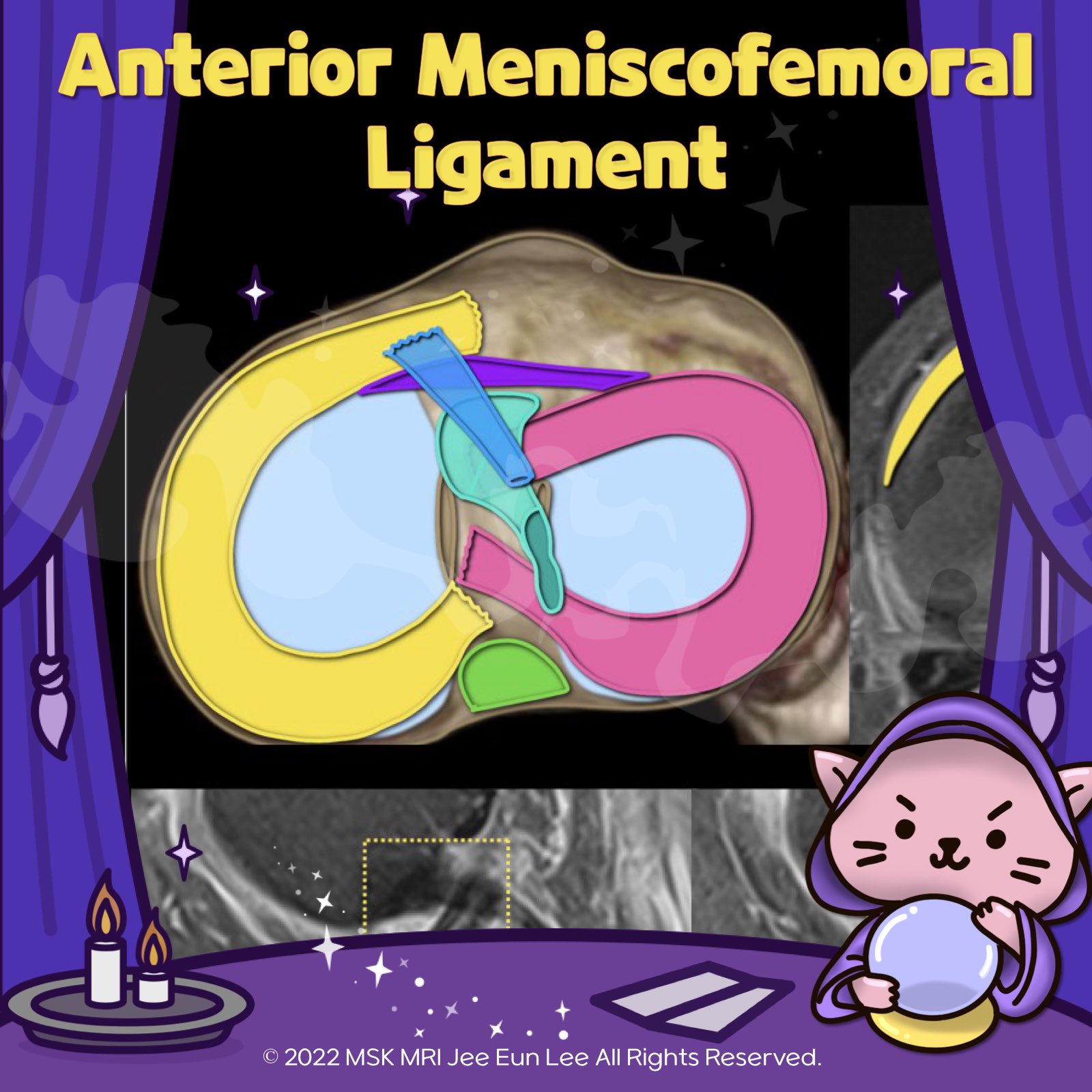
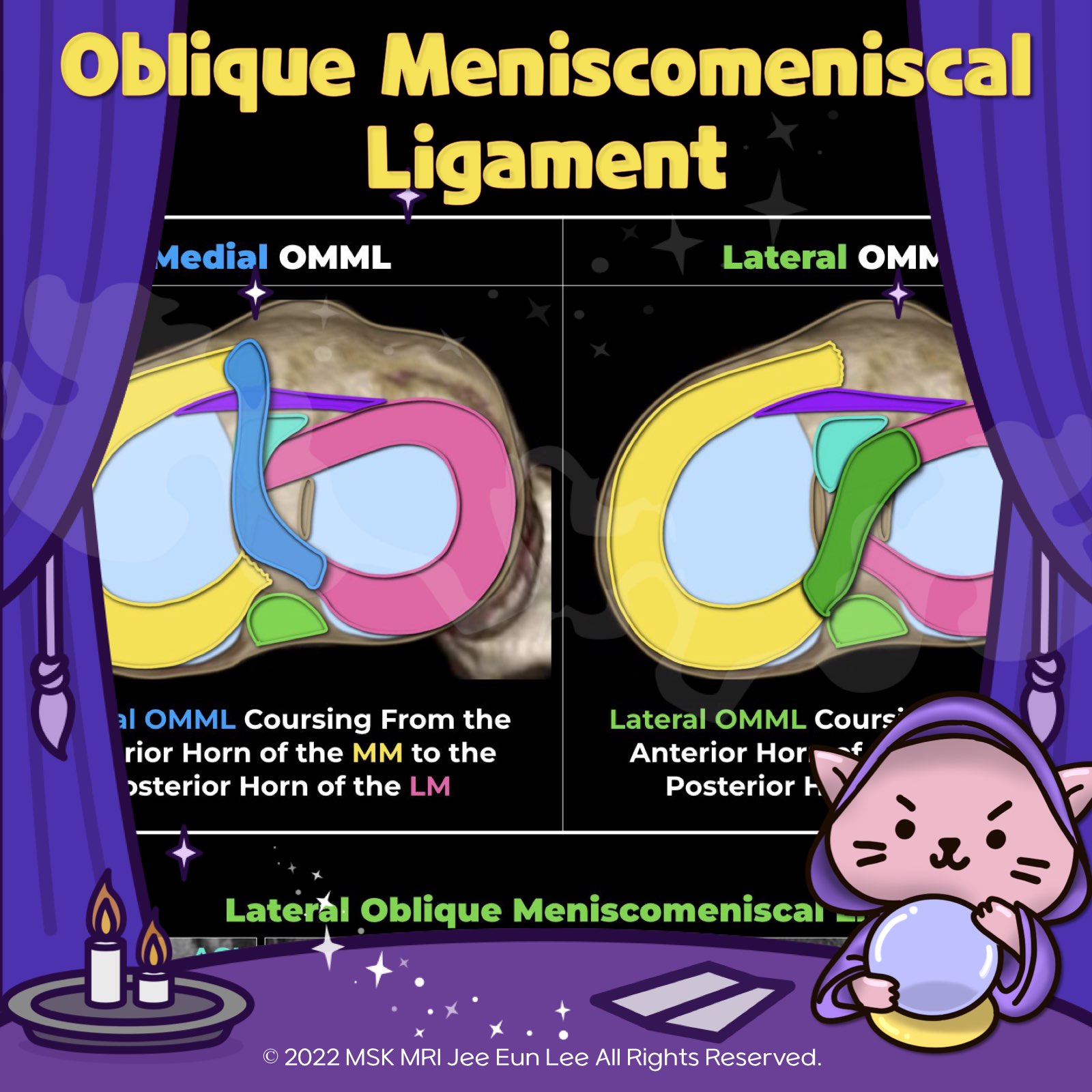
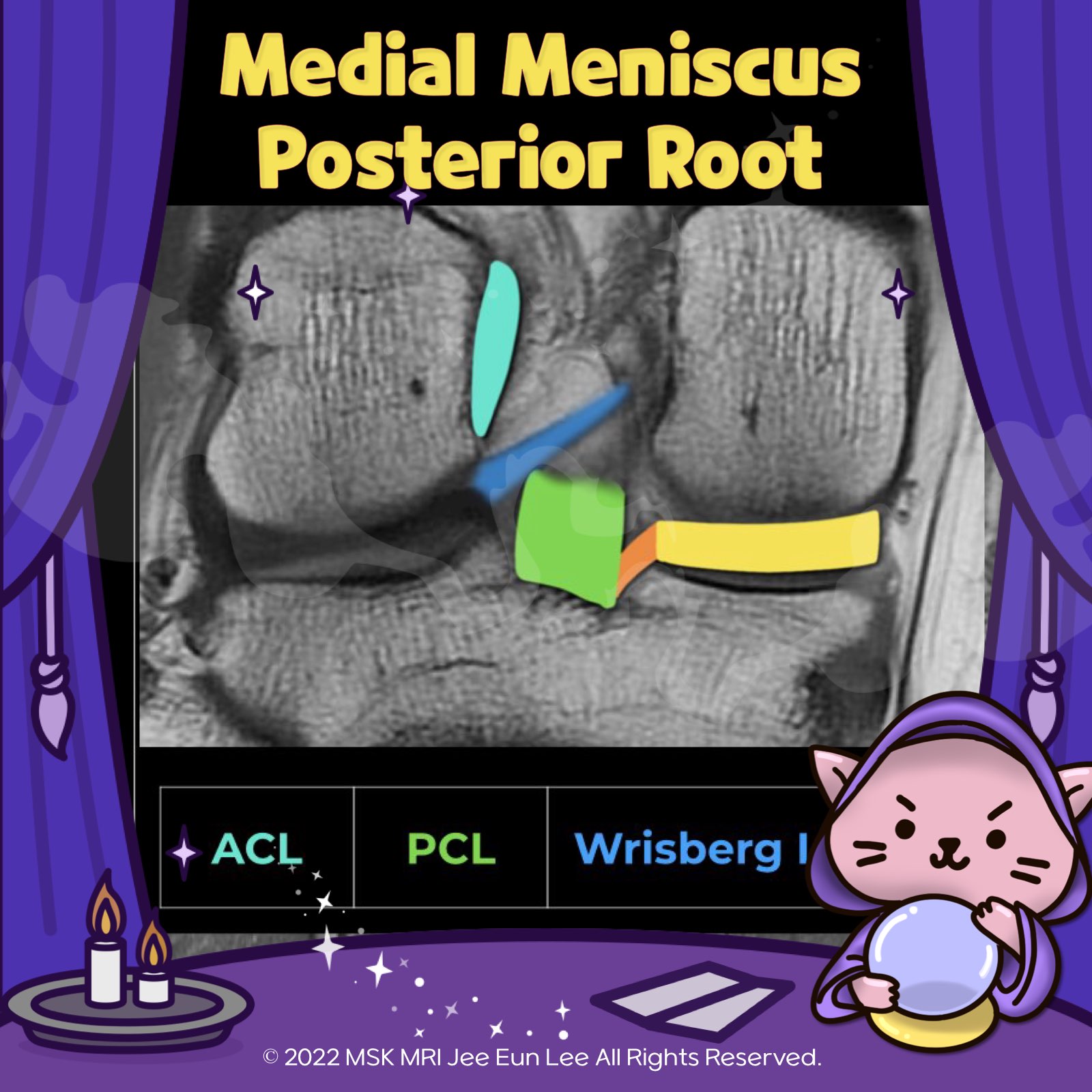
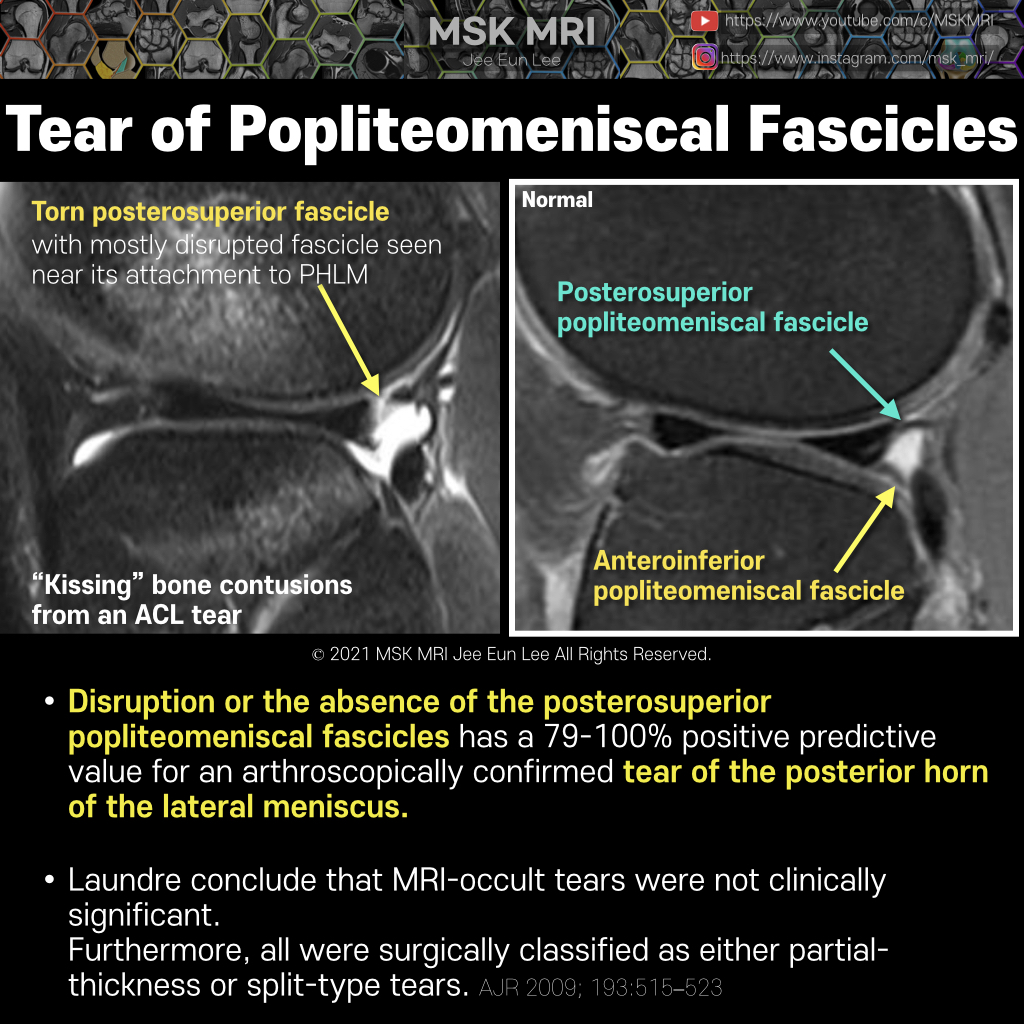
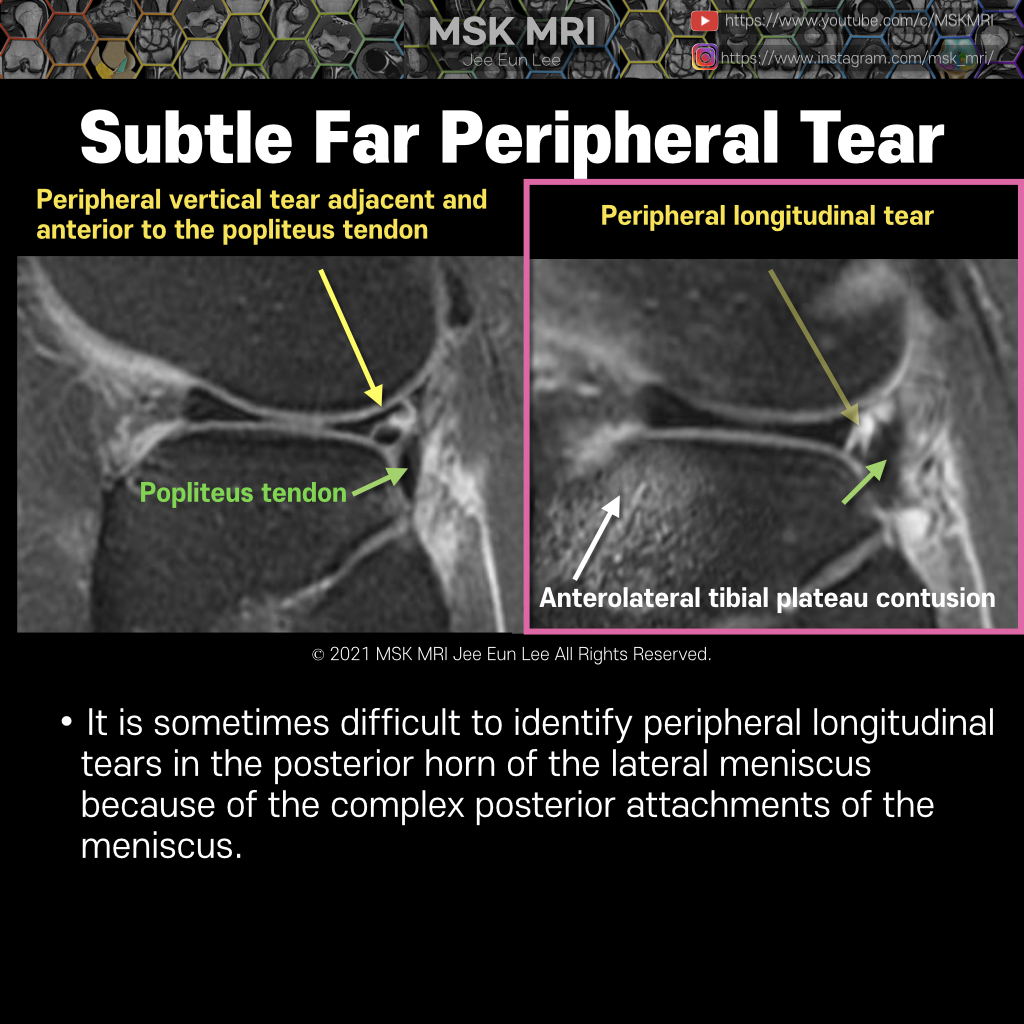
https://youtu.be/mxyxCuCKwzM https://youtu.be/kEuMzUrHD0M https://youtu.be/kEuMzUrHD0M"Anomalous insertion of the medial meniscus (AIMM) into the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an uncommon condition, seen in about 0.52% of arthroscopy cases. It involves a ligament extending to the ACL from the anterior horn of the medial meniscus, near the root. This variant accessory insertion appears on s..