Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
📌 Articular Cartilage: Structure, Composition & Tidemark
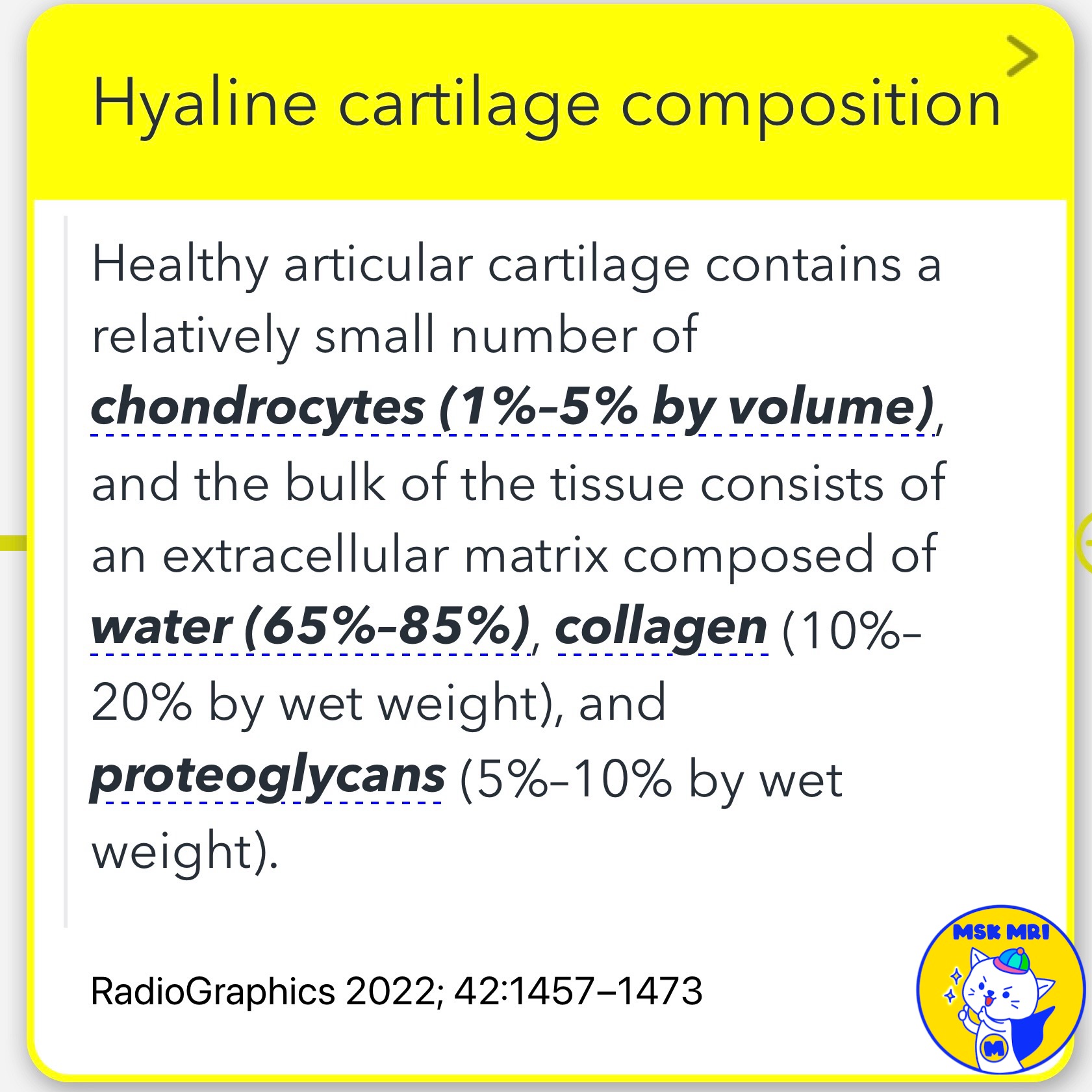
✅ Hyaline Cartilage Composition
- Healthy articular cartilage is primarily composed of an extracellular matrix that includes water (65%–85%), collagen (10%–20% by wet weight), and proteoglycans (5%–10% by wet weight).
- The chondrocytes, which comprise 1%–5% by volume, are sparsely distributed within this matrix.
✅ Four Layers of Articular Cartilage
1️⃣ Superficial Zone:
- This zone consists of a thin mat of densely packed, interwoven collagen fibrils aligned roughly parallel to the articular surface, resisting shear forces.
2️⃣ Middle and Deep Zones:
- The middle and deep zones feature densely packed collagen fibrils in a columnar organization that handles compressive loads. In the deep zone, these fibrils radiate from the bone like blades of grass and curve through 90° arcs in the middle zone.
3️⃣ Deepest Calcified Cartilage Layer:
- Located at the interface with the subchondral bone plate, this layer of compact cortical bone overlies the cancellous marrow-containing trabecular bone.
- In imaging, the calcified cartilage and subchondral bone appear as a single low-signal-intensity band, often referred to as the subchondral bone plate.
✅ Subchondral Bone
1️⃣ Subchondral Bone Plate
- The subchondral plate comprises compact subchondral bone and calcified cartilage, collectively termed the subchondral plate.
- This plate is not uniform in thickness; it is thicker in weight-bearing areas and thinner in the peripheral regions of the condyle.
2️⃣ Subchondral bone
- The subchondral bone consists of the subchondral bone plate (or articular bone plate) and the subarticular spongiosa.
- In radiology, "subchondral bone" or "subchondral region" generally refers to the subchondral plate and nearby cancellous bone.
- Osteochondral lesions encompass diseases affecting both the articular cartilage and subchondral bone.
- The thickness of the bone plate varies both within and between joints, with CT being the best assessment method.
✅ Tidemark
- The tidemark is the interface between the calcified cartilage and the overlying noncalcified cartilage.
- It is vulnerable to damage from shear forces, potentially resulting in cartilage delamination.
- Collagen fibrils pass only into this calcified layer of cartilage, not into the bone plate.
References
- RadioGraphics 2022; 42:1457–1473.
- RadioGraphics 2018; 38:1478–1495.
- Jpn J Radiol. 2022 May;40(5):443-457.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#ArticularCartilage, #OsteochondralUnit, #HyalineCartilage, #Chondrocytes, #ExtracellularMatrix, #SubchondralBone, #Tidemark, #Radiology, #CartilageHealth, #JointFunction
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5AB. Chondral and osteochondral' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-A.05) T2 Mapping Techniques (0) | 2024.07.02 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-A.04) Chemical Shift Artifact (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| (Fig 5-A.03) T2 Anisotropy and Magic Angle Effect (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| Dislocation of Polyethylene Insert (0) | 2023.12.30 |
| Polyethylene wear–induced synovitis (0) | 2023.12.29 |