Dislocation of a polyethylene insert Mechanism of Dislocation (DPI in TKA) Proposed Cause
| Atraumatic nature | No clear cause identified |
| Traumatic mechanism (insert dislocation) | Repeated posteriorly directed compressive force on the polyethylene insert from the femur |
| Biomechanical basis for dislocation | During knee flexion, femoral tibial contact moves posteriorly, leading to anterior lift-off of the insert |
| Possible causes of anterior lift-off | - Failure to secure the insert at surgery <br> - Overt locking mechanism failure <br> - Repeated stress causing wear on the locking mechanism and eventual failure |
| Uneven load distribution | Ligament laxity leading to point bearing of the lateral femoral condyle onto the posterolateral corner of the polyethylene insert, leading to accelerated wear and failure of the insert's retaining lip |
| Impingement on soft tissues or osseous structures | Impingement of the insert on soft tissues or osseous structures can lead to DPI; a case with a large posterior osteophyte was observed, suggesting it may be responsible for dislocation |
Ahmed I, Murray J. Dislocation of a polyethylene insert in an infected knee joint after a Triathlon total knee arthroplasty. J Surg Case Rep. 2020 Aug 14;2020(8):rjaa287.
Complete dislocation of the polyethylene insert in fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty.
※ Risk Factors of Polyethylene Insert Dislocation
- Varus alignment may impact long-term survival.
- Anterior tilt of tibial baseplate or mismatch between tibial and femoral components increases risk
- None of the known risk factors observed in the 3 cases at the institution. (J Arthroplasty. 2011 Feb;26(2):339.e1-4)
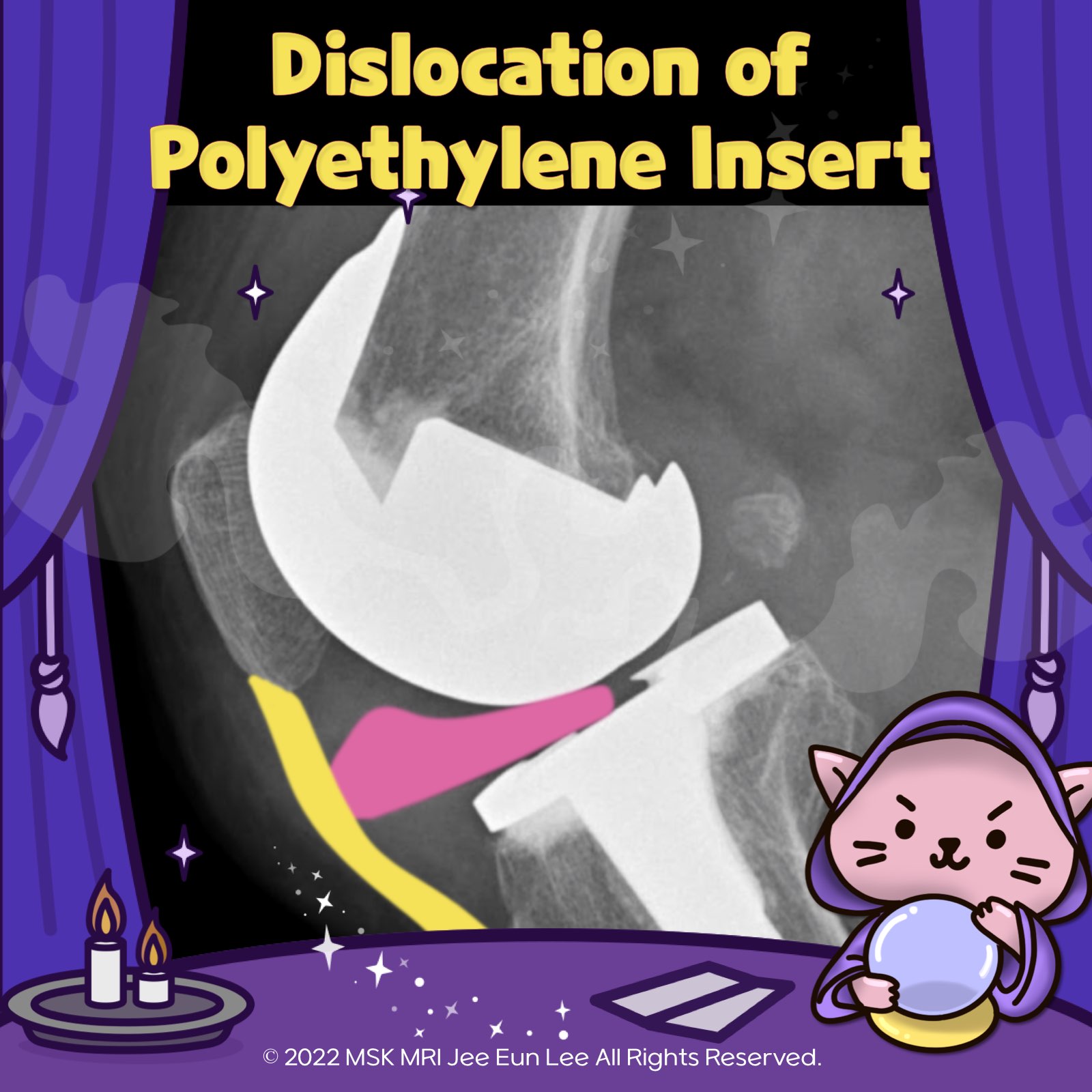
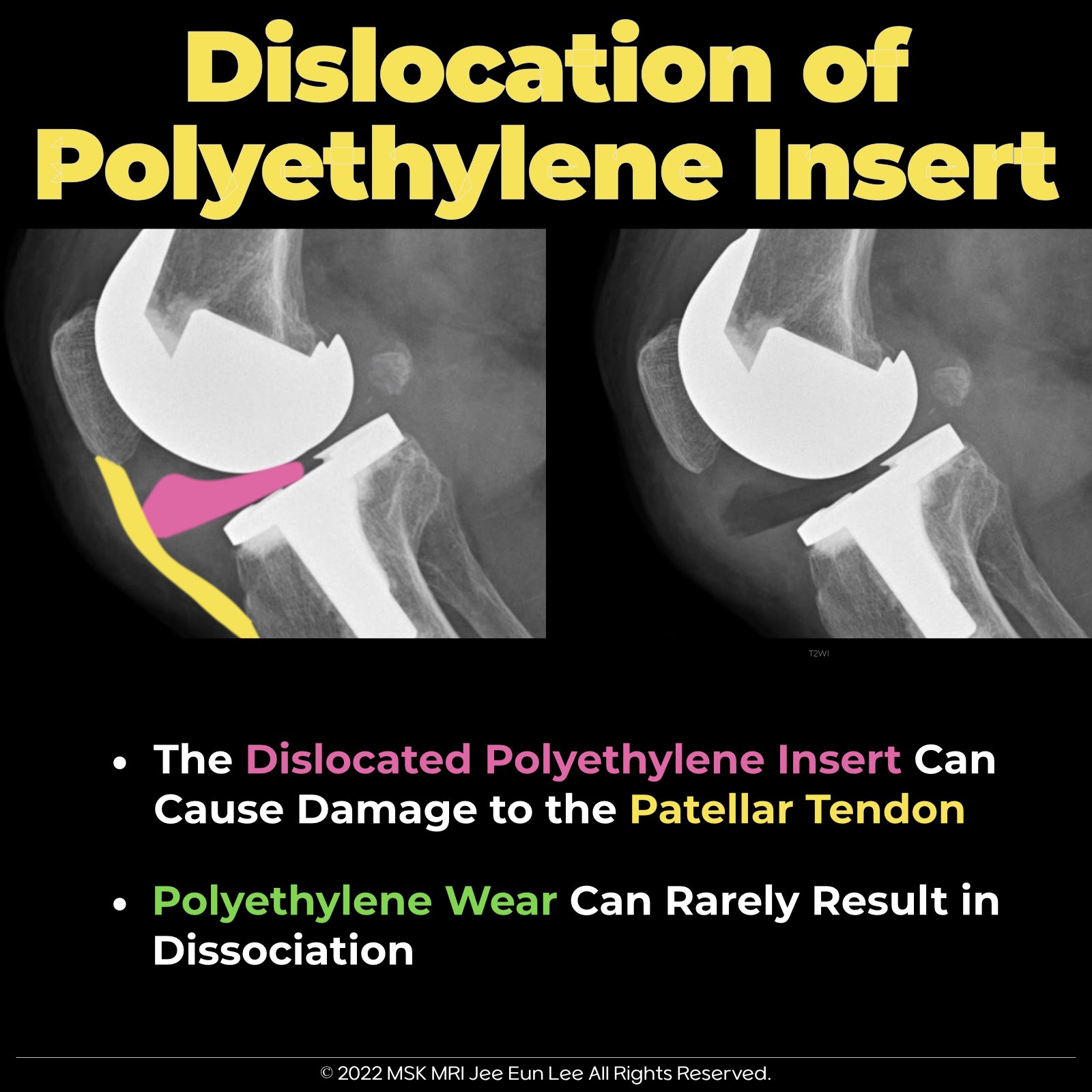
The dislocated polyethylene insert can cause significant damage to the patellar tendon.




'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5AB. Chondral and osteochondral' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-A.05) T2 Mapping Techniques (0) | 2024.07.02 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-A.04) Chemical Shift Artifact (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| (Fig 5-A.03) T2 Anisotropy and Magic Angle Effect (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| (Fig 5-A.01) Articular Cartilage: Structure, Composition & Tidemark: Part 1 (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| Polyethylene wear–induced synovitis (0) | 2023.12.29 |