| Polyethylene Wear |
Polyethylene components used in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) can experience wear on the articular surfaces due to abrasion and fatigue This wear generates polyethylene debris, which triggers an inflammatory response. Over time, this response can lead to osteolysis and loosening. |
|
| Radiographic Findings of Polyethylene Wear | ||
| Progressive joint space narrowing | Sequential radiographs show a joint space narrowing over the medial and lateral compartments, indicating polyethylene wear. | |
| Asymmetric wear | An uneven polyethylene wear pattern was observed on weight-bearing views, leading to valgus or varus deformities or patellar tilt. | |
| Moderate to severe wear | The obvious joint space narrowing indicates significant polyethylene wear. | |
| MRI findings of Polyethylene Wear | ||
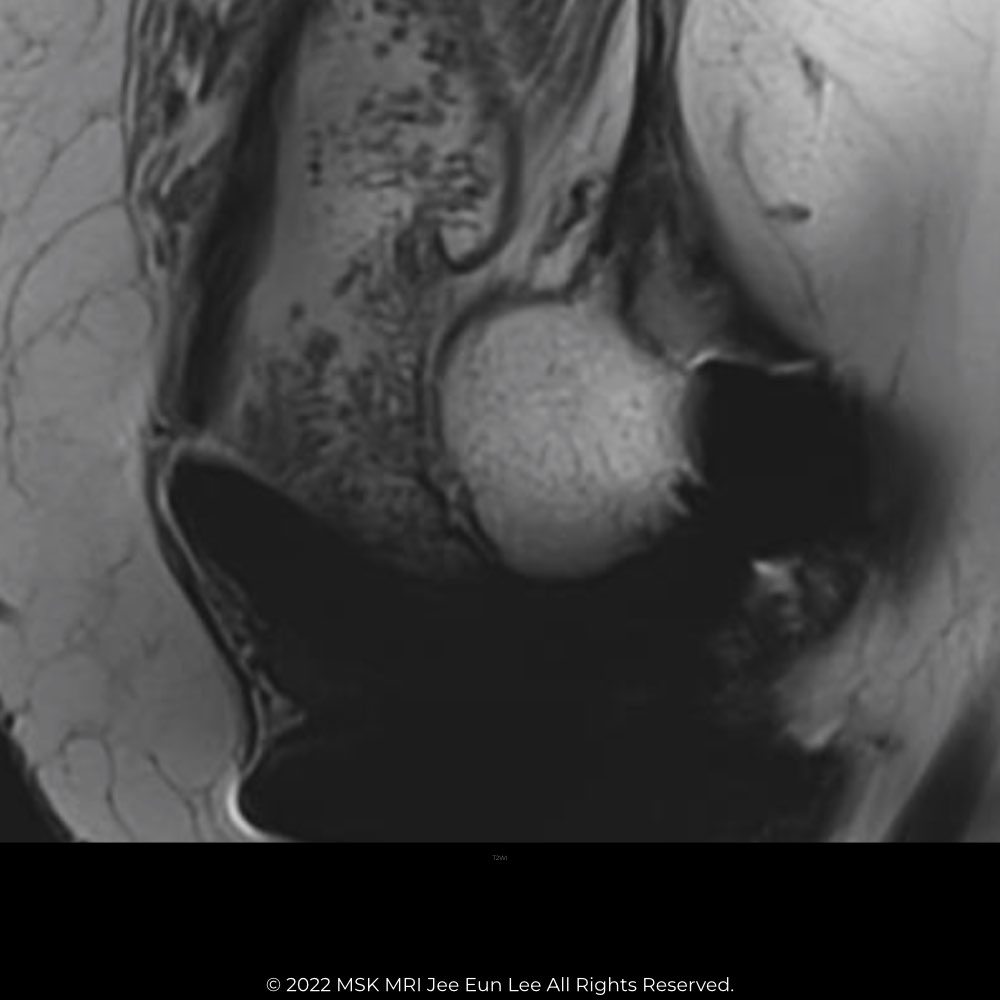
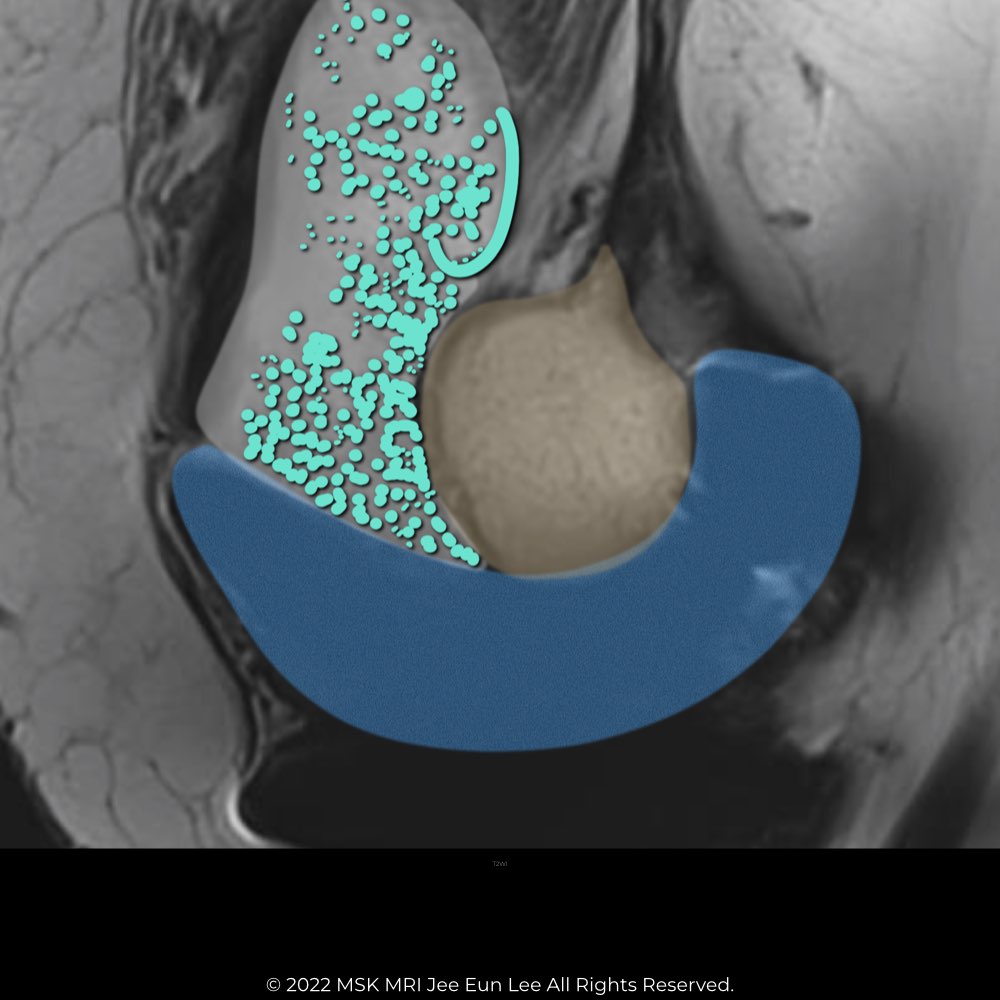
| Polyethylene wear–induced synovitis (61) (60) | Greater synovial proliferation observed on MRI corresponds with increased polyethylene wear. Frondlike synovial proliferation, thickened synovium, and intra-articular debris are seen. |
|
| Dissociation of Polyethylene Insert (53) | Rare occurrence where the polyethylene tibial insert becomes dislodged due to the dislodgement of the locking screw or pin. Linear signal hyperintensity observed between the polyethylene tibial insert and tibial tray on MRI indicates the presence of dissociation. |
|
https://youtube.com/shorts/yw3haK4l0-Y?si=aSg-xoxJDtZybUiI
- YouTube
www.youtube.com




'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 5AB. Chondral and osteochondral' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 5-A.05) T2 Mapping Techniques (0) | 2024.07.02 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 5-A.04) Chemical Shift Artifact (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| (Fig 5-A.03) T2 Anisotropy and Magic Angle Effect (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| (Fig 5-A.01) Articular Cartilage: Structure, Composition & Tidemark: Part 1 (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| Dislocation of Polyethylene Insert (0) | 2023.12.30 |