https://youtube.com/shorts/nmC8DVtHVzY
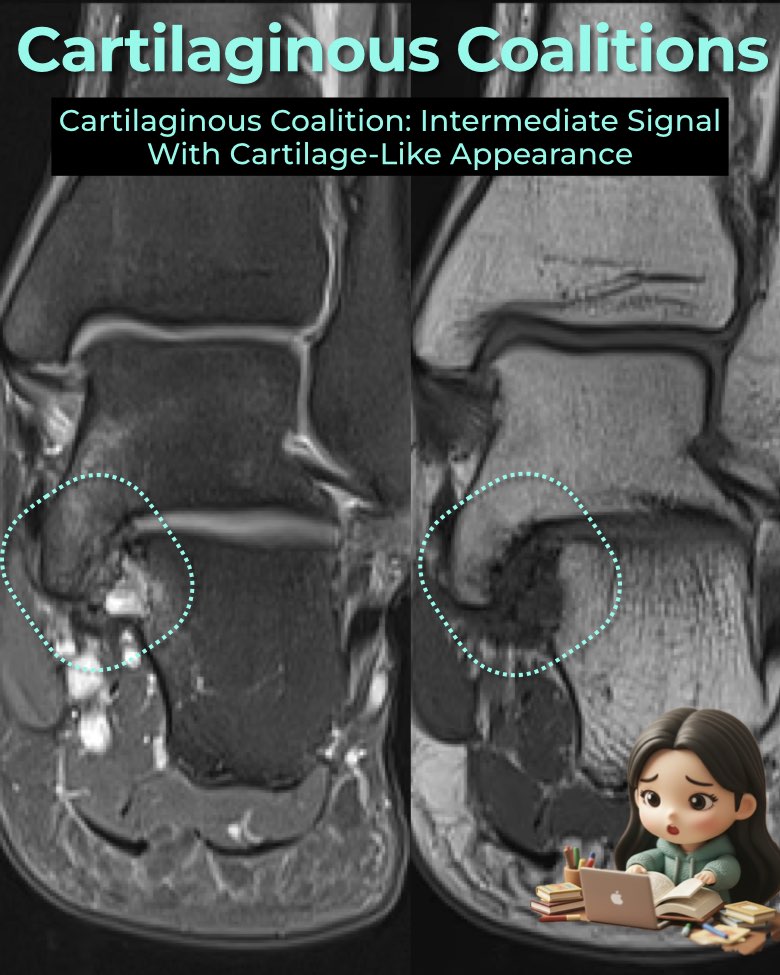
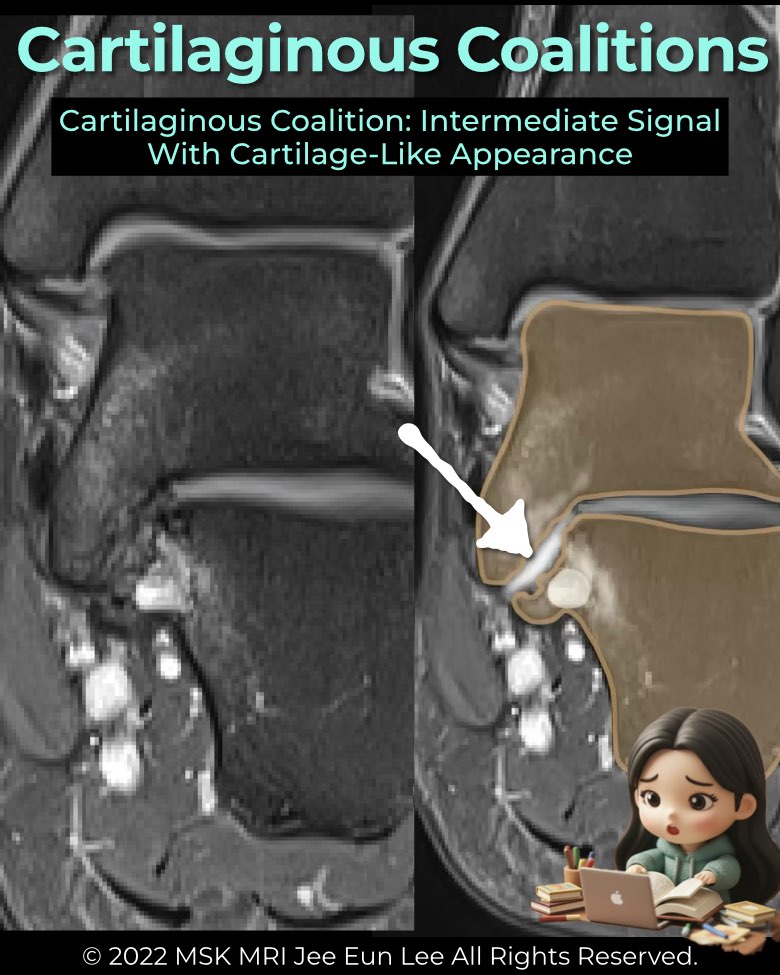
A cartilaginous coalition (synchondrosis) is a non-osseous union of tarsal bones bridged by cartilage.
MRI appearance
- Bridging tissue has signal intensity similar to hyaline cartilage or fluid.
- T1: intermediate signal.
- T2 / fluid-sensitive: intermediate-to-high signal.
- Facet contour is broadened and abnormally oriented.
- Subchondral plate often deficient; cartilage thickness may be irregular.
Anatomic features
- Best appreciated on coronal MRI (and CT for morphology).
- Commonly involves the middle facet of the subtalar joint.
- Represents a transitional stage between fibrous and osseous coalition.
Radiology perspective
Cartilaginous coalitions are subtle on radiographs but well depicted on MRI. Recognizing the intermediate signal tissue and deficient subchondral plate is critical for diagnosis, especially in younger patients with unexplained hindfoot pain.
#Radiology, #MSKMRI, #CartilaginousCoalition, #SubtalarJoint, #CoalitionImaging, #FootMRI, #OrthopedicImaging, #RadiologyEducation, #MSKImaging, #RadiologistLife
Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.