Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
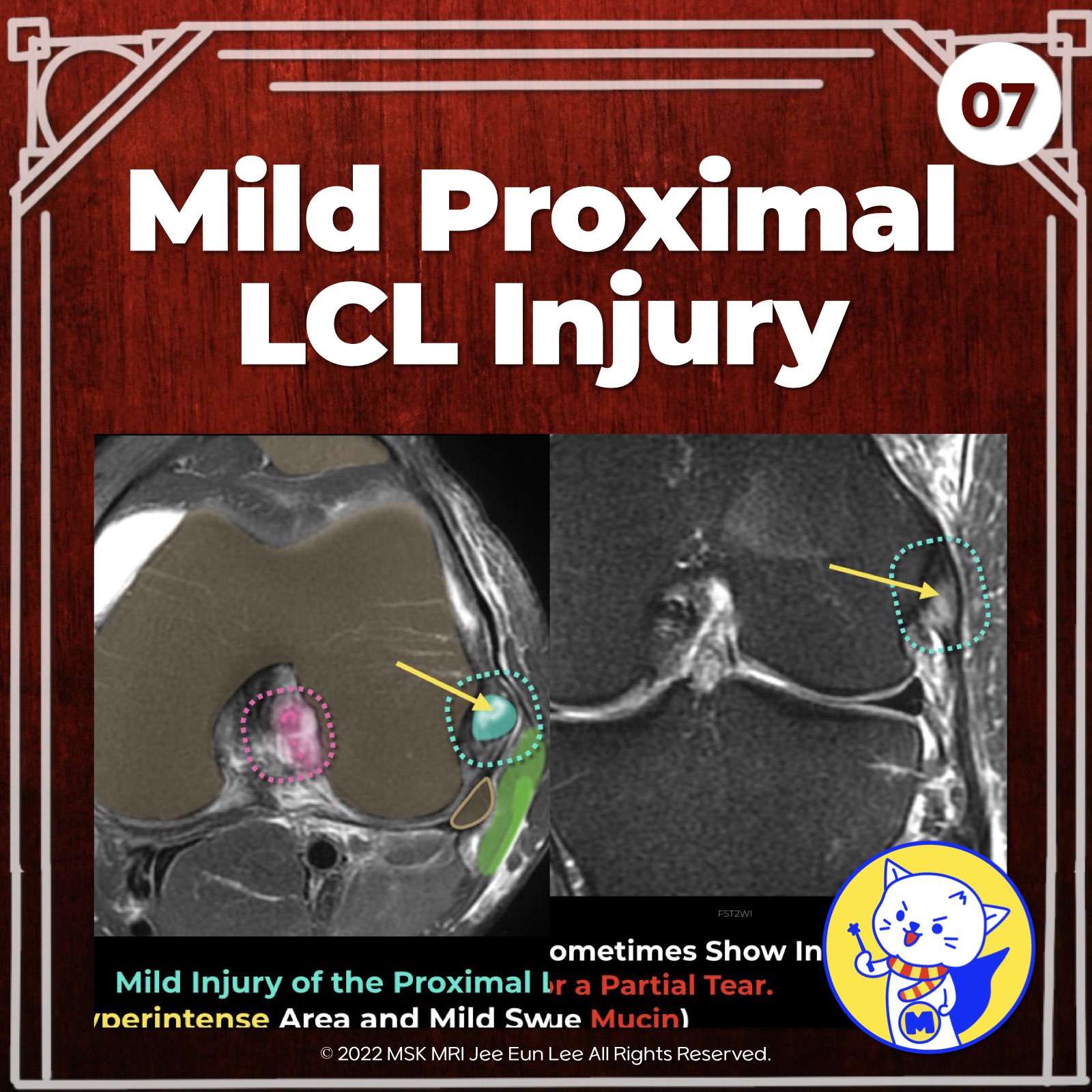
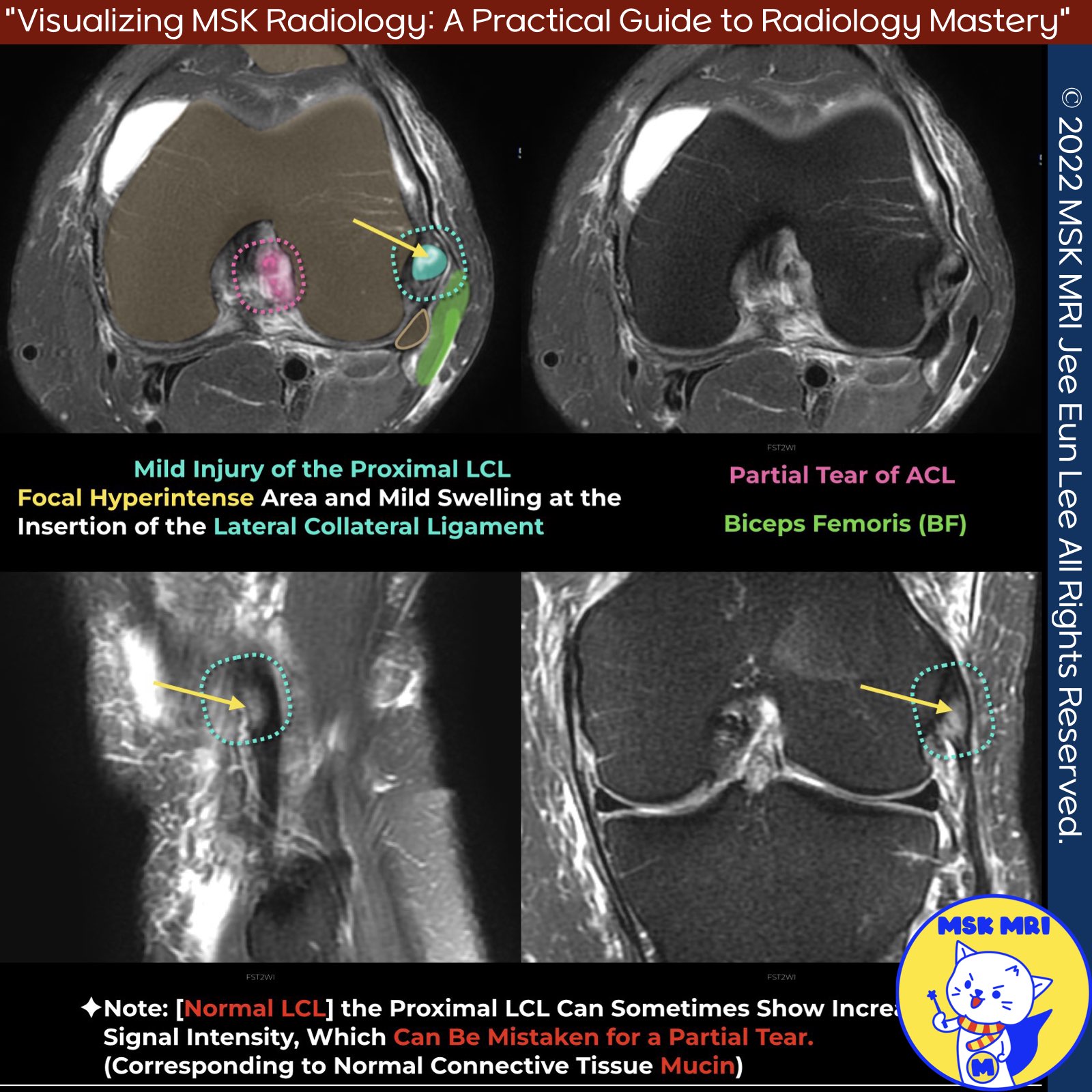
🧐 Case Presentation
- Focal hyperintense area and mild swelling at the insertion of the lateral collateral ligament
- Suggestive of mild injury of the proximal lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
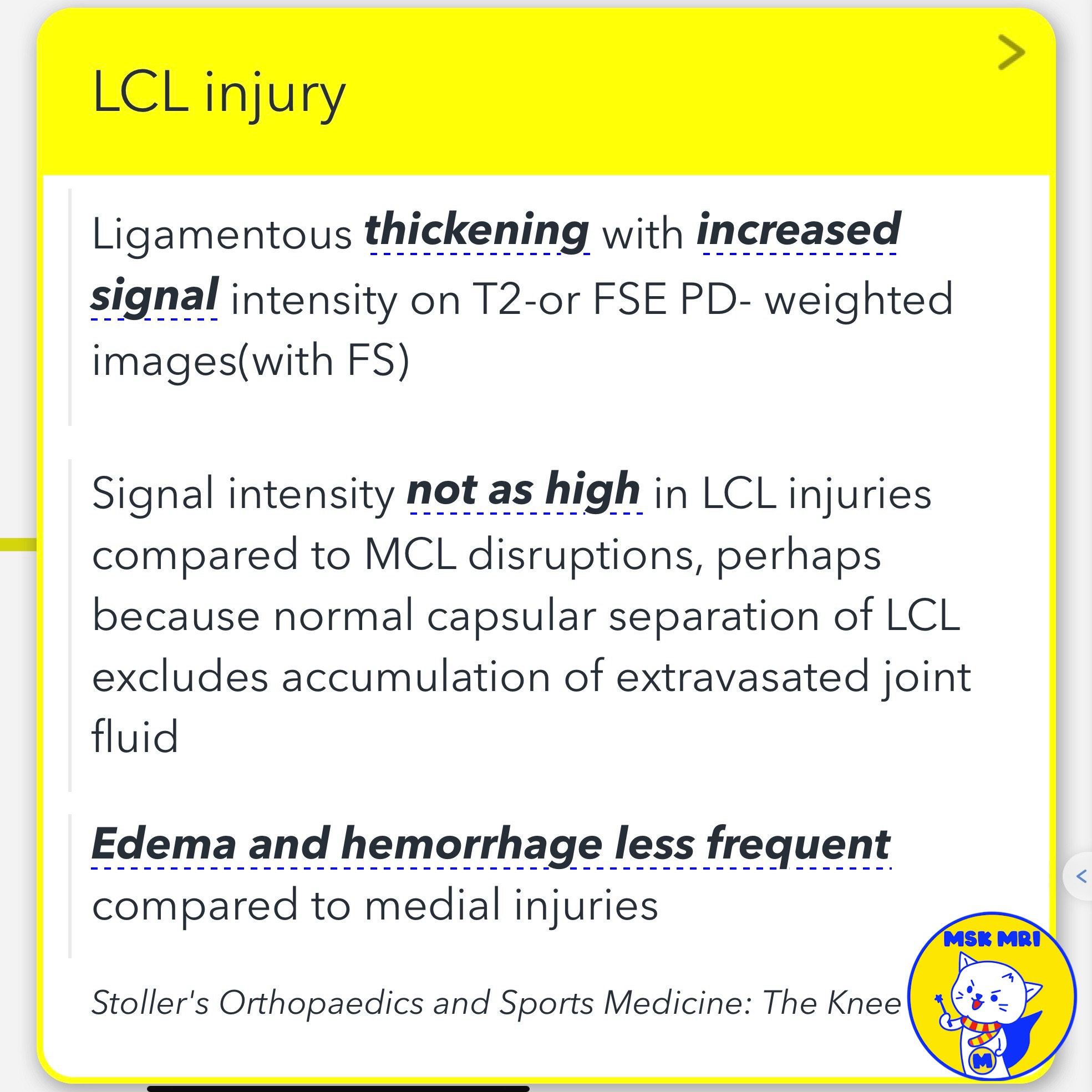
✅ Point 1: Less Edema and Hemorrhage in LCL Injuries
- In LCL injuries, edema and hemorrhage are less frequent compared to medial injuries involving the medial collateral ligament (MCL)
- Even a grade 1 MCL injury, characterized by subcutaneous edema adjacent to an intact MCL, can demonstrate more surrounding soft tissue edema than an LCL injury
- In a grade 2 MCL injury, there is proximal MCL intraligamentous hyperintensity and thickening due to a partial tear of the superficial fibers
✅Point 2: Increased Signal in Proximal LCL
- The proximal LCL can sometimes show increased signal intensity
- This increased signal could be mistaken for a partial tear
- However, it may correspond to normal connective tissue mucin, especially in cases without a clear trauma history
- This possibility should be considered when interpreting such findings
Stoller's Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine: The Knee
J Ultrasound Med. 2022 Apr;41(4):827-834
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#LCLInjury, #MCLInjury, #LigamentInjury, #MRIFindings, #SoftTissueEdema, #Hyperintensity, #TraumaHistory, #ConnectiveTissueMucin,
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 3.Collateral Ligaments' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 3-B.09) Complete Distal LCL Tear with Retraction (0) | 2024.05.21 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 3-B.08) Distal LCL Attachment Tear (0) | 2024.05.21 |
| (Fig 3-B.06) Lateral Collateral Ligament Anatomy: Part 2 (0) | 2024.05.20 |
| (Fig 3-B.05) Lateral Collateral Ligament Anatomy: Part 1 (0) | 2024.05.20 |
| (Fig 3-B.02) Posterolateral Capsular Support Structures (0) | 2024.05.20 |