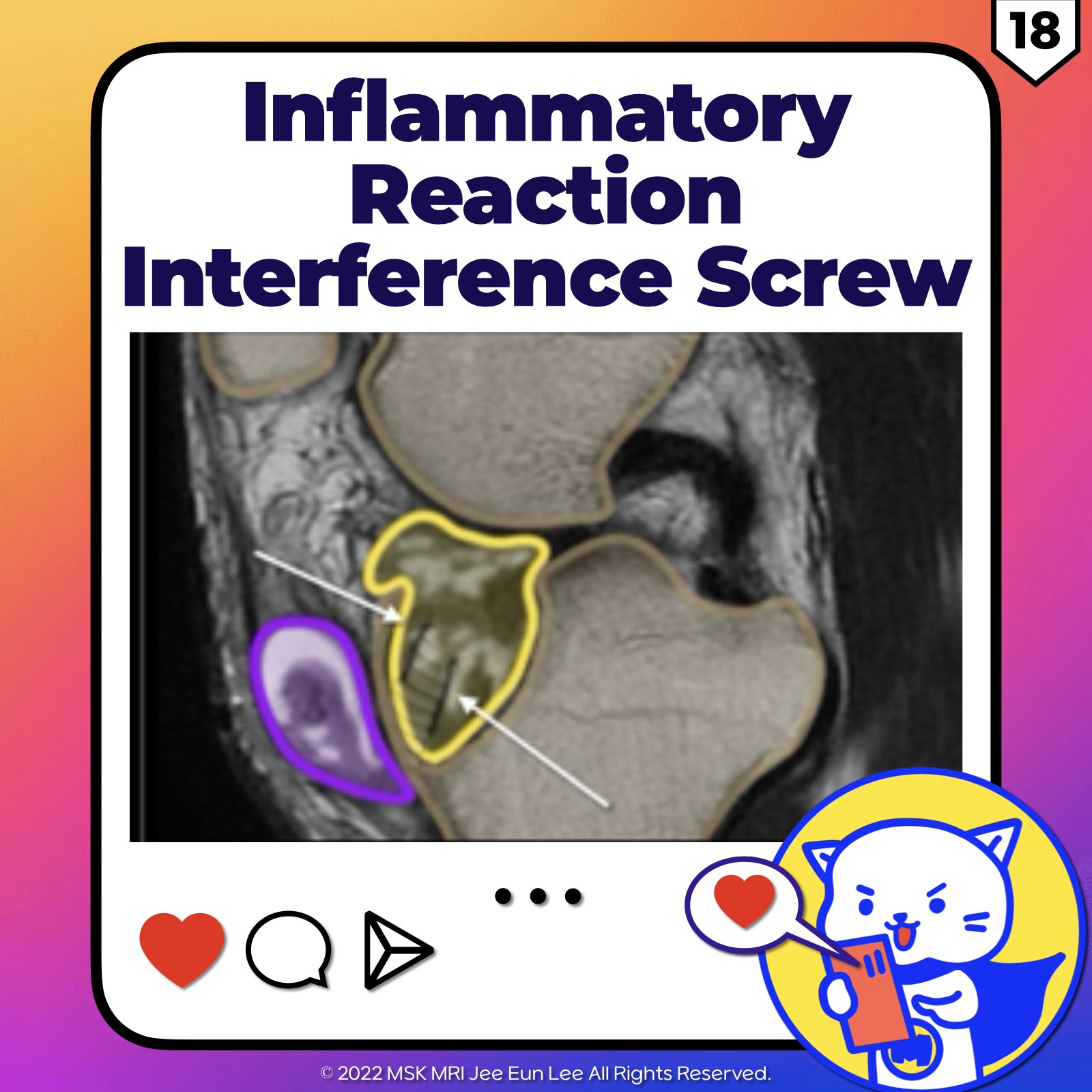
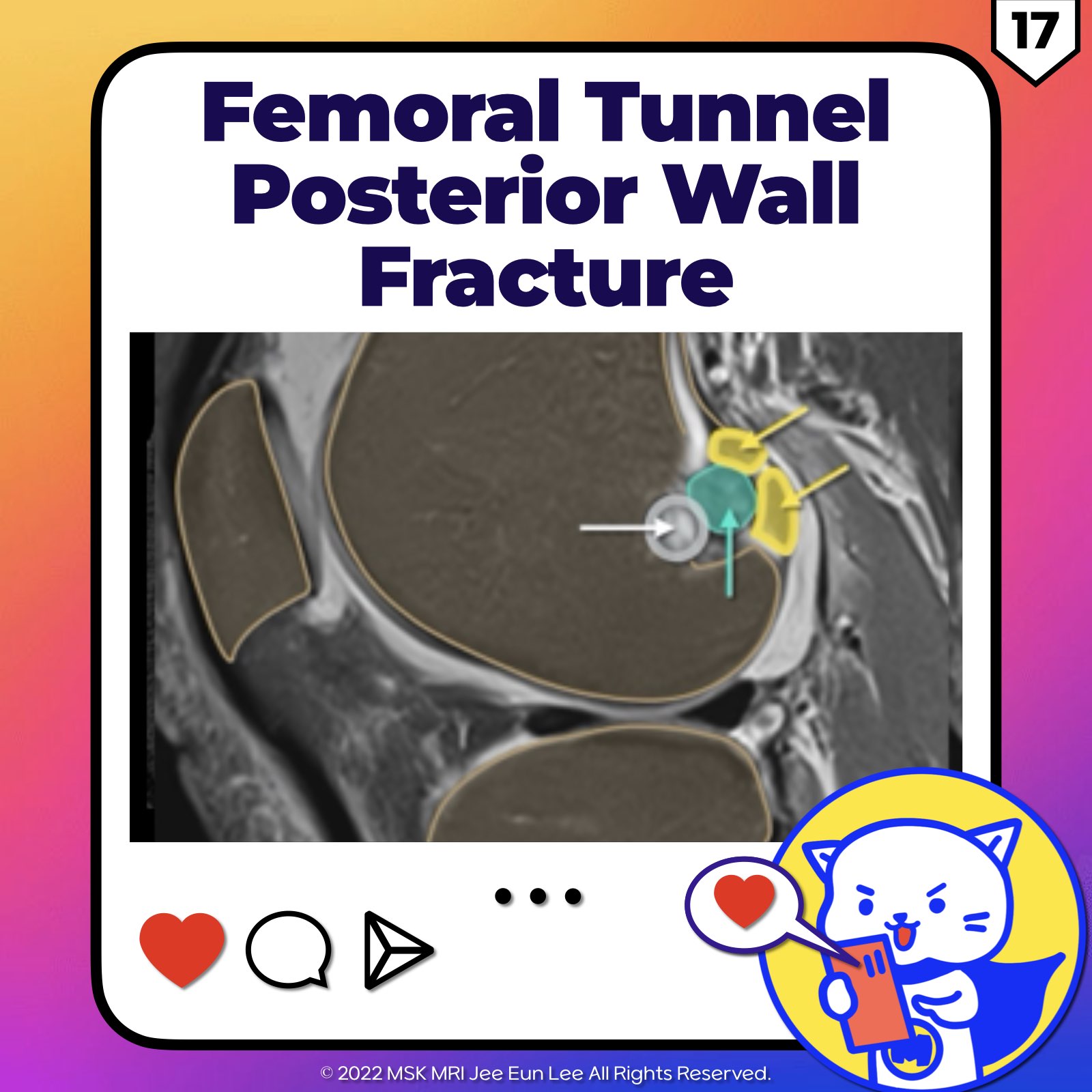
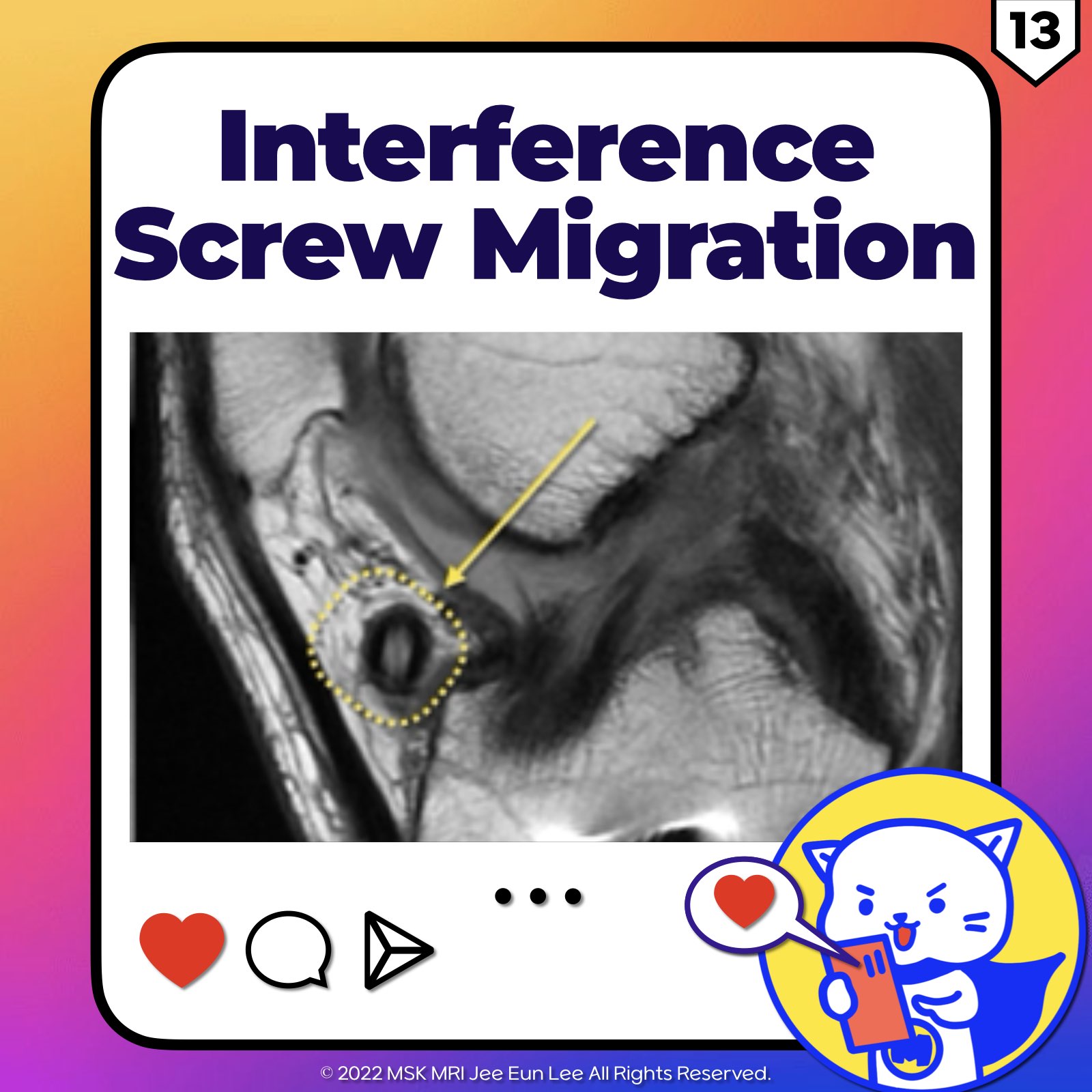
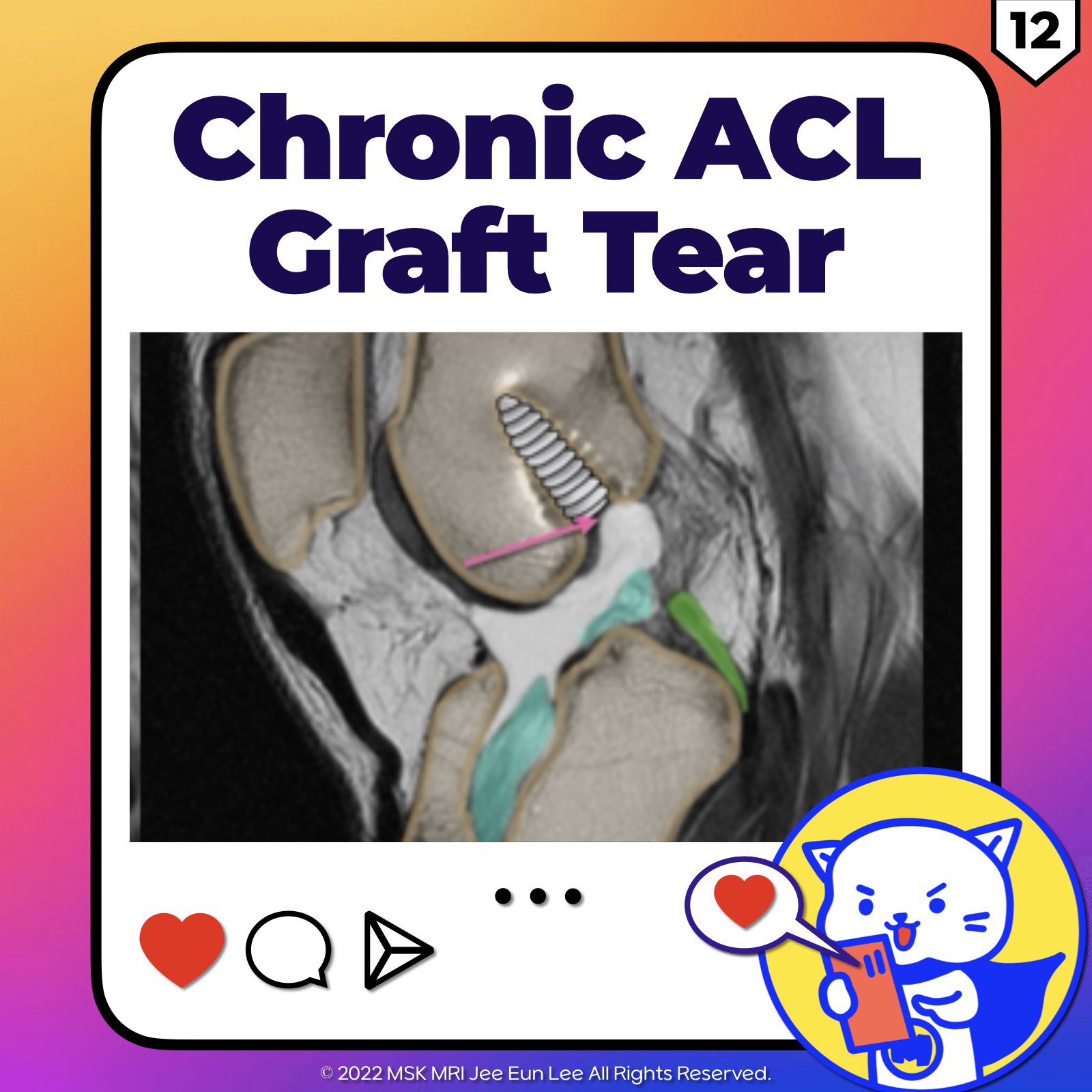
https://youtu.be/52WbP6MeYvkhttps://youtu.be/rbdodKV6lpE==============================================⬇️✨⬇️🎉⬇️🔥⬇️📚⬇️Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚==============================================🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blo..