Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
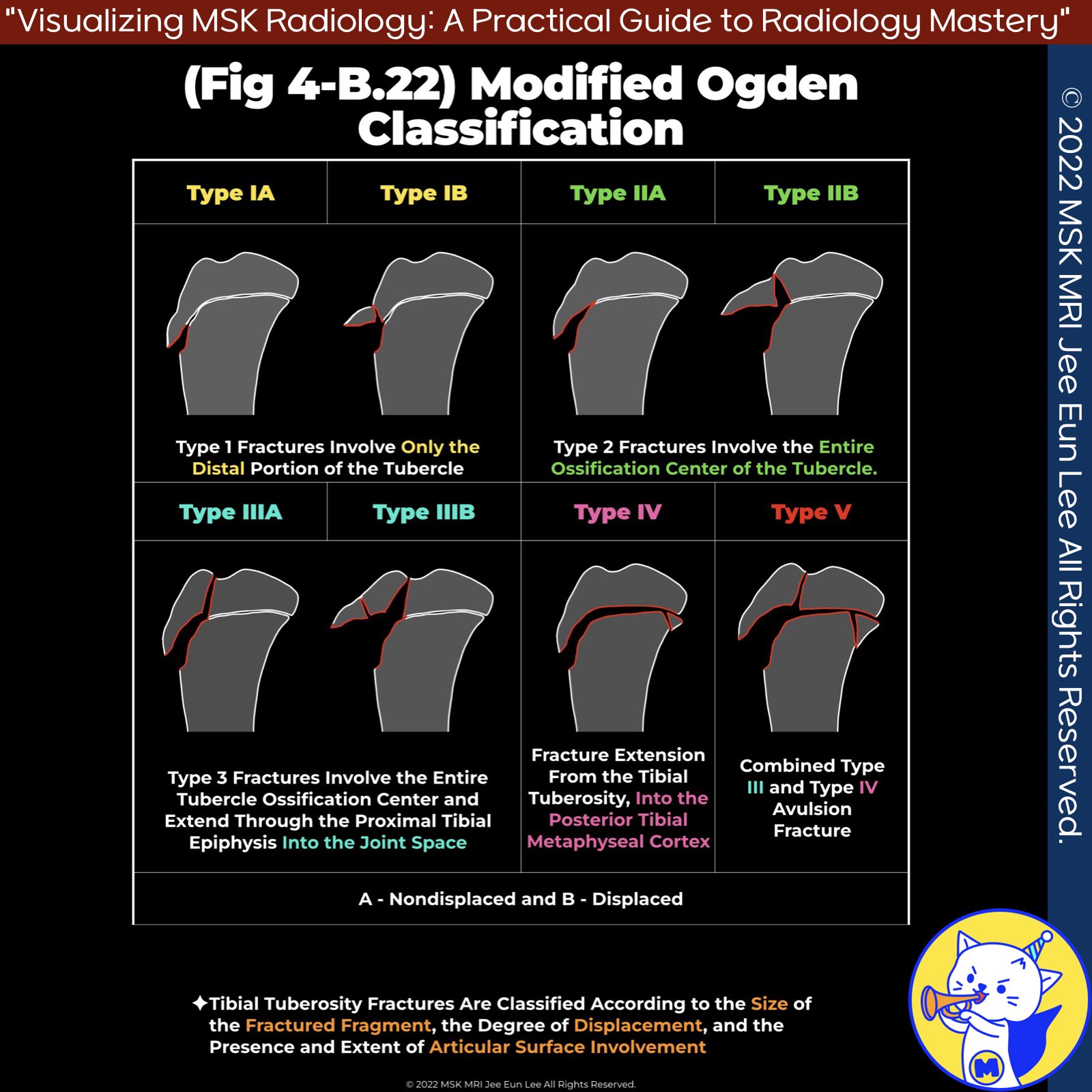
📌Ogden Classification System for Tibial Tubercle Fractures
The Ogden classification system categorizes tibial tubercle fractures into five types, each with subtypes describing the fracture's extent and nature.
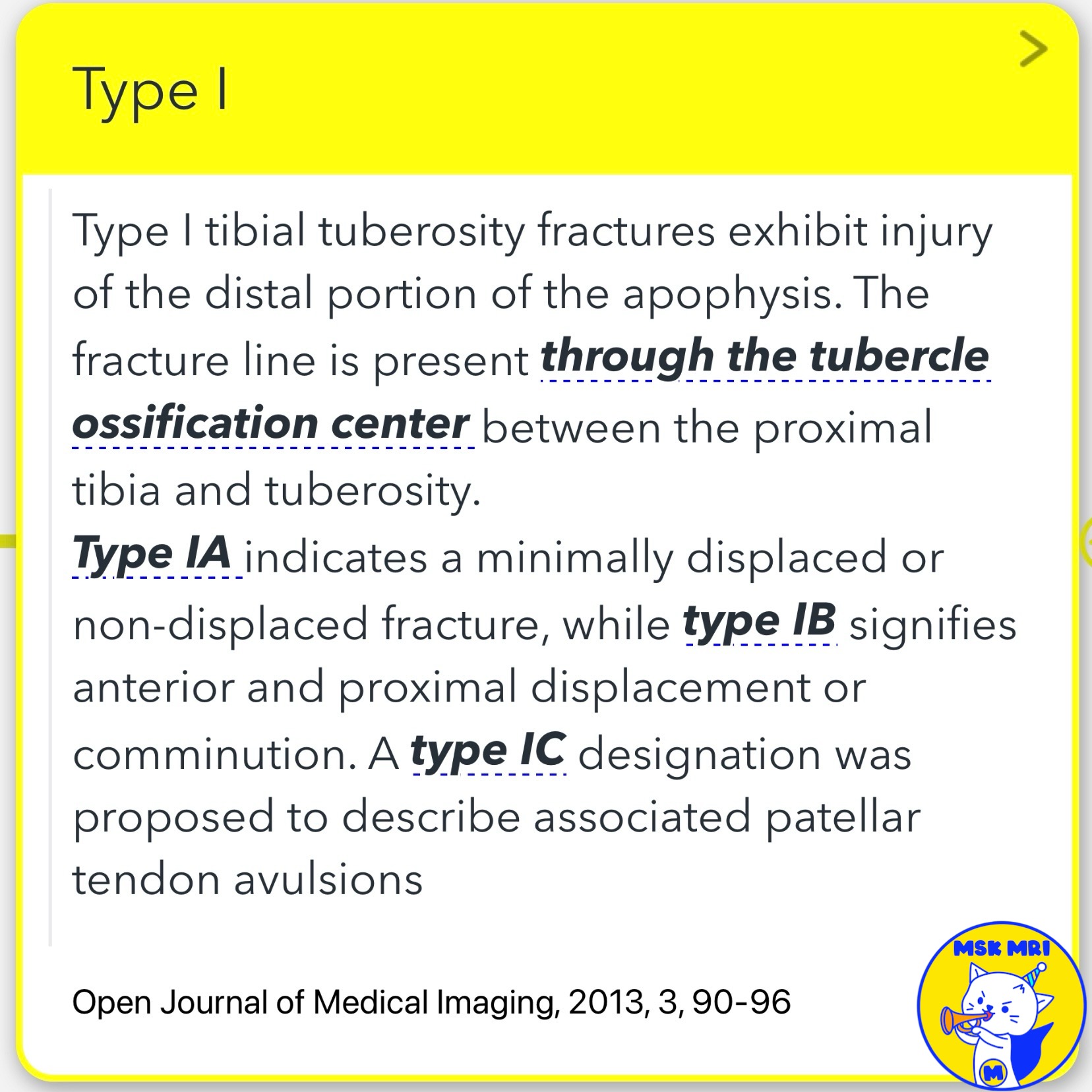
1️⃣ Type I Fractures
Type I fractures involve only the distal portion of the tubercle.
- Type IA: Minimally displaced or non-displaced fracture.
- Type IB: Anterior and proximal displacement or comminution.
- Type IC: Proposed subtype for associated patellar tendon avulsions.
References:
- RadioGraphics 2009; 29:877–886
- Open Journal of Medical Imaging, 2013, 3, 90-96
- EFORT Open Rev. 2020 May 5;5(5):260-267
2️⃣ Type II Fractures
Type II fractures involve the entire ossification center of the tubercle.
- Type IIA: Separation of the tubercle from the proximal tibia, minimally or non-displaced.
- Type IIB: Anterior displacement and/or comminution.
References:
- RadioGraphics 2009; 29:877–886
- Open Journal of Medical Imaging, 2013, 3, 90-96
- EFORT Open Rev. 2020 May 5;5(5):260-267
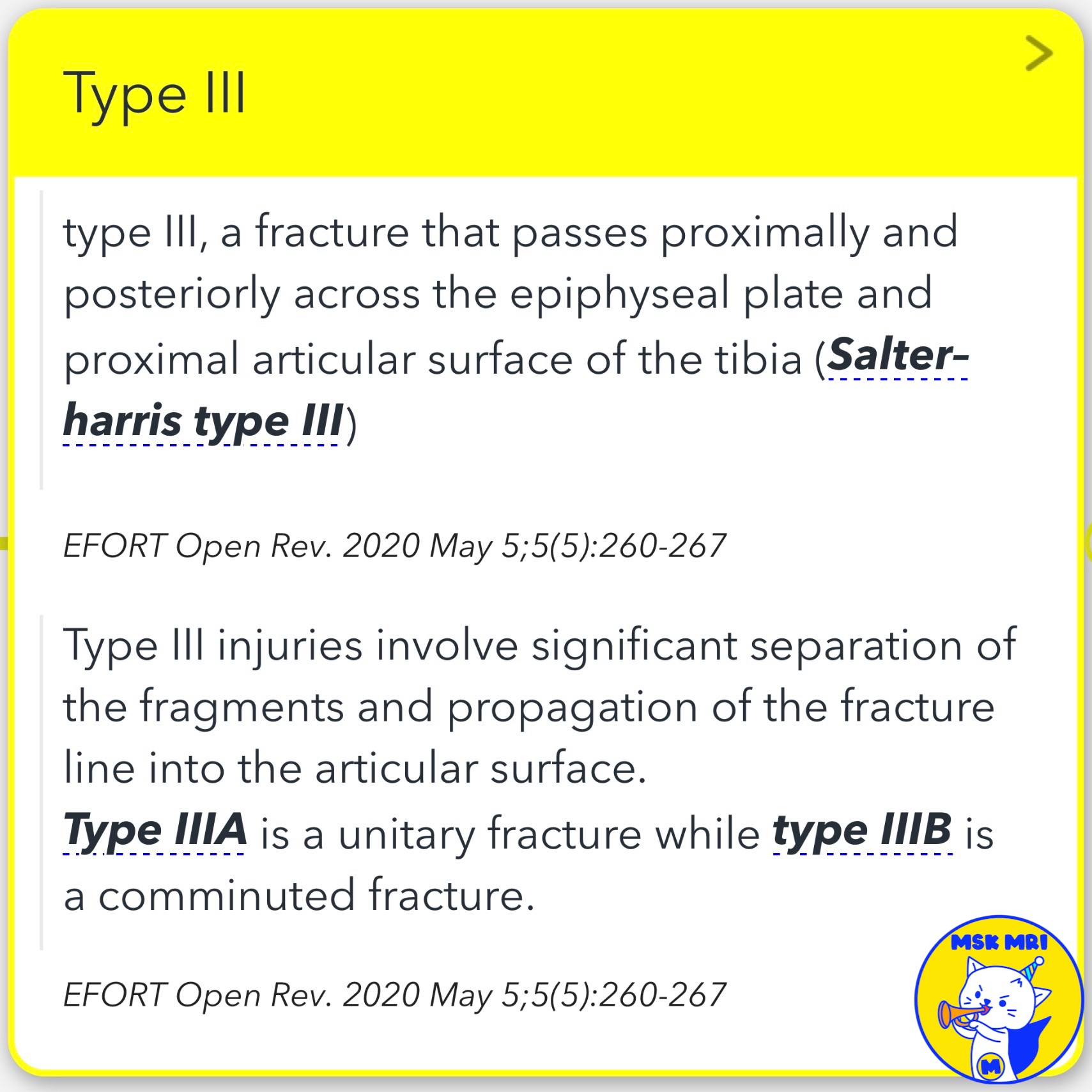
3️⃣ Type III Fractures
Type III fractures extend through the proximal tibial epiphysis into the joint space.
- Type IIIA: Non-displaced fracture.
- Type IIIB: Comminuted fracture.
References:
- RadioGraphics 2009; 29:877–886
- Open Journal of Medical Imaging, 2013, 3, 90-96
- Radiol Clin N Am 51 (2013) 393–411
- EFORT Open Rev. 2020 May 5;5(5):260-267
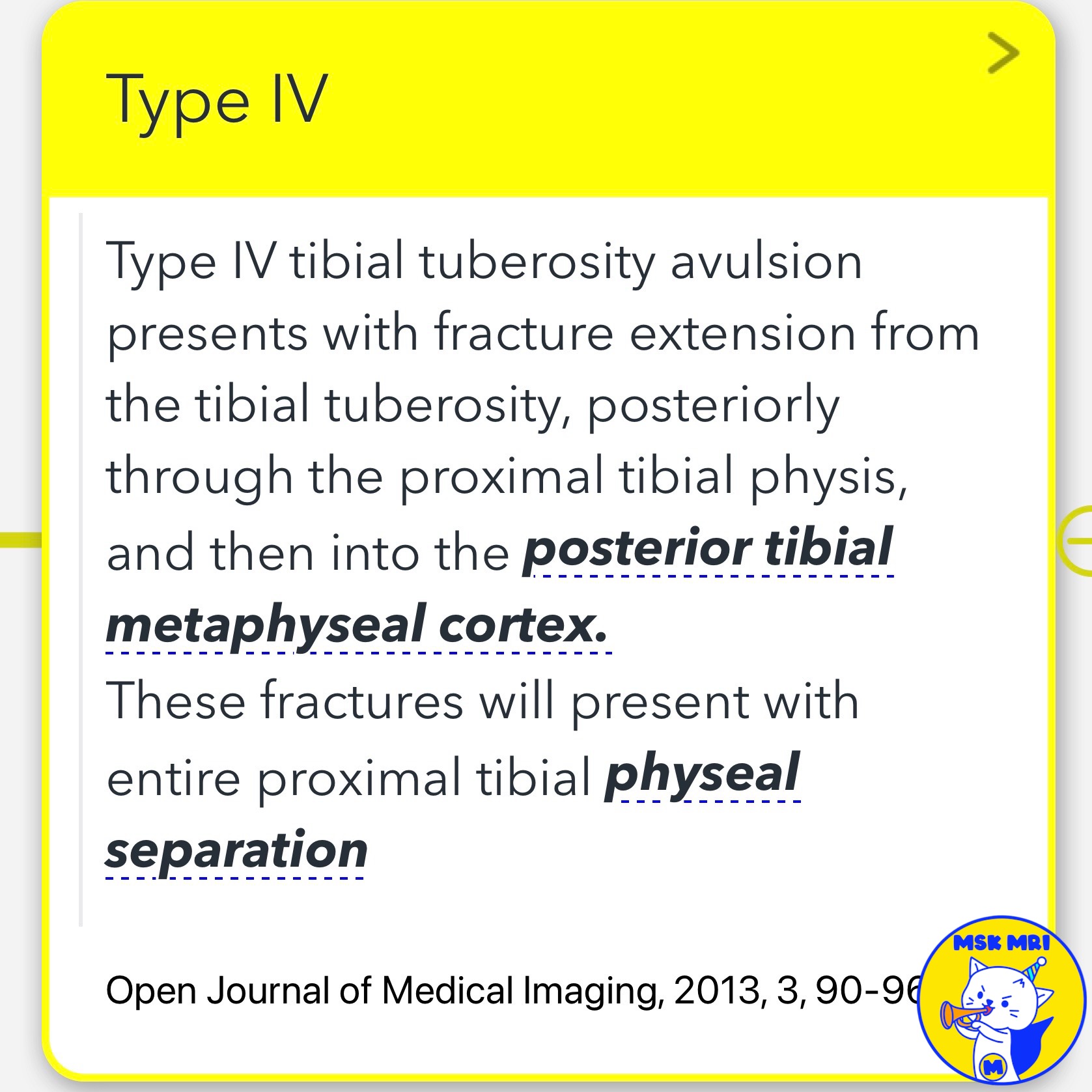
4️⃣Type IV Fractures
Type IV fractures present with fracture extension from the tibial tuberosity through the proximal tibial physis into the posterior tibial metaphyseal cortex.
References:
- Open Journal of Medical Imaging, 2013, 3, 90-96
- EFORT Open Rev. 2020 May 5;5(5):260-267
5️⃣ Type V Fractures
Type V fractures consist of a combined type III and type IV avulsion fracture, resulting in an inverted “Y” configuration.
References:
- Open Journal of Medical Imaging, 2013, 3, 90-96
- EFORT Open Rev. 2020 May 5;5(5):260-267
Treatment Guidelines
- Type I Fractures: Usually treated with knee immobilization in complete extension.
- Type II and III Fractures: Typically require osseous fixation with pins or screws.
Reference:
- RadioGraphics 2009; 29:877–886
Further Reading
- Journal of Children’s Orthopaedics, Vol. 2, No. 6, 2008, pp. 469-474
- Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, No. 194, 1980, pp. 181-184
- Orthopedic Clinics of North America, Vol. 34, No. 3, 2003, pp. 397-403
- Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (American Volume), Vol. 72, No. 9, 1990, pp. 1411-1413
#TibialFractures, #OgdenClassification, #TypeIFractures, #TypeIIFractures, #TypeIIIFractures, #TypeIVFractures, #TypeVFractures, #Orthopedics, #Radiology, #SportsMedicine
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 4BCD. Anterior knee' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 4-B.24) Ogden Type IIIA Tibial Tuberosity Fracture (1) | 2024.06.15 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 4-B.23) Ogden Type IA Tibial Tuberosity Fracture (0) | 2024.06.15 |
| (Fig 4-B.21) Patellar Sleeve Fracture and Repair (1) | 2024.06.15 |
| (Fig 4-B.20) Patellar Sleeve Fracture at the Superior Pole (0) | 2024.06.15 |
| (Fig 4-B.19) Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Syndrome (0) | 2024.06.15 |