Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
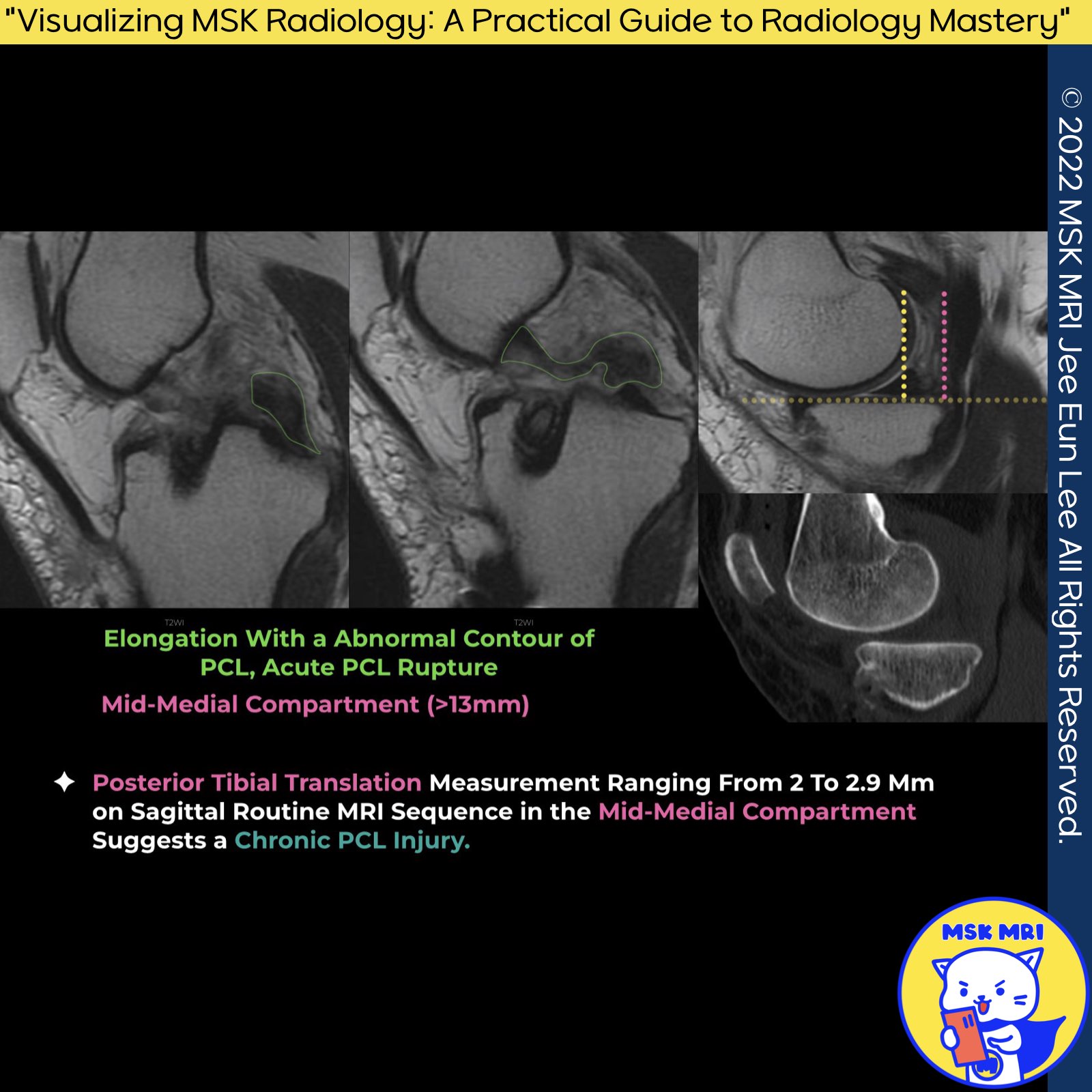
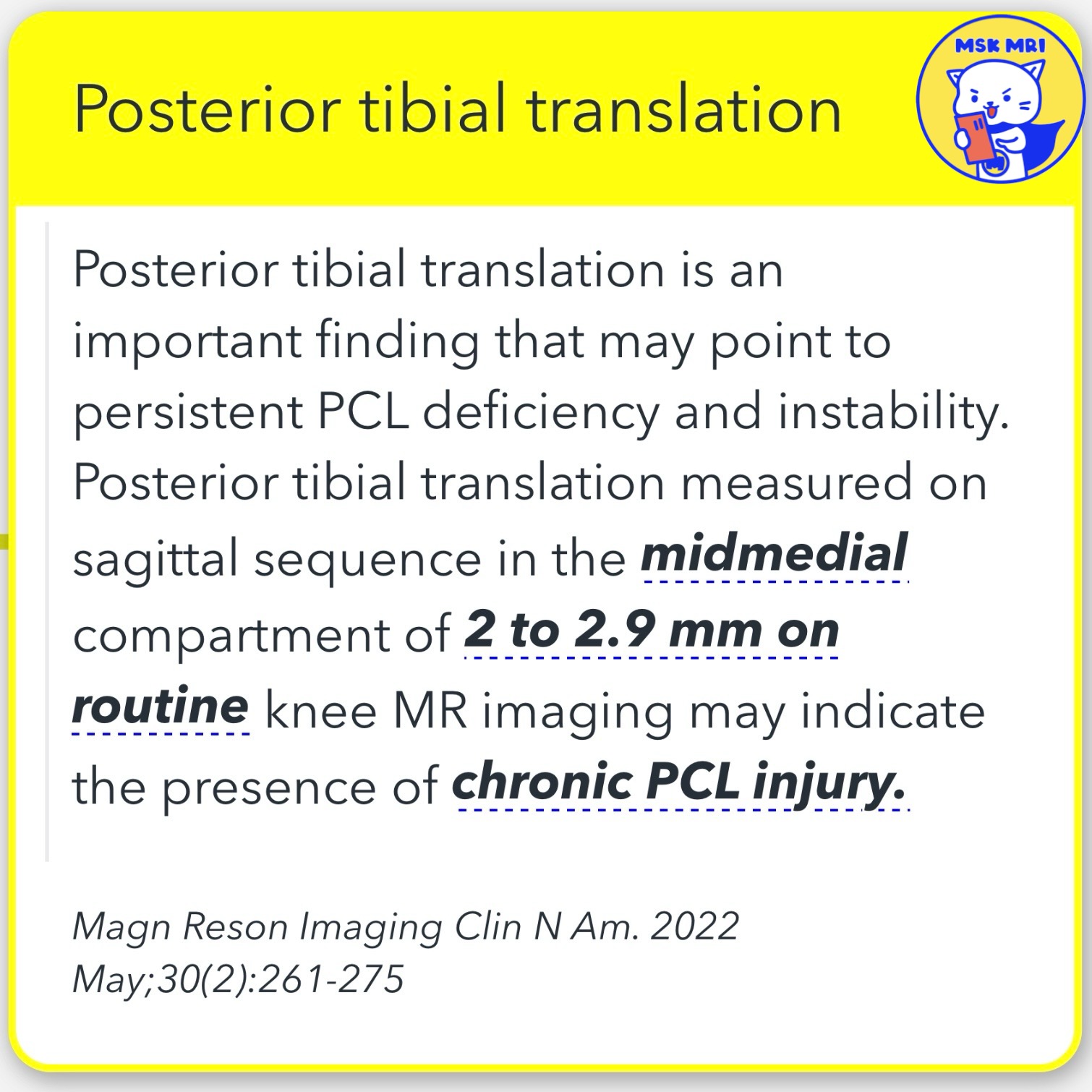
📌Posterior Tibial Translation
- Context: MR imaging has limitations in detecting chronically injured and functionally deficient PCL.
- Important Finding: Posterior tibial translation is a crucial indicator of persistent PCL deficiency and instability.
- Measurement Details: A posterior tibial translation of 2 to 2.9 mm measured on the sagittal sequence in the midmedial compartment, as seen on routine knee MR imaging, may suggest the presence of chronic PCL injury.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Clinics of North America, May 2022; 30(2): 261-275.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#pcltear, #pcl, #pclinjury, #kneemri
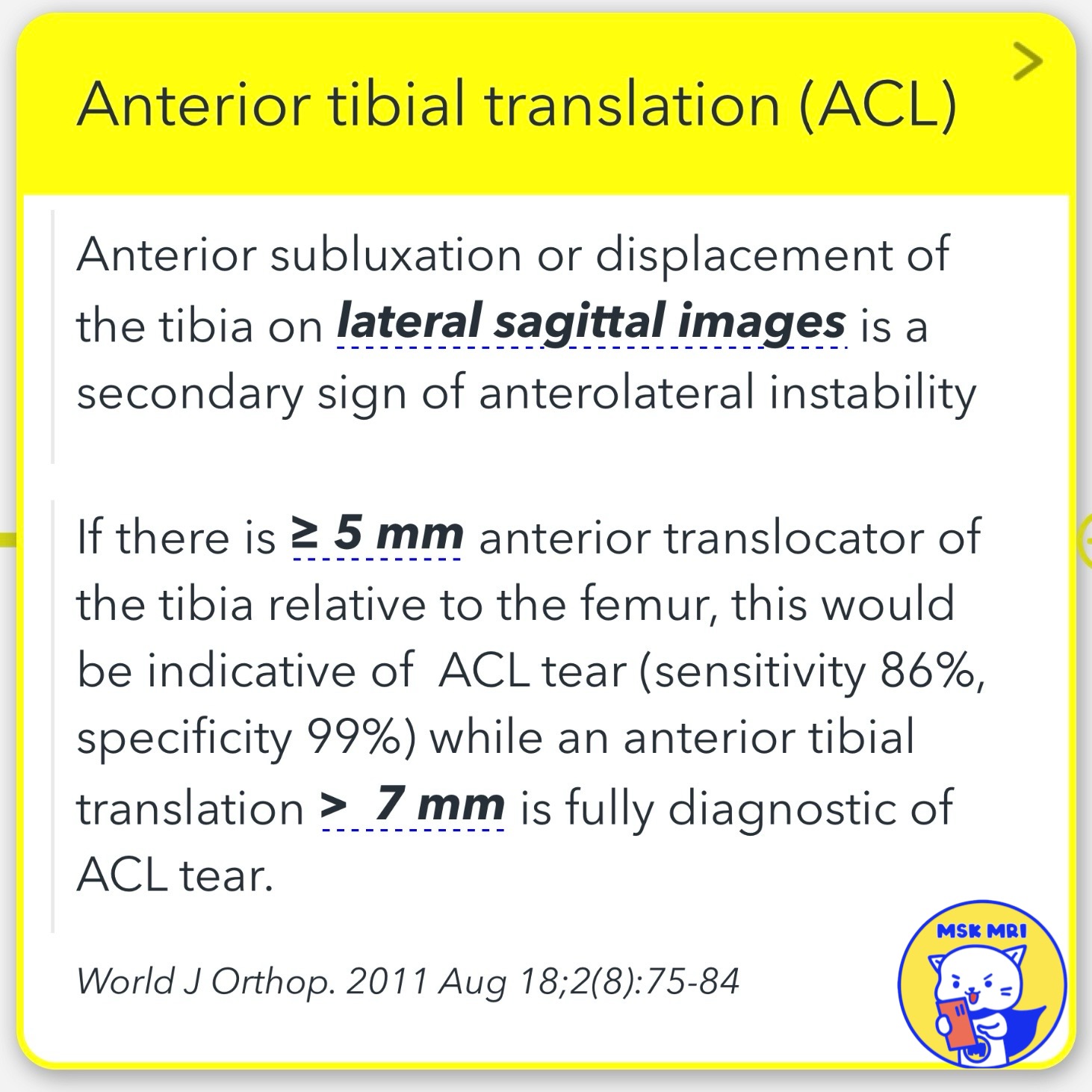
📌Anterior Tibial Translation and ACL Injury:
- Context: Anterior subluxation or displacement of the tibia on lateral sagittal images serves as a secondary sign of anterolateral instability.
- Diagnostic Criteria:
Anterior subluxation or displacement of the tibia on lateral sagittal images is a secondary sign of anterolateral instability
If there is ≥ 5 mm anterior translocator of the tibia relative to the femur, this would be indicative of ACL tear (sensitivity 86%, specificity 99%) while an anterior tibial translation > 7 mm is fully diagnostic of ACL tear.
Source: World Journal of Orthopedics, August 18, 2011; 2(8): 75-84.
World J Orthop. 2011 Aug 18;2(8):75-84
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 2.ACL and PCL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 2-E.24) Chronic Complete Tear of the PCL - Part 2 (0) | 2024.04.28 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 2-E.23) Chronic Complete Tear of the PCL - Part 1 (2) | 2024.04.28 |
| (Fig 2-E.21) Radiographic Assessment of Posterior Knee Laxity (0) | 2024.04.27 |
| (Fig 2-E.20) PCL Deficient Knee with Delayed Imaging (0) | 2024.03.18 |
| (Fig 2-E.19) PCL Bony Avulsion At Tibial Insertion (0) | 2024.03.17 |