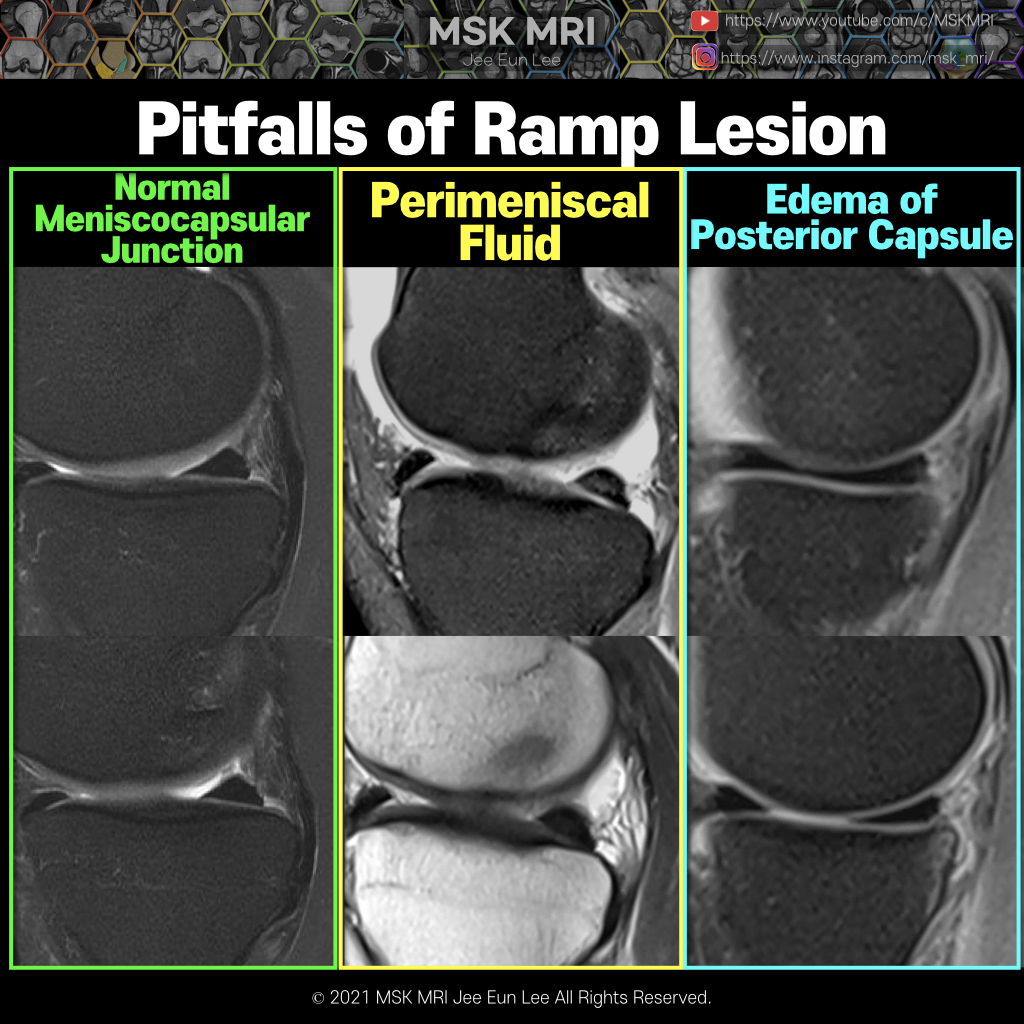
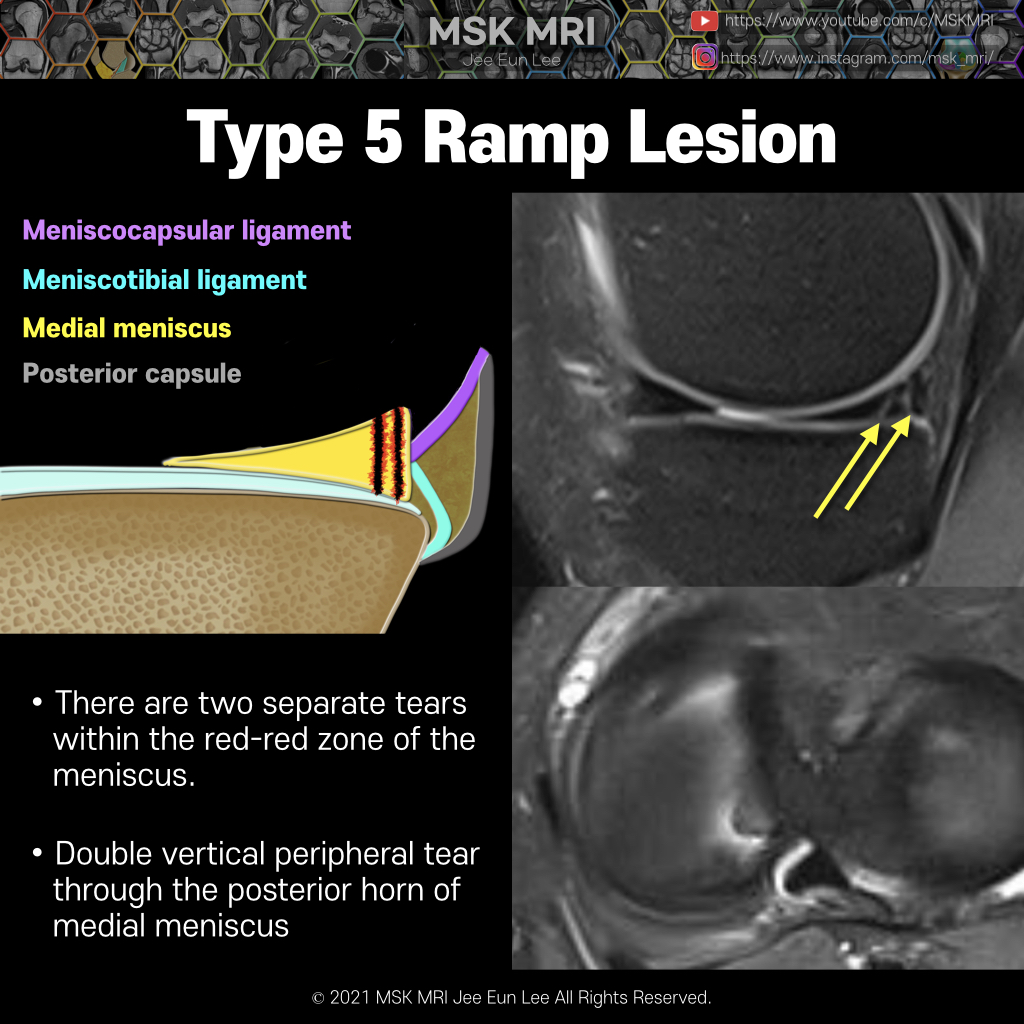
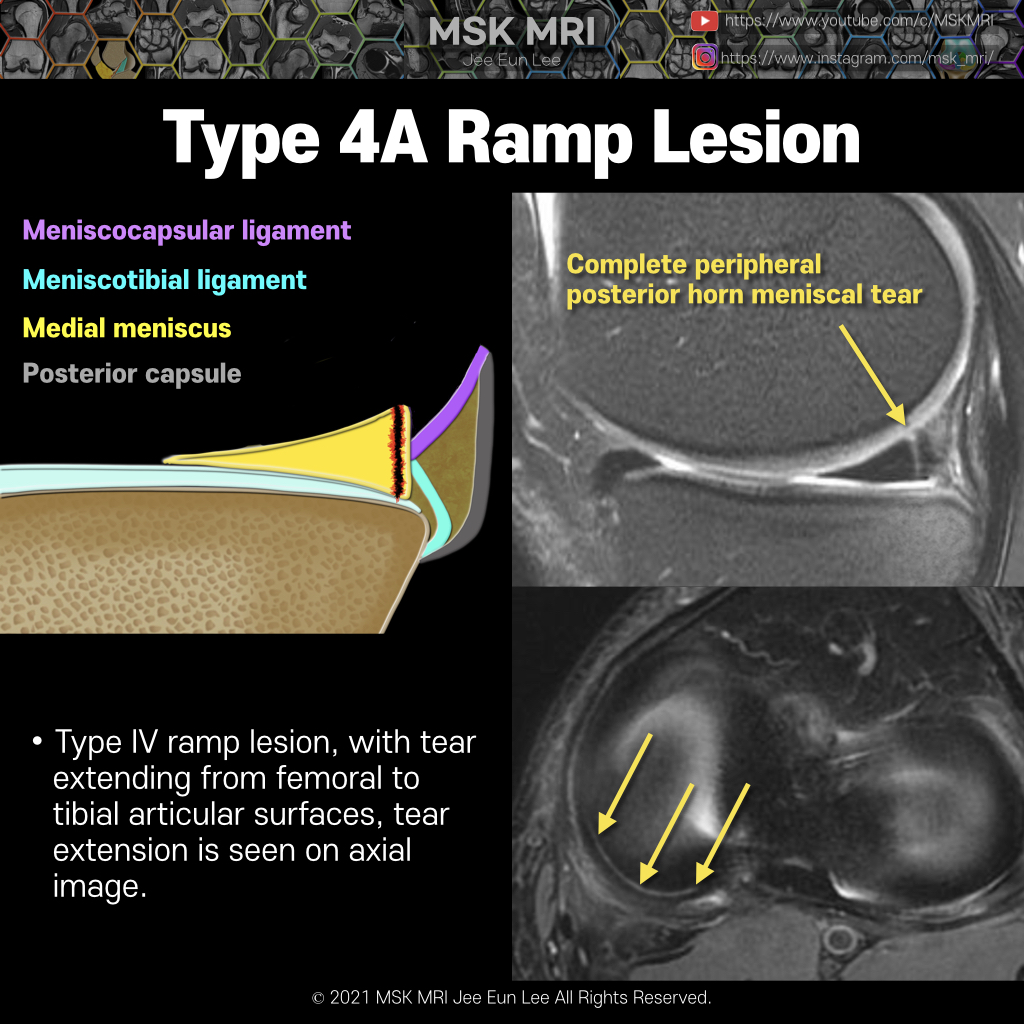
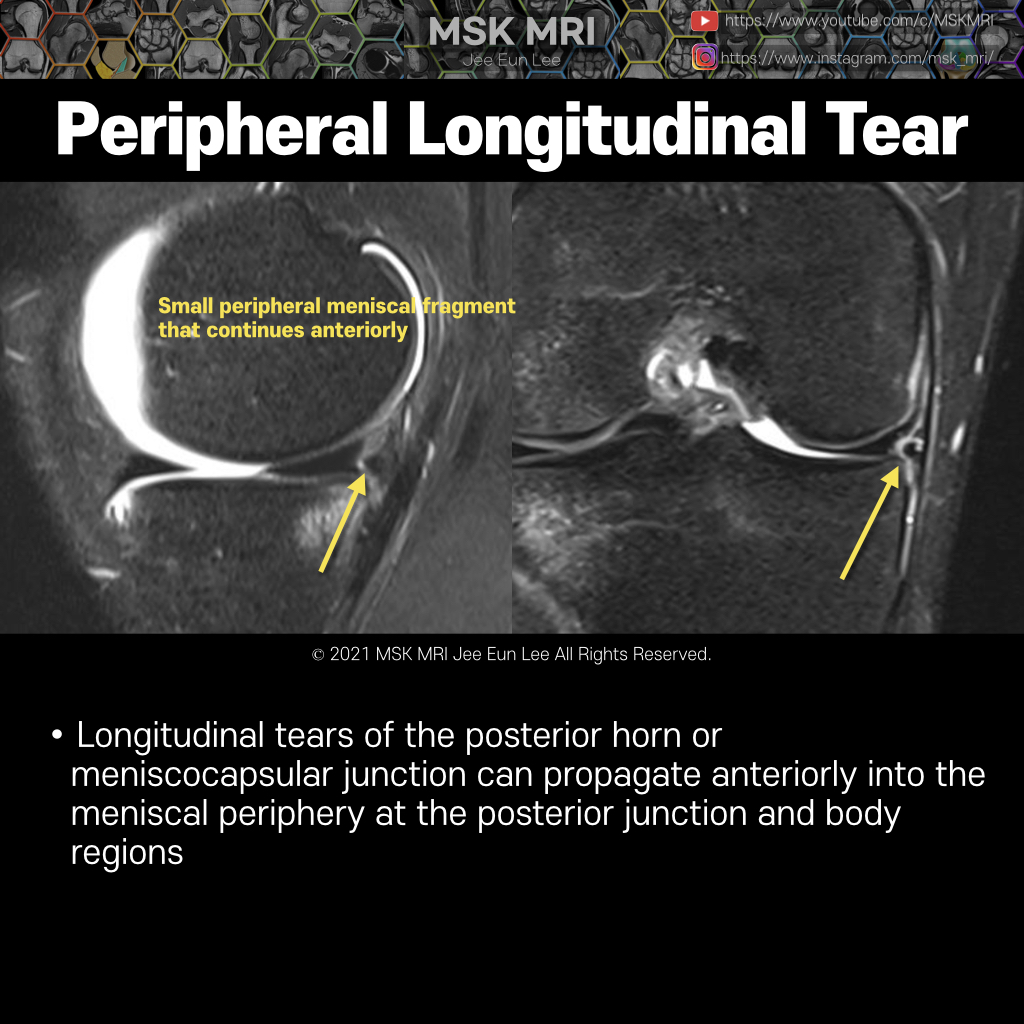
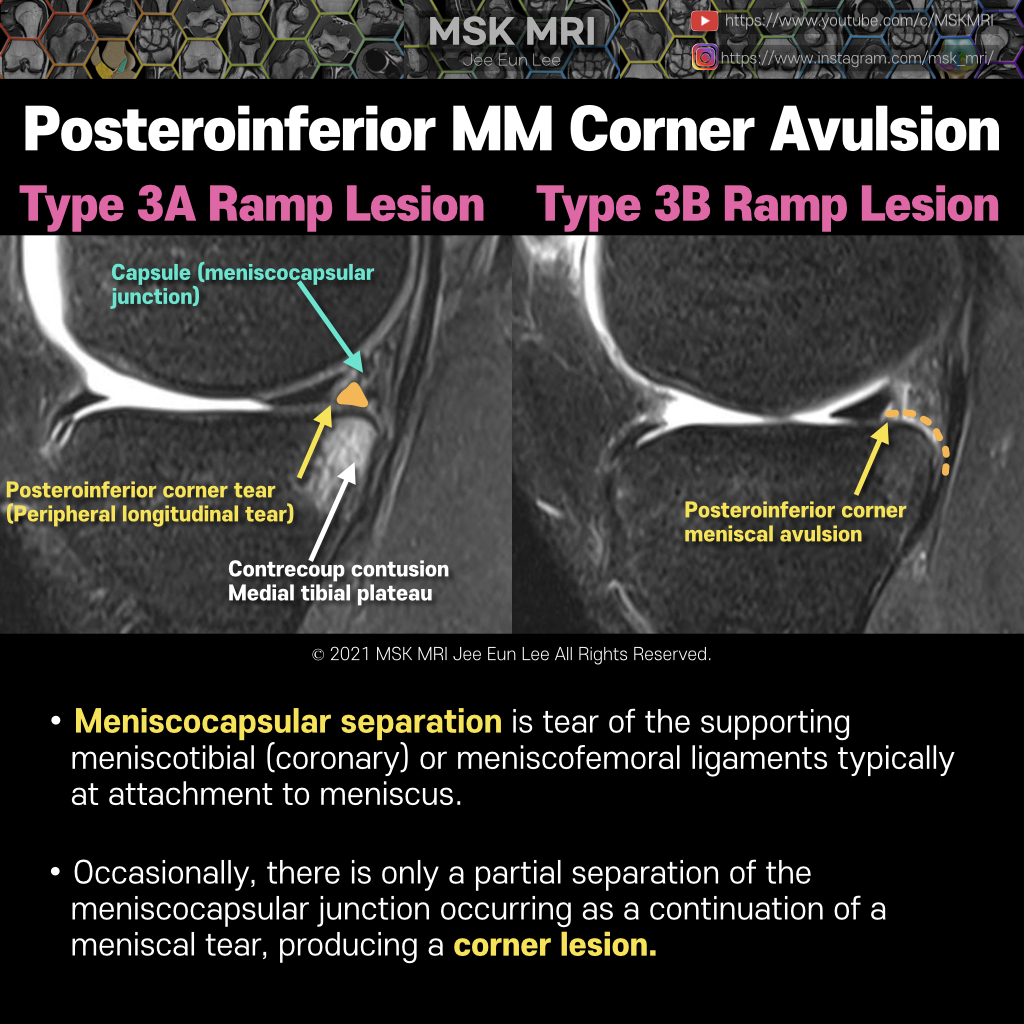
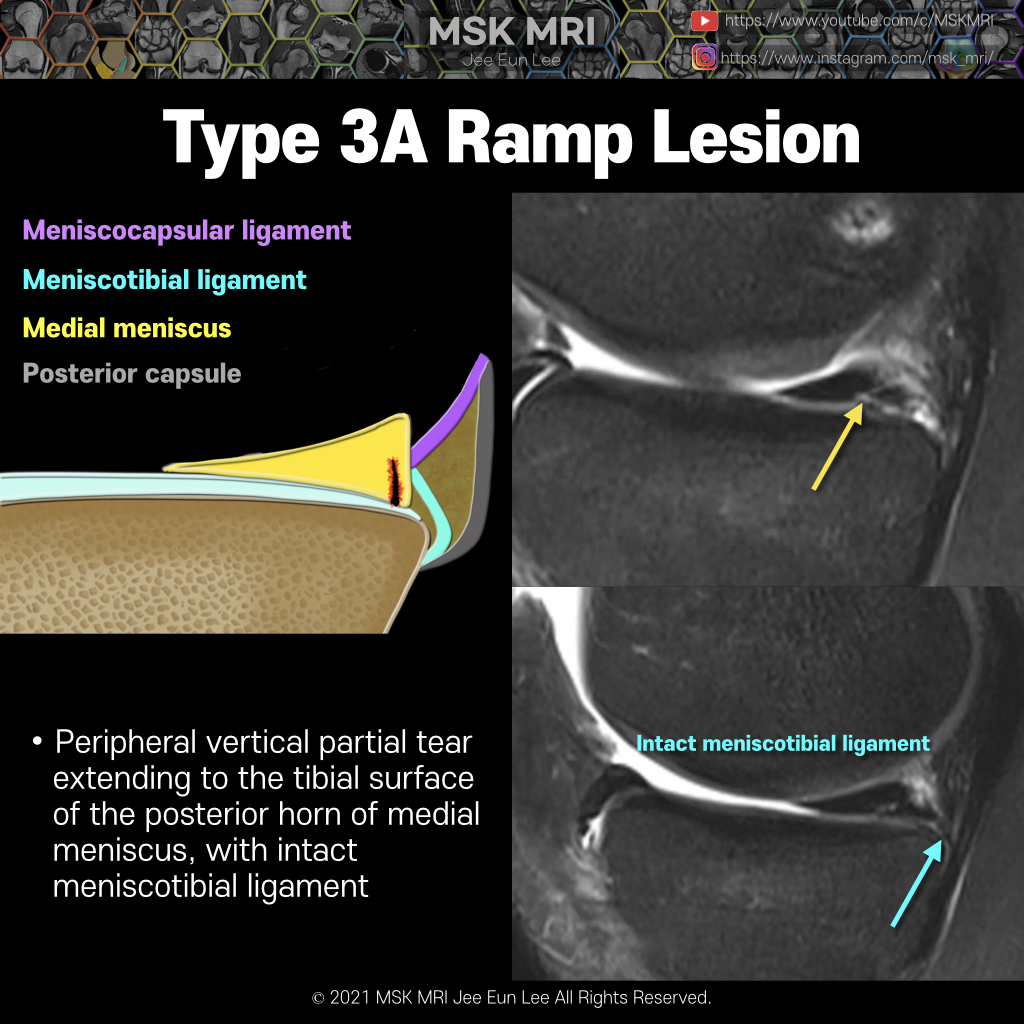
Meniscal ramp lesions can be defined as longitudinal vertical and/or oblique peripheral tears in the posterior horn of medial meniscus, in a mediolateral direction of less than 2.0 cm, that may lead to meniscocapsular or meniscotibial disruption with a concomitant ACL injury. There are few classifications regarding meniscal ramp lesions. Thaunat et al. approached a more comprehensive classificat..