Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
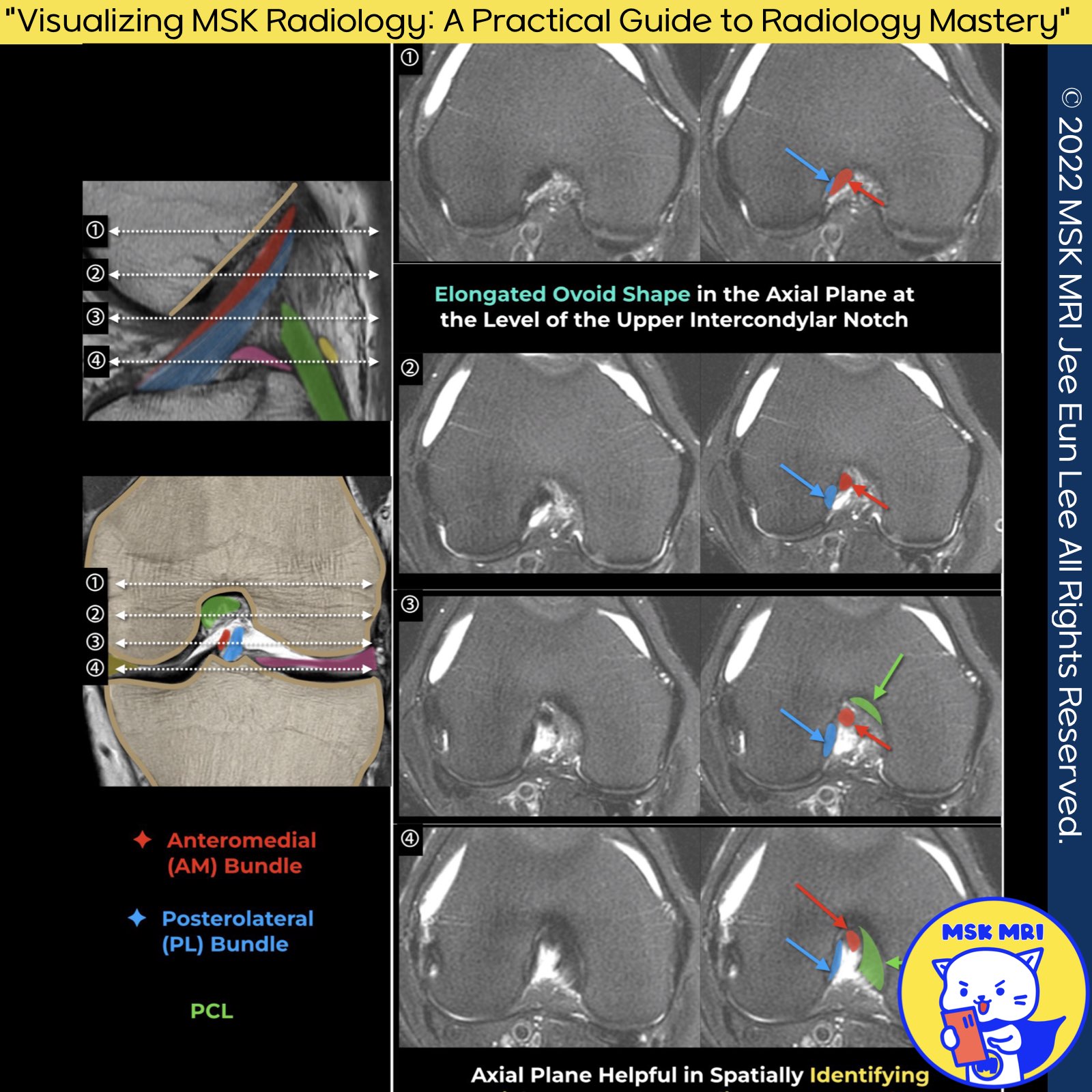
Normal ACL on axial images
The ACL is distinguished by its unique structural features and attachments, which are critical for its function in stabilizing the knee joint.
✅ On axial MRI images, the ACL can be observed with distinct characteristics at different segments:
- Anteromedial (AM) Bundle: This portion of the ACL attaches to the proximal part of the femoral attachment site and extends to the anteromedial aspect of the tibial attachment.
- Posterolateral (PL) Bundle: The PL bundle connects distally to the femur and posterolaterally to the tibia.
✅ On MRI, the ACL exhibits specific signal characteristics:
- Proximal Intercondylar Notch: Through this area, the ACL appears as an elliptical structure with homogeneous low signal intensity on axial images. This uniform appearance is indicative of the ligament's intact and healthy state in this segment.
- Distal to the Notch: More distally, both on axial and coronal images, the ACL presents a heterogeneous appearance. This variability in signal intensity can be attributed to the complex anatomy and varying orientations of the ligament fibers as they extend through the notch.
Axial images are particularly effective for identifying fluid presence within the proximal ligament fibers or in the space between a torn ACL and the lateral femoral condyle sidewall. This detail is crucial for diagnosing ACL injuries and assessing the extent of damage.
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
#VisualizingMSK #aclanatomy #ACL #aclbundles #anteromedialbundle #axialimage
You may not distribute or commercially exploit the content. Nor may you transmit it or store it on any other website or other forms of the electronic retrieval system.
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 2.ACL and PCL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 2-A.09) Cruciate or Intercondylar notch cysts, ACL ganglion cyst (0) | 2024.02.16 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 2-A.07) Normal ACL on oblique coronal images (0) | 2024.02.16 |
| (Fig 2-A.04) Normal ACL on coronal images, anteromedial and posterolateral bundles of ACL (0) | 2024.02.16 |
| (Fig 2-A.03) Normal ACL on Sagittal images (0) | 2024.02.16 |
| (Fig 2-A.02) Tibial attachment of the ACL, ACL footprint (0) | 2024.02.16 |