==============================================
⬇️✨⬇️🎉⬇️🔥⬇️📚⬇️
Click the link to purchase on Amazon 🎉📚
==============================================
🎥 Check Out All Videos at Once! 📺
👉 Visit Visualizing MSK Blog to explore a wide range of videos! 🩻
https://visualizingmsk.blogspot.com/?view=magazine
📚 You can also find them on MSK MRI Blog and Naver Blog! 📖
https://www.instagram.com/msk_mri/
Click now to stay updated with the latest content! 🔍✨
==============================================
📌 Quadriceps Tendon Disease
- Disease affecting the quadriceps tendon parallels that affecting tendons throughout the body, ranging from tendinosis to varying degrees of partial tears to complete rupture, characterized by transection of all of its layers.
1️⃣ Quadriceps Tendinosis
- Less common than patellar tendinosis
- Typically related to overuse in athletes involved in jumping sports
- Results in a thickened heterogeneous tendon with altered echotexture and increased signal intensity at MRI
2️⃣ Quadriceps Tears
- Typically occur in the setting of underlying tendinosis
- Partial tears are more common than complete tears
- Tearing usually occurs 1-2 cm proximal to the patella
- Lacks a tendon sheath and derives its blood supply primarily via the genicular arteries, relatively avascular
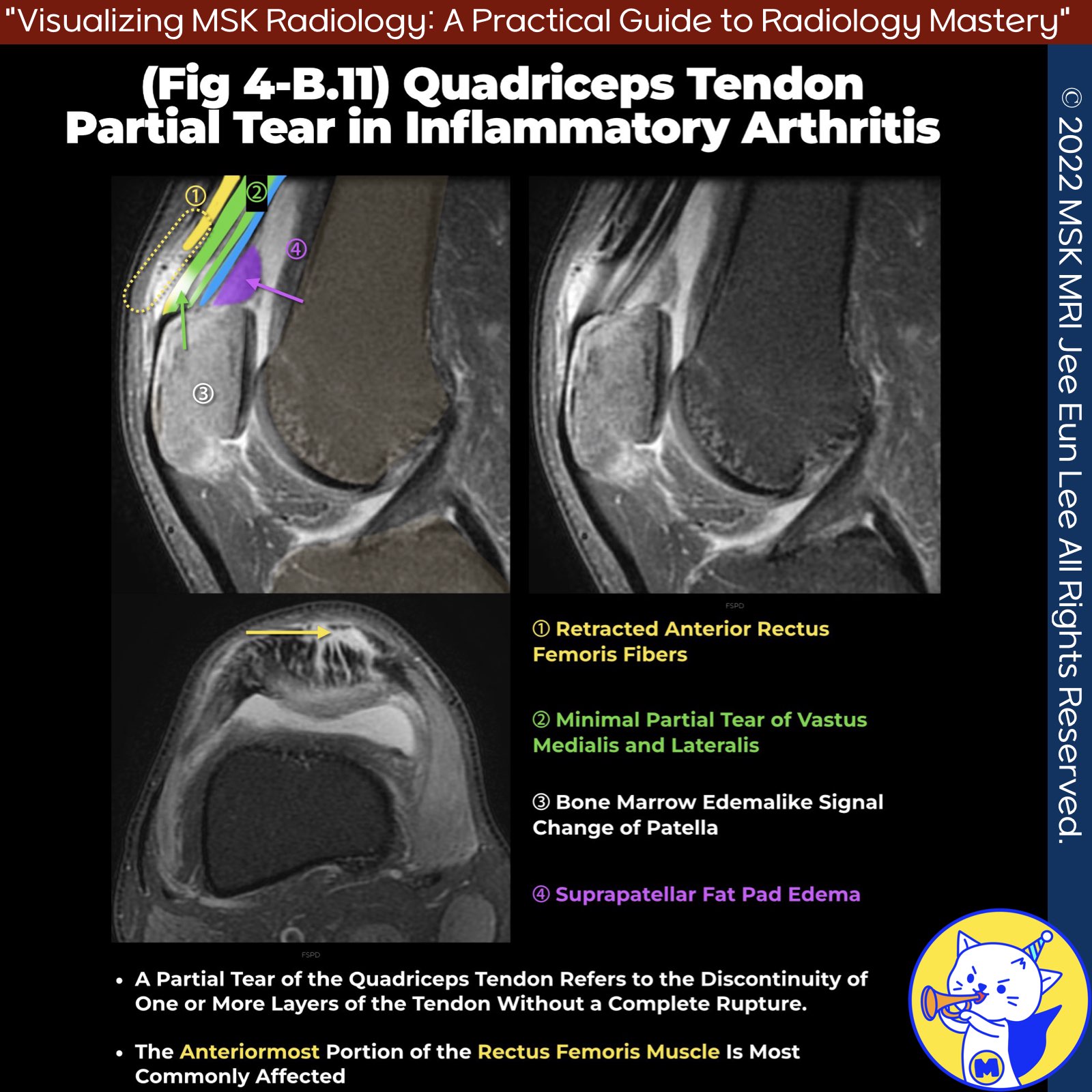
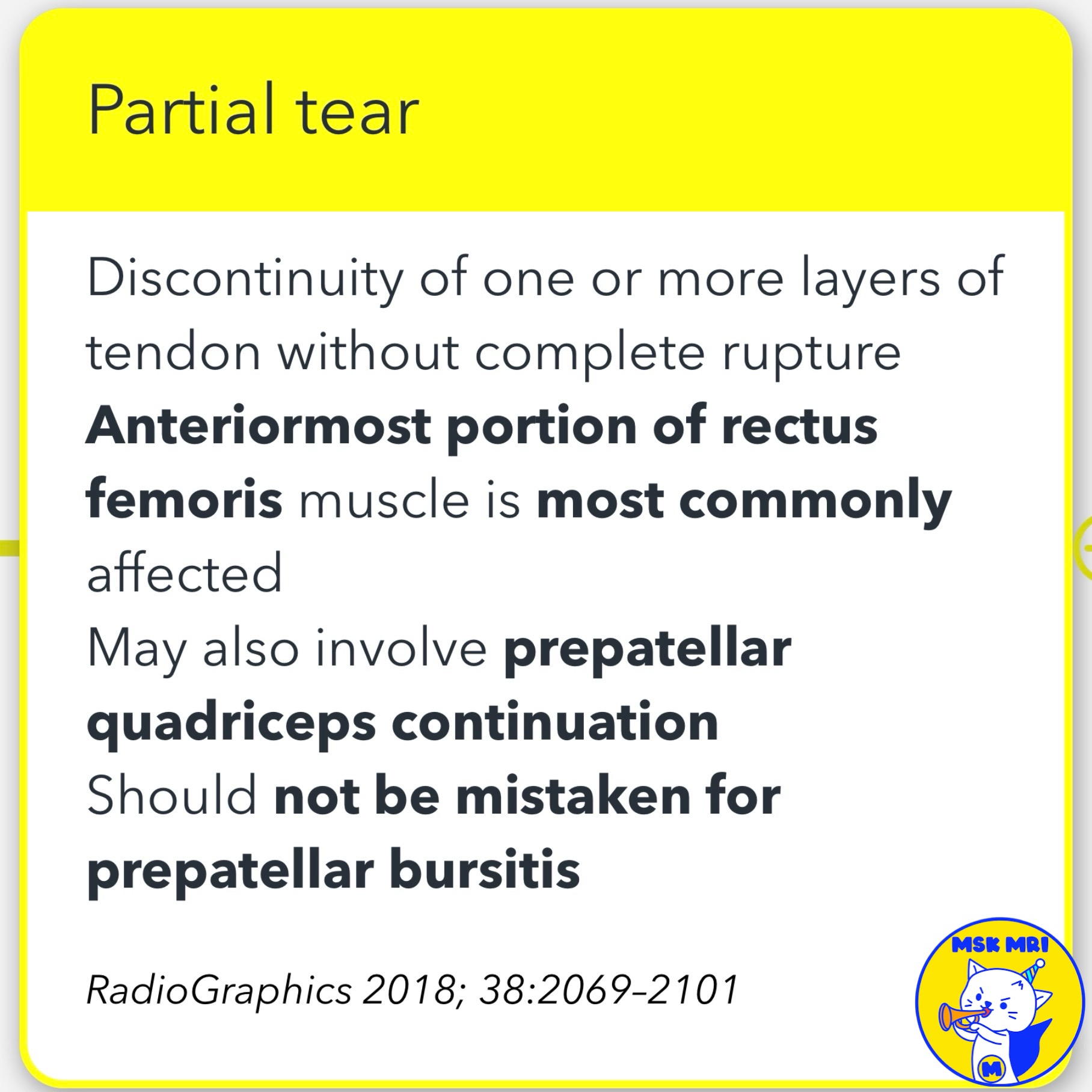
3️⃣ Partial Tears
- May be limited to the anterior, central, and/or posterior laminae, most commonly affecting the anterior rectus femoris portion
- Produce anterior soft-tissue swelling and bruising, may be associated with a palpable gap
- Torn rectus femoris tendon can retract far proximally, often overlooked at dedicated knee MRI examination
- Less common and more challenging to identify clinically, seen at imaging as defects in the tendon filled with fluid
- Function is typically preserved and can be managed conservatively
4️⃣ Complete Tears
- Far more common in males than in females
- Typically occur after the age of 50 years from decelerating trauma superimposed on a tendon weakened by underlying tendinosis
- May be limited to the tendon or associated with an avulsion fracture of the superior patella
- Uncommon directly at the osseous attachment due to strong fibrocartilage at the quadriceps enthesis
- Appear as a fluid-filled gap between the torn and retracted tendon ends
- Often associated with flexion and caudal migration of the patella and a wrinkled appearance of the patellar tendon
- Undisplaced tears may be overlooked; imaging is crucial for diagnosis and surgical planning
✅ Atraumatic Tears
- Associated with systemic disorders such as hyperlipidemia, thyroid dysfunction, chronic renal failure, rheumatoid arthritis, corticosteroid use, gout, and diabetes
- May be bilateral
- Underlying medical comorbidities are more common in women than in men
RadioGraphics 2018; 38:2069–2101
"Visualizing MSK Radiology: A Practical Guide to Radiology Mastery"
© 2022 MSK MRI Jee Eun Lee All Rights Reserved.
No unauthorized reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training.
#QuadricepsTendon, #RectusFemorisTear, #PartialTear, #KneeInjury, #SportsMedicine, #MRI, #BoneMarrowEdema, #SuprapatellarFatPadEdema, #Orthopedics, #TendonInjury
'✅ Knee MRI Mastery > Chap 4BCD. Anterior knee' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Fig 4-B.13) Traumatic Separation of Prepatellar Quadriceps Continuation (0) | 2024.06.12 |
|---|---|
| (Fig 4-B.12) Quadriceps Tendinosis (0) | 2024.06.12 |
| (Fig 4-B.10) Prepatellar Bursa Compartmentalization (0) | 2024.06.11 |
| (Fig 4-B.09) Prepatellar Soft Tissue Anatomy (2) | 2024.06.11 |
| (Fig 4-B.08) Anatomy of Prepatellar Quadriceps Continuation (0) | 2024.06.11 |